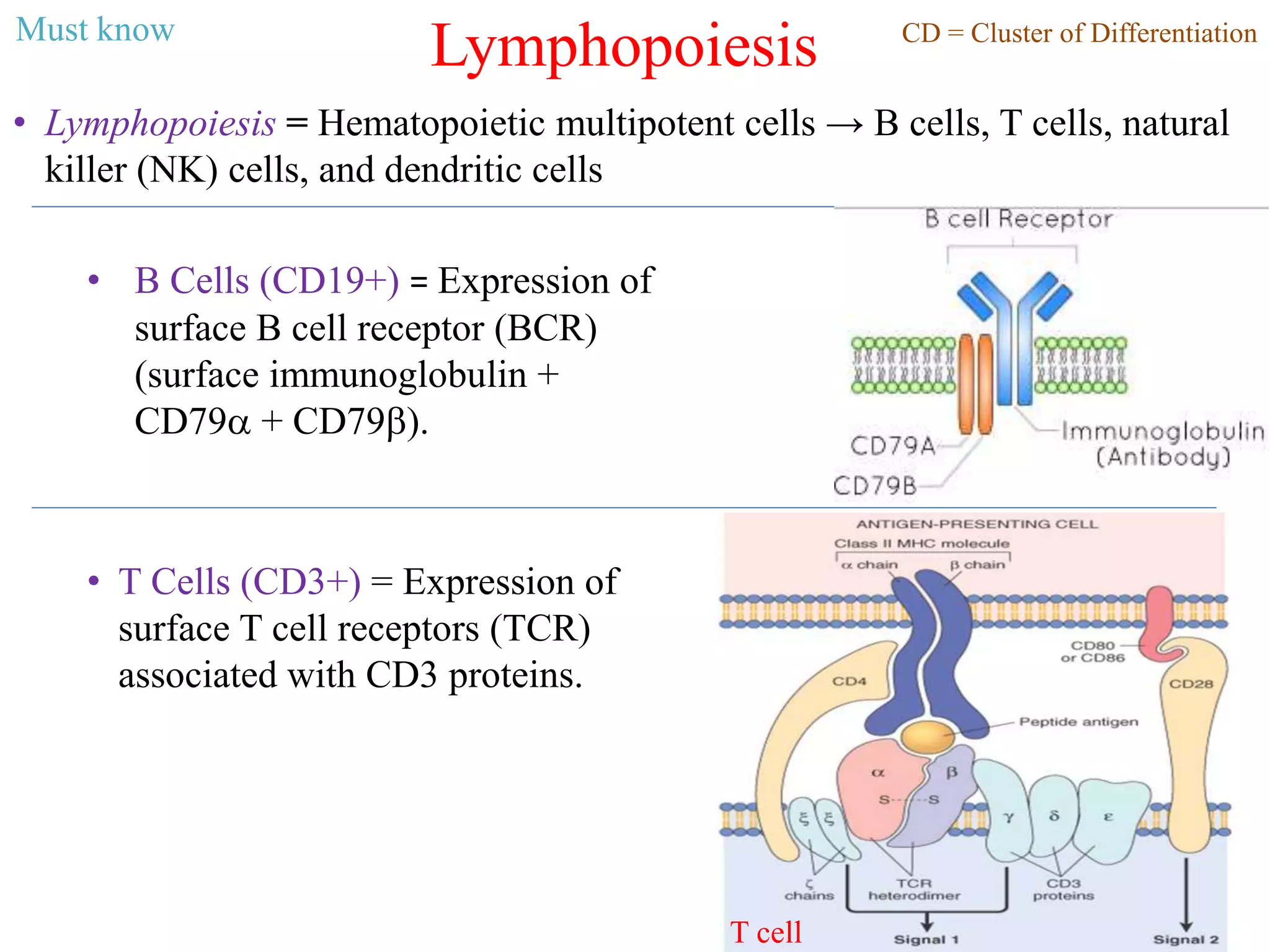
The document discusses primary immune deficiency (PID), highlighting increased risk of infections, autoimmunity, inflammation, and malignancies associated with various types of PID, including B cell and T cell deficiencies. It outlines the specific deficiencies, genetic mutations linked to conditions like agammaglobulinemia and DiGeorge syndrome, and provides indicators for early diagnosis in infants. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of avoiding live vaccines in PID patients and the necessity for screenings to diagnose immunodeficiencies.