Embed presentation
Downloaded 11 times

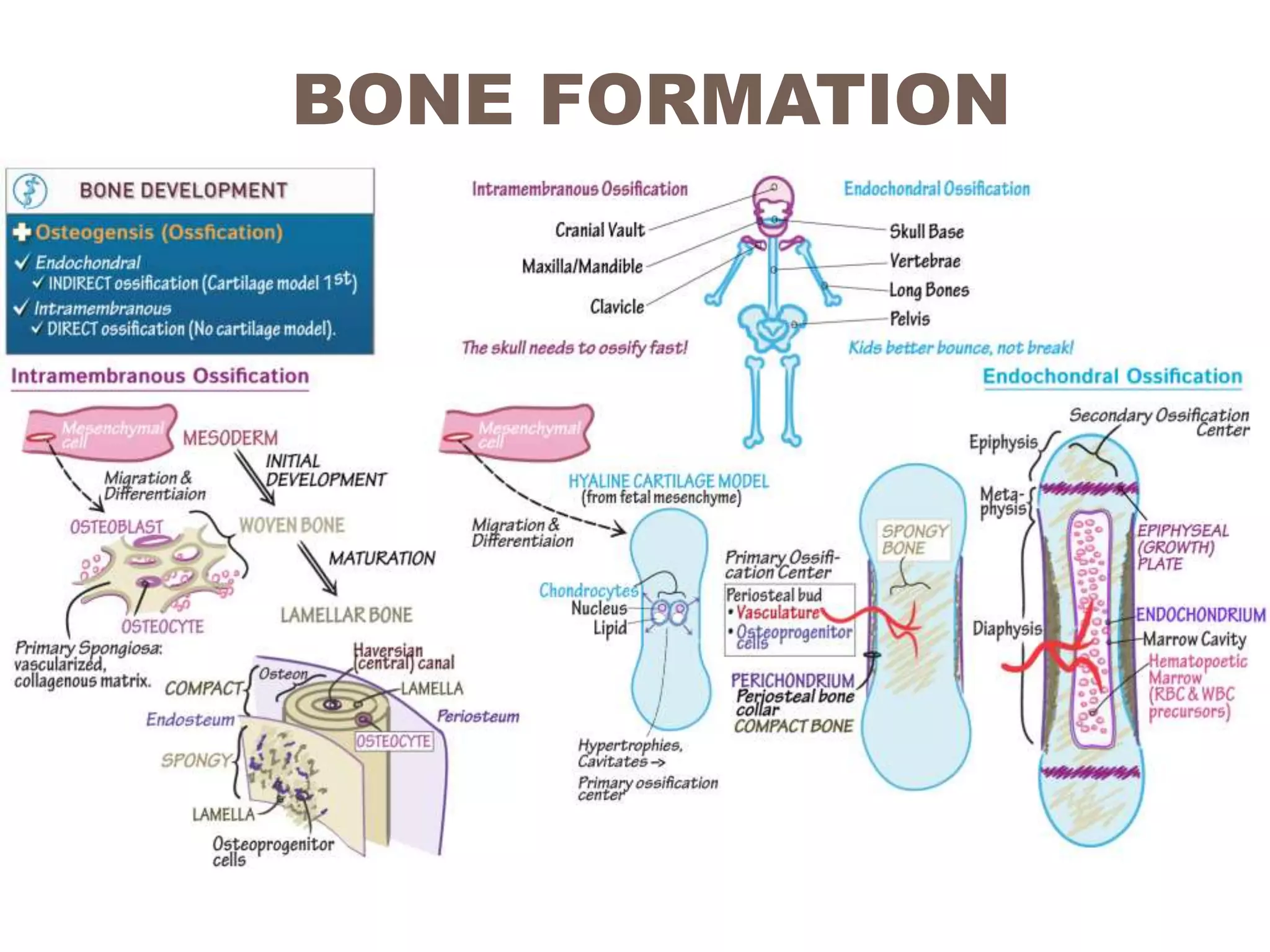

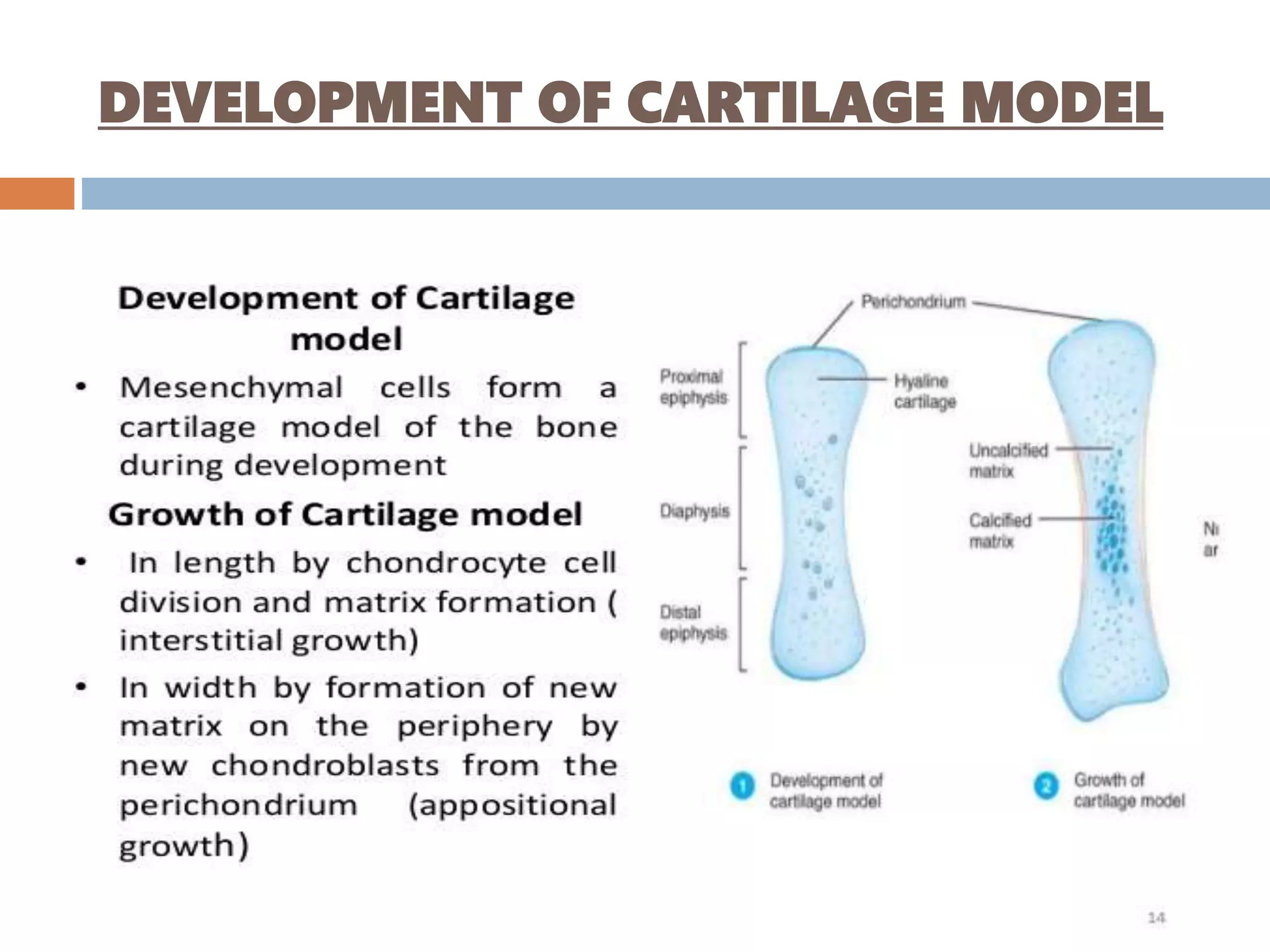



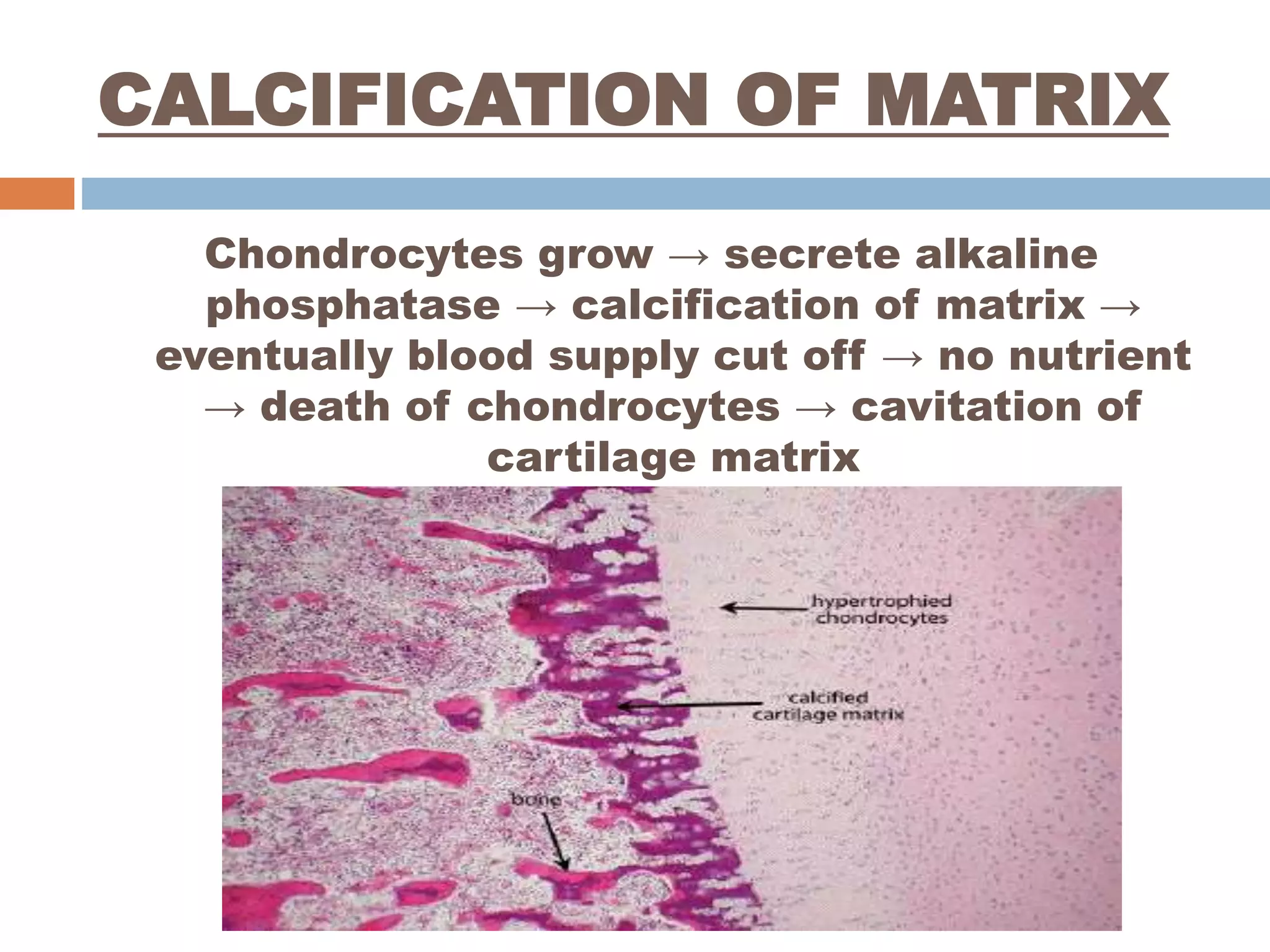

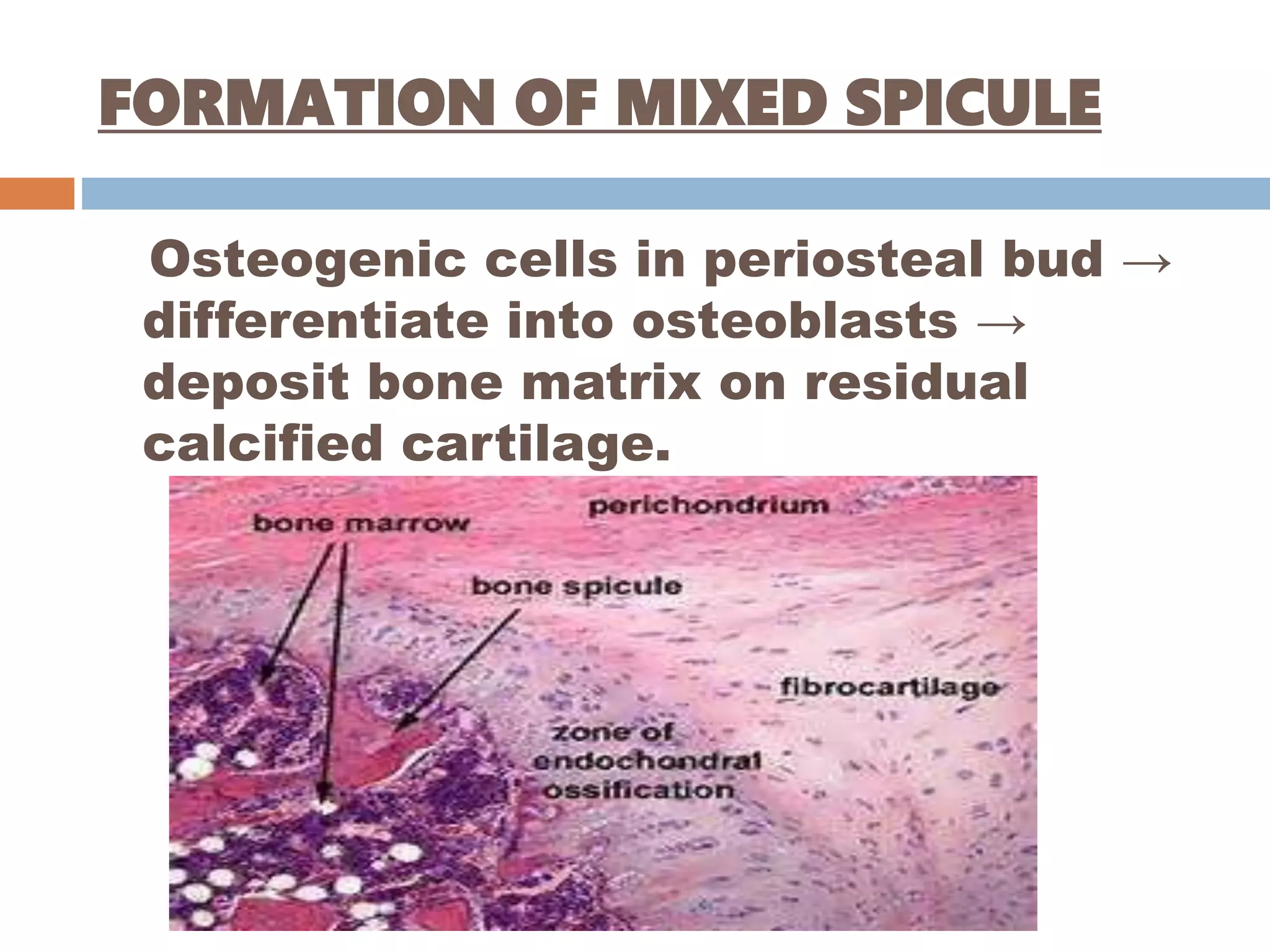








Endochondral bone formation is the process where cartilage is replaced by bone. It occurs in long bones, vertebrae, ribs and other bones. First, mesenchymal cells form a cartilaginous model surrounded by perichondrium. The model grows in size through the division and maturation of chondrocytes. Osteoblasts then deposit bone collagen on the calcified cartilage, forming mixed bone-cartilage spicules. Meanwhile, blood vessels invade the midsection and form a primary ossification center, with marrow cavity developing within. Later, secondary ossification centers form in the epiphyses, completing bone growth.




















