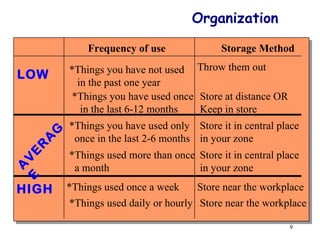
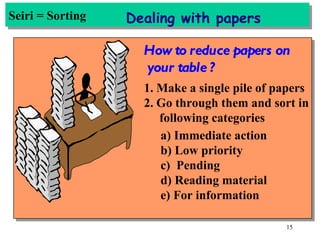
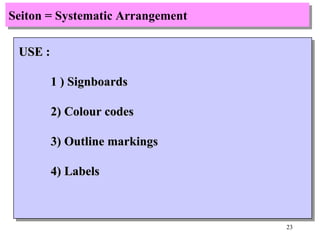
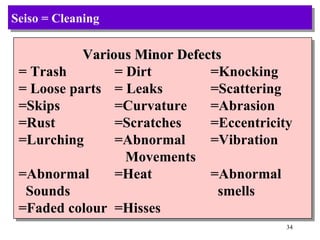
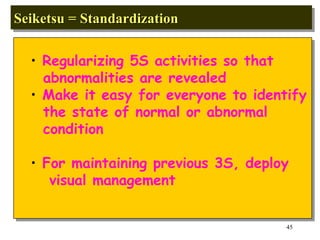
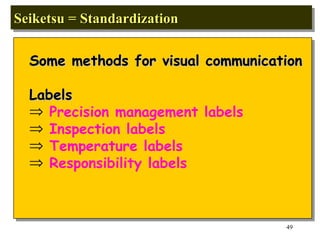
The document discusses the principles and objectives of 5S, which are a set of five organizational techniques used to improve the workplace. The 5S's are Seiri (sorting), Seiton (systematic arrangement), Seiso (cleaning), Seiketsu (standardization), and Shitsuke (self-discipline). Each S is defined in 1-2 sentences with its meaning and the activities involved. Methods for implementing each S like visual controls, checklists, and establishing self-discipline through committees and training are also summarized briefly.