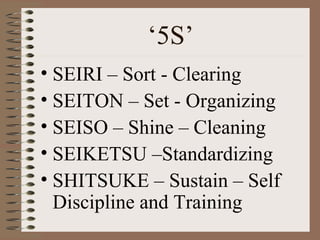
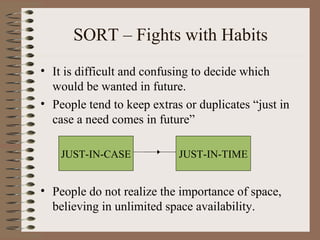
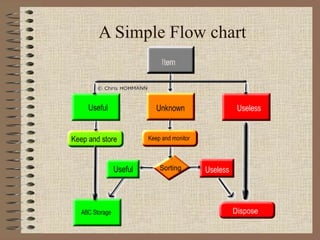
The document describes the 5S methodology for organizing and visual controls in the workplace. It consists of 5 steps - Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain. Common objections to 5S include that it is an additional burden or takes too much time. However, companies that implement 5S successfully see benefits like improved efficiency, cost reductions of 20%, and increased productivity and safety. The document outlines each of the 5 steps and provides examples of how 5S can organize tools, work areas, and storage.