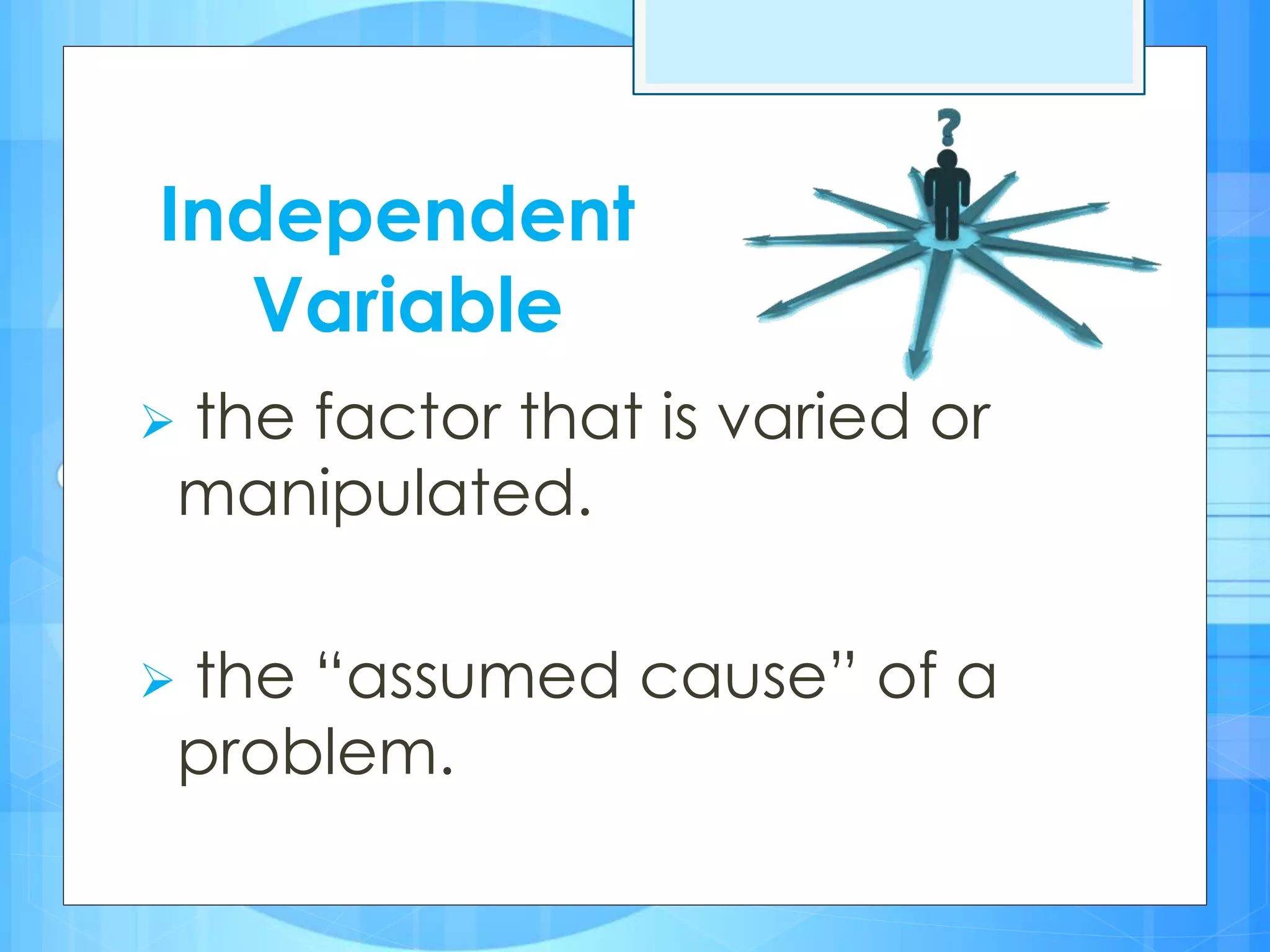
The document discusses various types of variables in research, including independent, dependent, controlled, intervening, moderator, and extraneous variables, highlighting their roles and examples in scientific experiments. It explains the importance of controlling variables to maintain the validity of a study and describes how changes to independent variables affect dependent variables. Additionally, it provides resources for further reading on research methods.