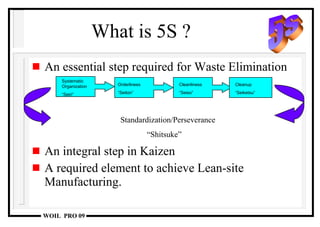
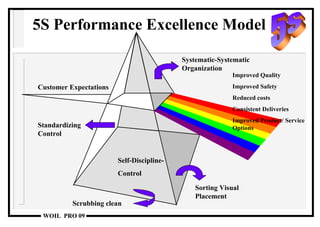
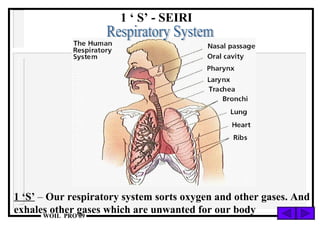
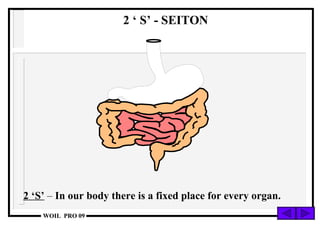
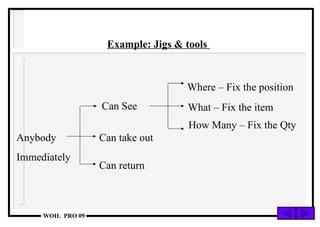
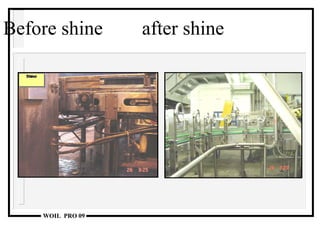
The document discusses the 5S methodology for performance excellence and continuous improvement. It describes the 5S principles as sort, set in order, shine, standardize, and sustain. When implemented, 5S helps eliminate waste, improve organization and visual control of the workplace, and standardize processes to maintain improvements and control critical parameters. Examples show how 5S can organize storage, clean work areas, and establish standard processes.