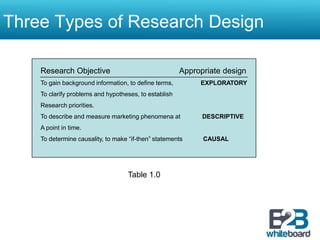
This document discusses different types of marketing research design. It begins by defining research design and explaining the three main categories: exploratory, descriptive, and causal research. Exploratory research is conducted when little is known about a problem and can involve secondary research, interviews, and focus groups. Descriptive research answers questions like who, what, where, and how through cross-sectional or longitudinal studies. Causal research determines cause-and-effect through experiments. The document also discusses test marketing and considerations for selecting test market cities.