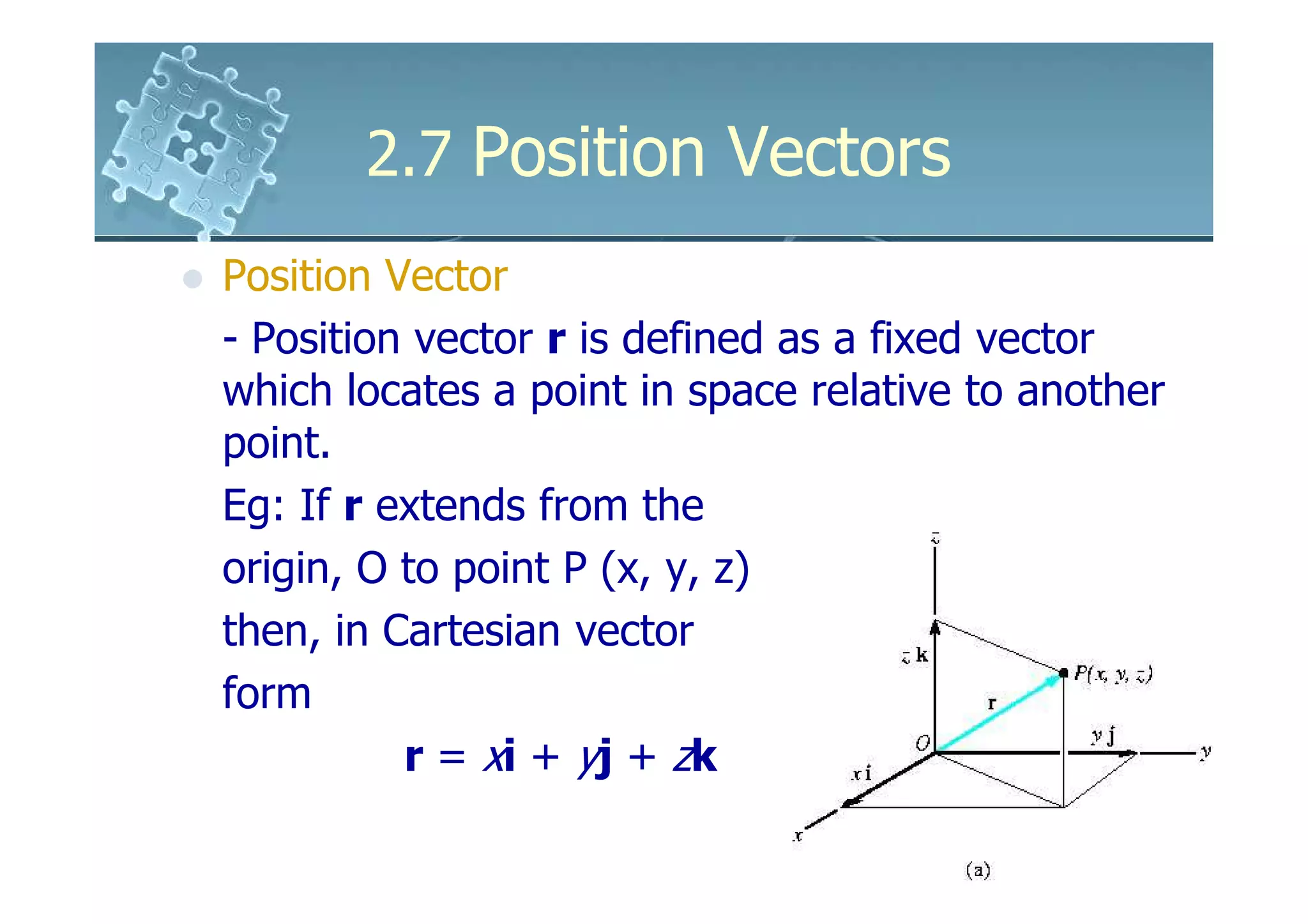
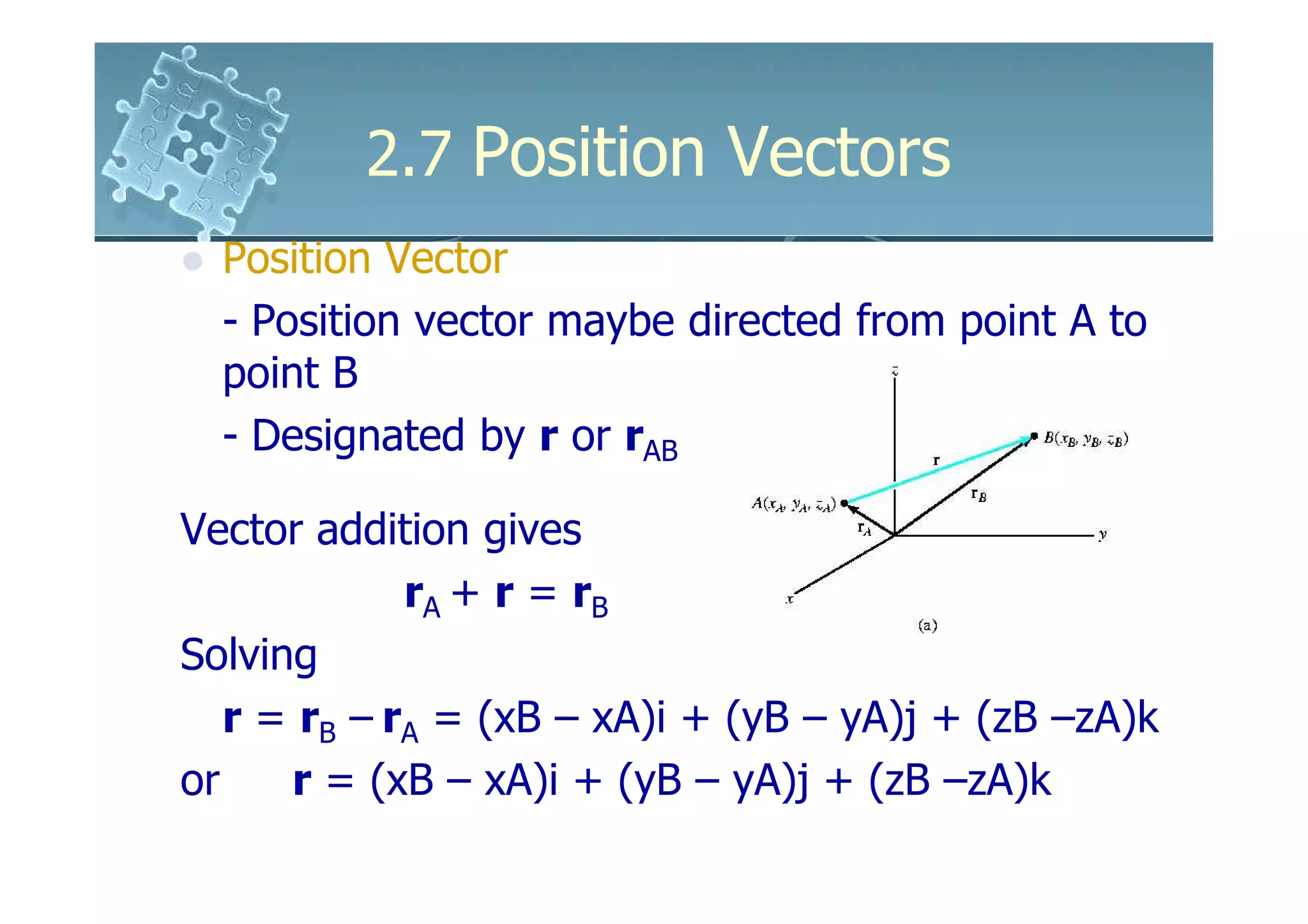
The document discusses position vectors in 3D coordinate systems. It defines a position vector r as a fixed vector that locates a point P(x,y,z) in space relative to another point, such as the origin O. The components of r are the distances from O to P along the x, y, and z axes. As an example, it shows calculating the position vector and length of an elastic rubber band attached between points A and B to determine the band's direction from A toward B.







![2.7 Position Vectors
Solution
Position vector
r = [-2m – 1m]i + [2m – 0]j + [3m – (-3m)]k
= {-3i + 2j + 6k}m
Magnitude = length of the rubber band
r= (− 3)2 + (2)2 + (6)2 = 7m
Unit vector in the director of r
u = r /r
= -3/7i + 2/7j + 6/7k](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/61611032-7positionvectors-120119010304-phpapp02/75/6161103-2-7-position-vectors-10-2048.jpg)
