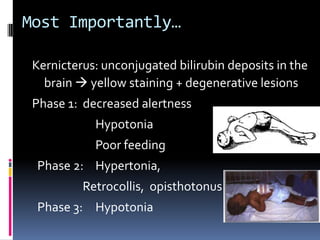
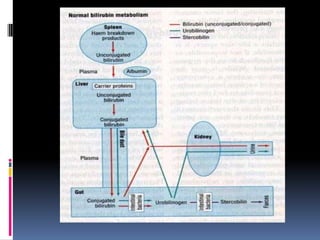
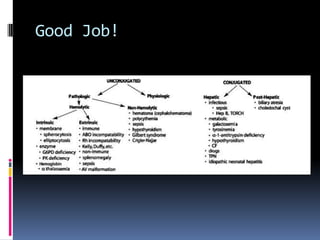
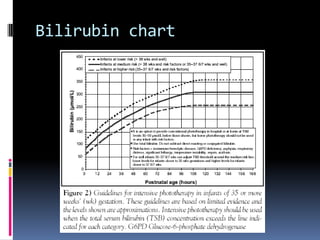
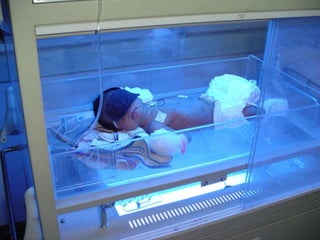
This document defines jaundice as hyperbilirubinemia, an excessive level of bilirubin in the blood, and differentiates between physiological and pathological jaundice. It states that kernicterus, caused by unconjugated bilirubin deposits in the brain, is the most dangerous complication. An approach to evaluating a jaundiced baby includes assessing age, risk factors, and signs of kernicterus, and determining if jaundice is physiological or pathological by considering time of onset and duration. Workup may include bilirubin levels, blood typing, and additional tests depending on the situation. Treatment options include increasing feeding, phototherapy, and exchange transfusion for more severe cases.