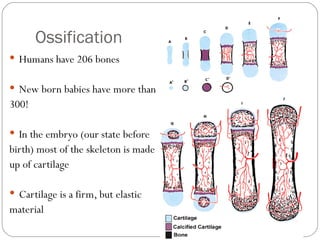
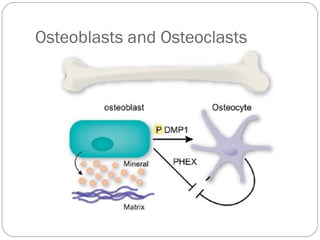
The document discusses the process of ossification where cartilage is changed to bone during human development. It explains that ossification is impacted by three key cells: osteoblasts, which build bone; osteocytes, which are trapped osteoblasts that give bone its star-shaped appearance; and osteoclasts, which break down old or damaged bone. The document also outlines factors like nutrition, vitamins, hormones, and growth that influence bone growth and remodeling throughout life.