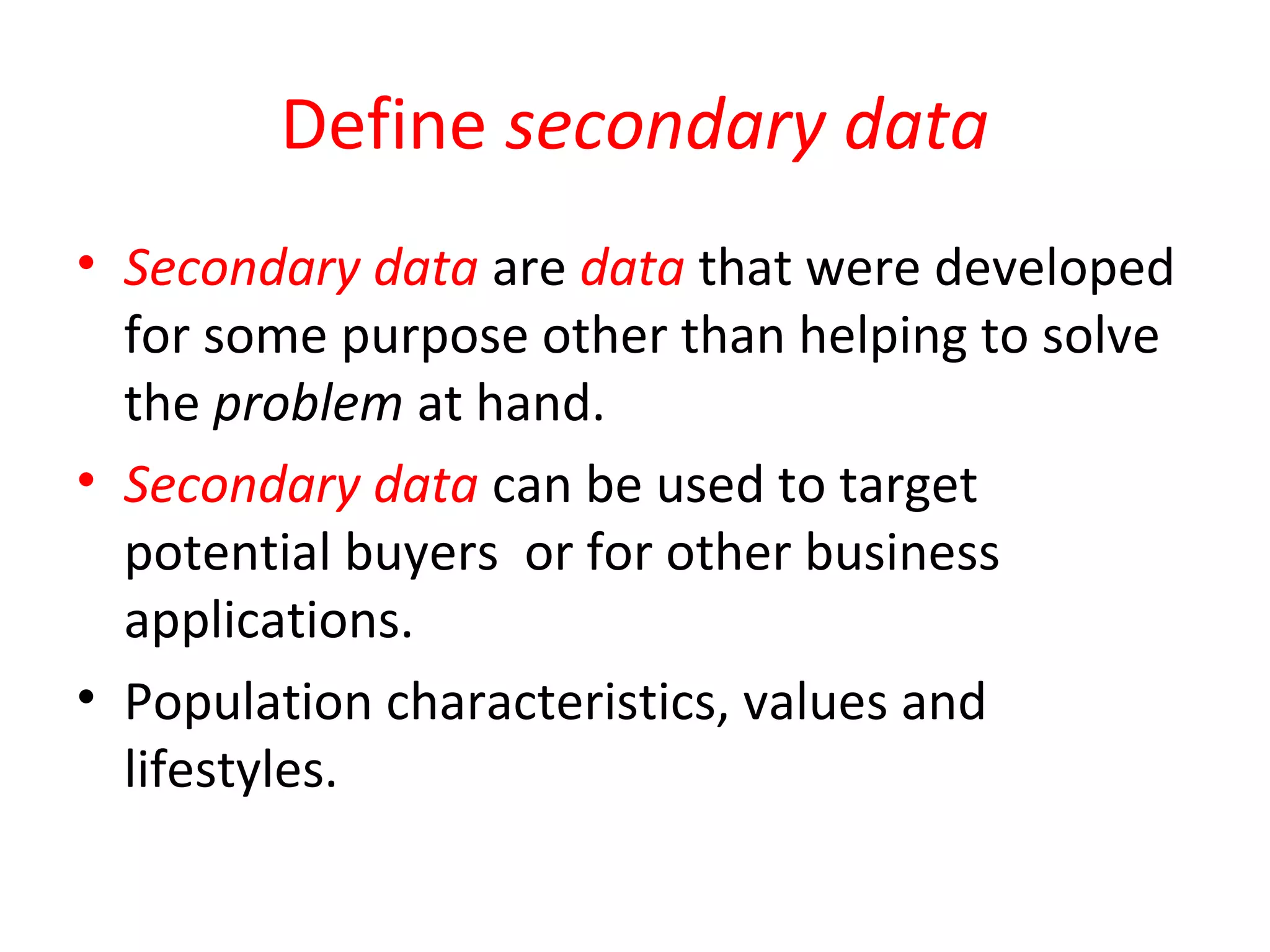
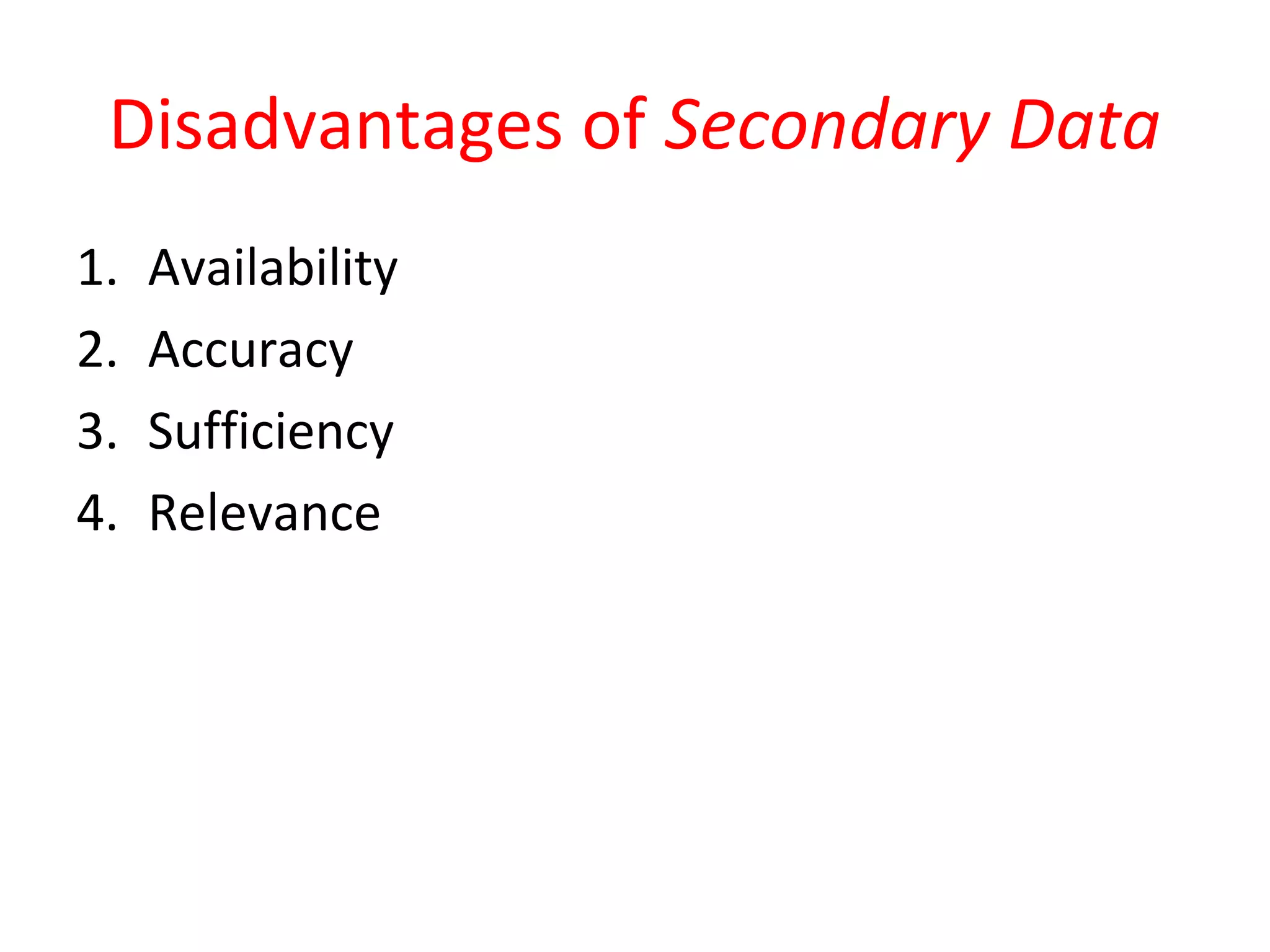
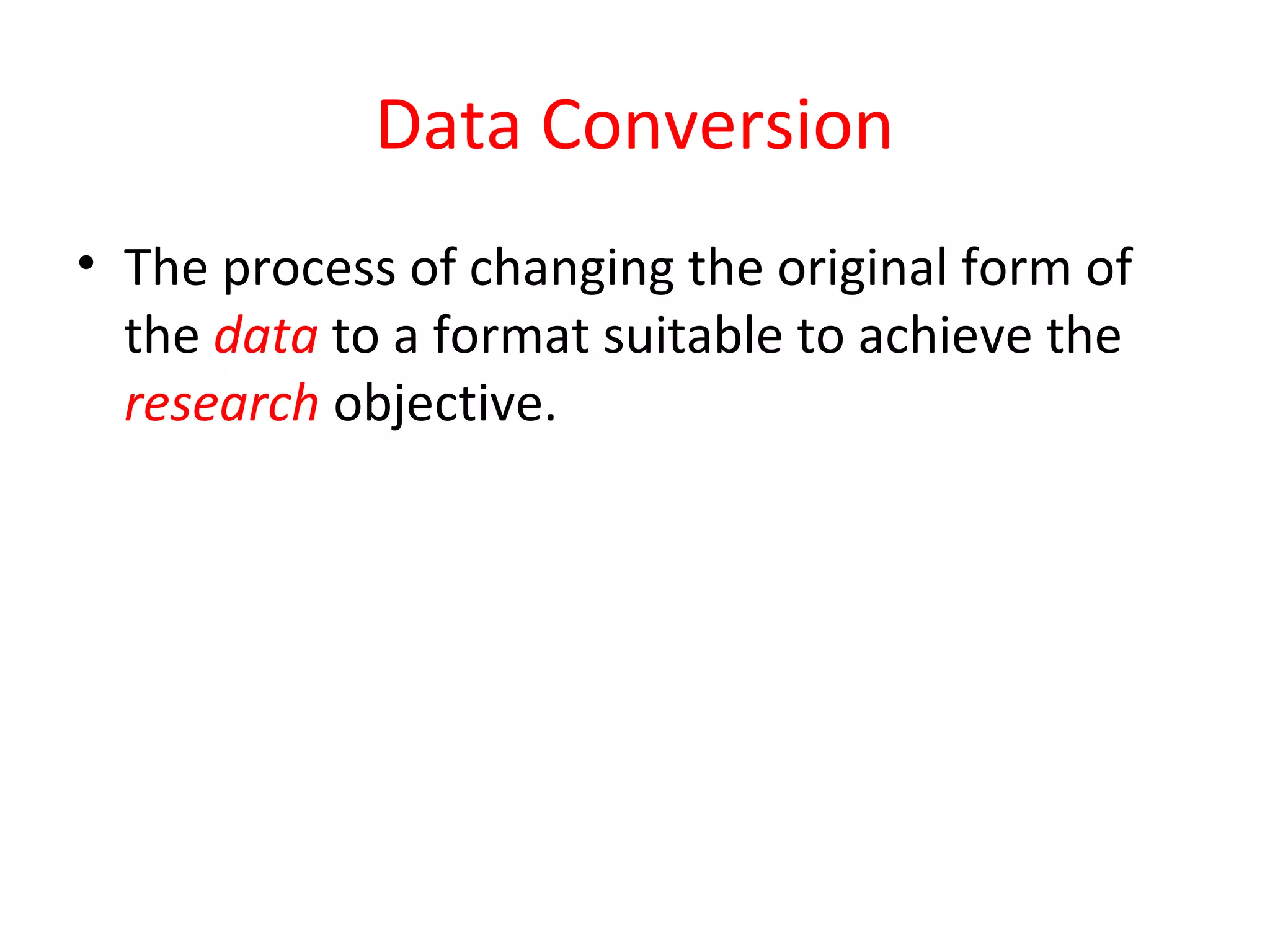
The document discusses secondary data sources for research. It defines secondary data as data collected for other purposes than the current problem. Secondary data has advantages of quick and cheap collection but disadvantages of potential inaccuracies or lack of relevance. The document outlines internal sources like accounting records and sales reports, as well as external sources including databases, government agencies, directories, and experts. It also discusses using secondary data for international research.