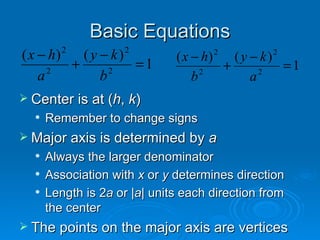
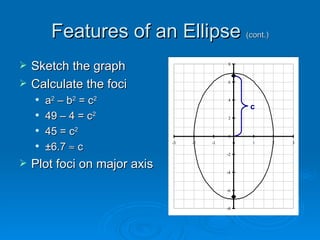
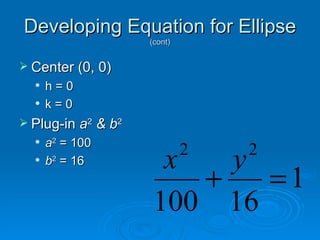
The document discusses the basic equations and features of ellipses. It explains that the center, major axis, minor axis, vertices and foci of an ellipse can be determined from its standard equation. It provides an example of developing the equation of an ellipse given its center, vertices and co-vertices. The major axis is determined by the larger denominator a and the minor axis by the smaller denominator b.