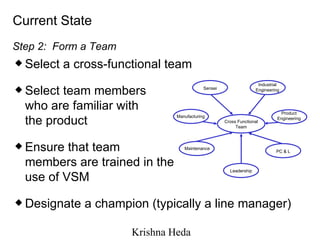
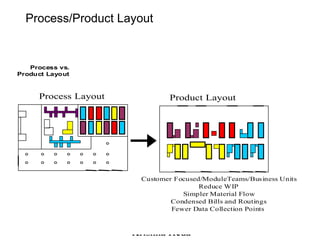
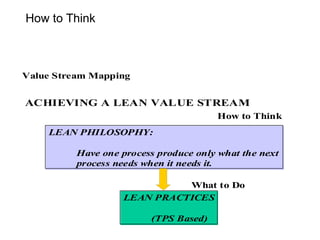
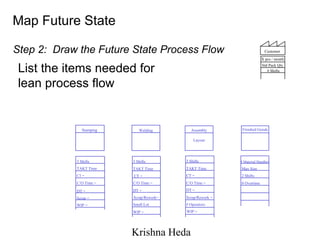
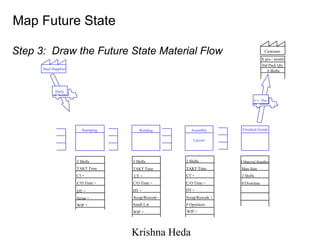
The document discusses Value Stream Mapping (VSM) as a method to identify and eliminate waste in manufacturing processes by analyzing the flow of materials and information. It outlines a total system strategy that requires leadership, knowledge, and action bias to succeed, and provides guidelines for mapping current and future states of the value stream. The process involves understanding customer demand, mapping processes, and strategizing improvements to enhance operational efficiency and reduce waste.