1. The mass defect for the helium nucleus is 0.03039 atomic mass units or 5.046×10−29 kg. This mass defect is equivalent to 4.54×10−12 J of energy needed to separate the nucleus according to Einstein's mass-energy equivalence formula.
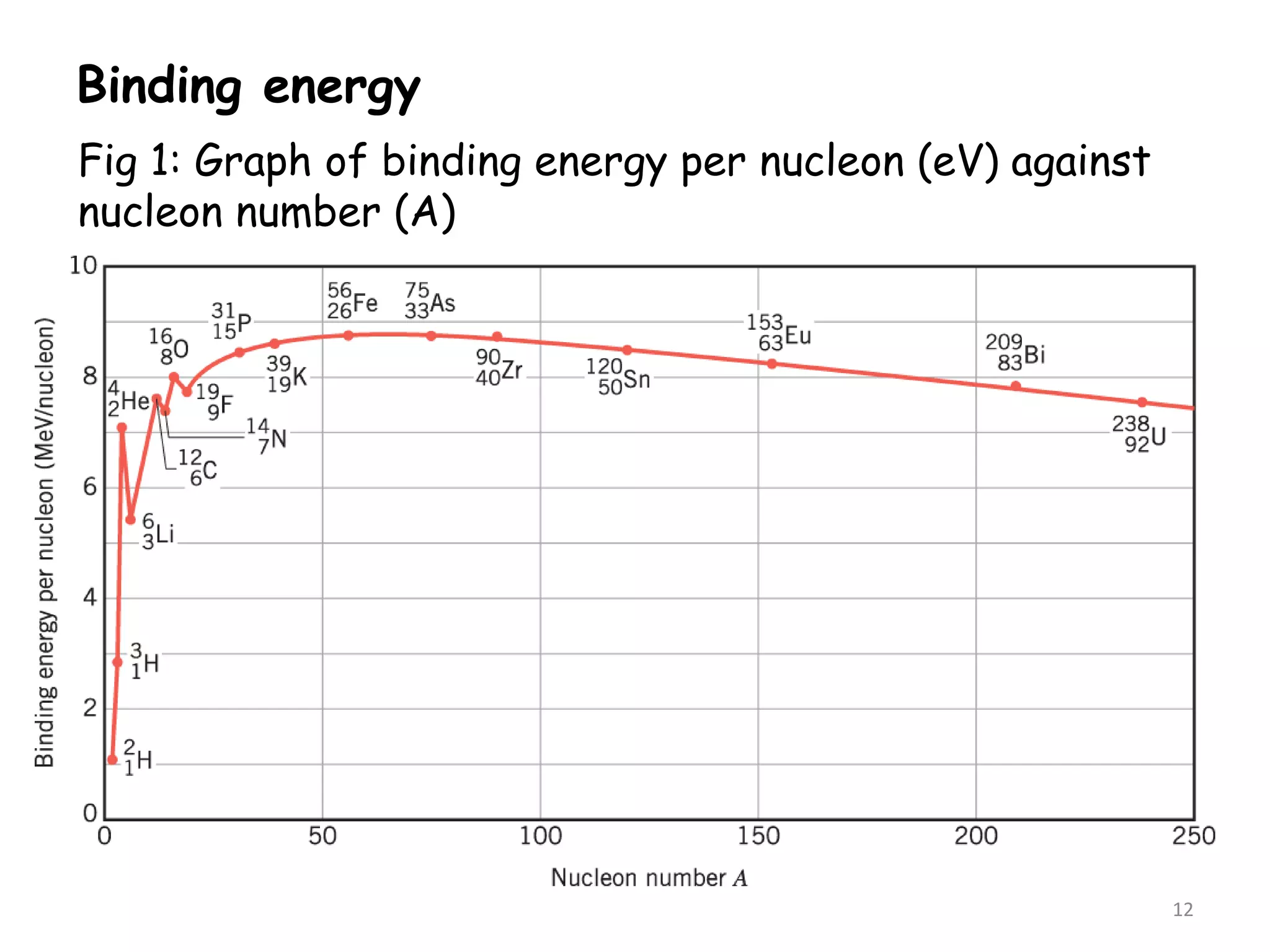
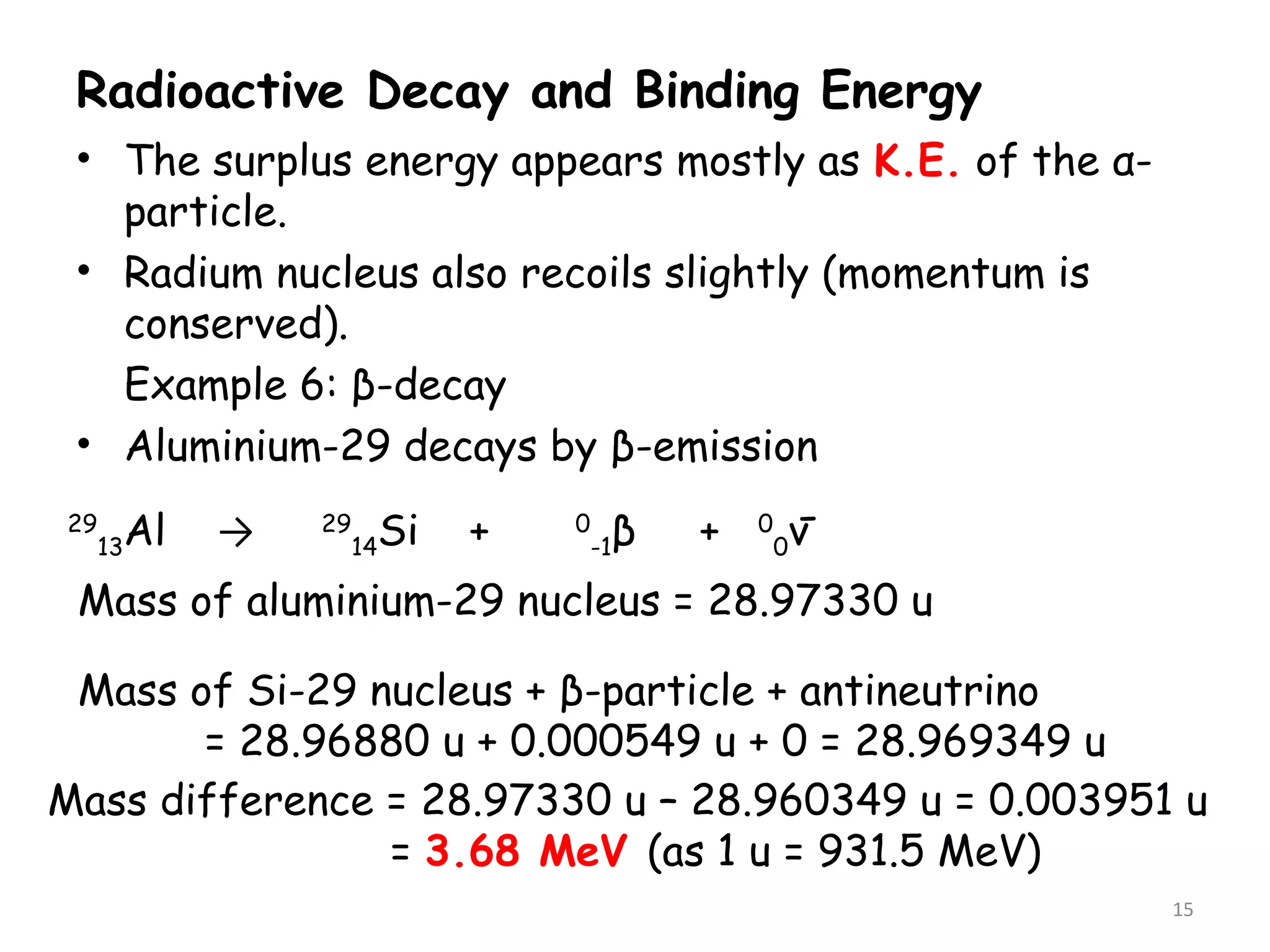
2. The binding energy per nucleon is typically around 8 MeV and indicates the stability of the nucleus. More stable nuclei have higher binding energies per nucleon. During radioactive decay, the daughter nucleus is more stable and has a higher binding energy per nucleon than the parent nucleus. The energy released during decay comes from the mass defect between the parent and daughter nuclei.
3. Calculating the mass defect and applying Einstein