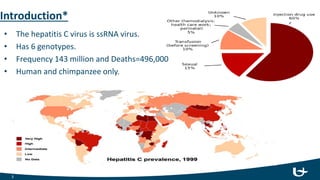
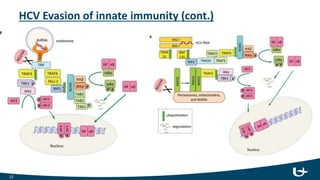
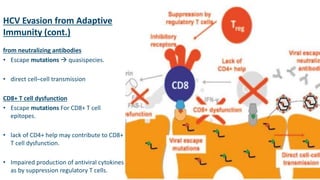
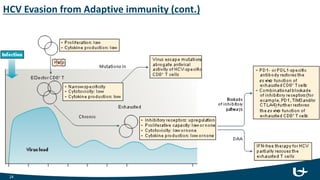
The document summarizes the hepatitis C virus (HCV) including its structure, life cycle, and interactions with the immune system. HCV is an RNA virus with 6 genotypes that infects humans and chimpanzees. It enters liver cells and replicates within the cytoplasm. Both innate and adaptive immune responses are believed to play a role in infection outcomes. Innate responses include interferons and liver macrophages, while adaptive responses involve CD4 and CD8 T cells, B cells, and antibodies. However, HCV has evolved mechanisms to evade these immune defenses through protein interference and rapid mutation of epitopes. Protective responses are thought to rely on CD8 cytotoxic T cells and CD4 helper functions. No approved vaccine currently exists, but