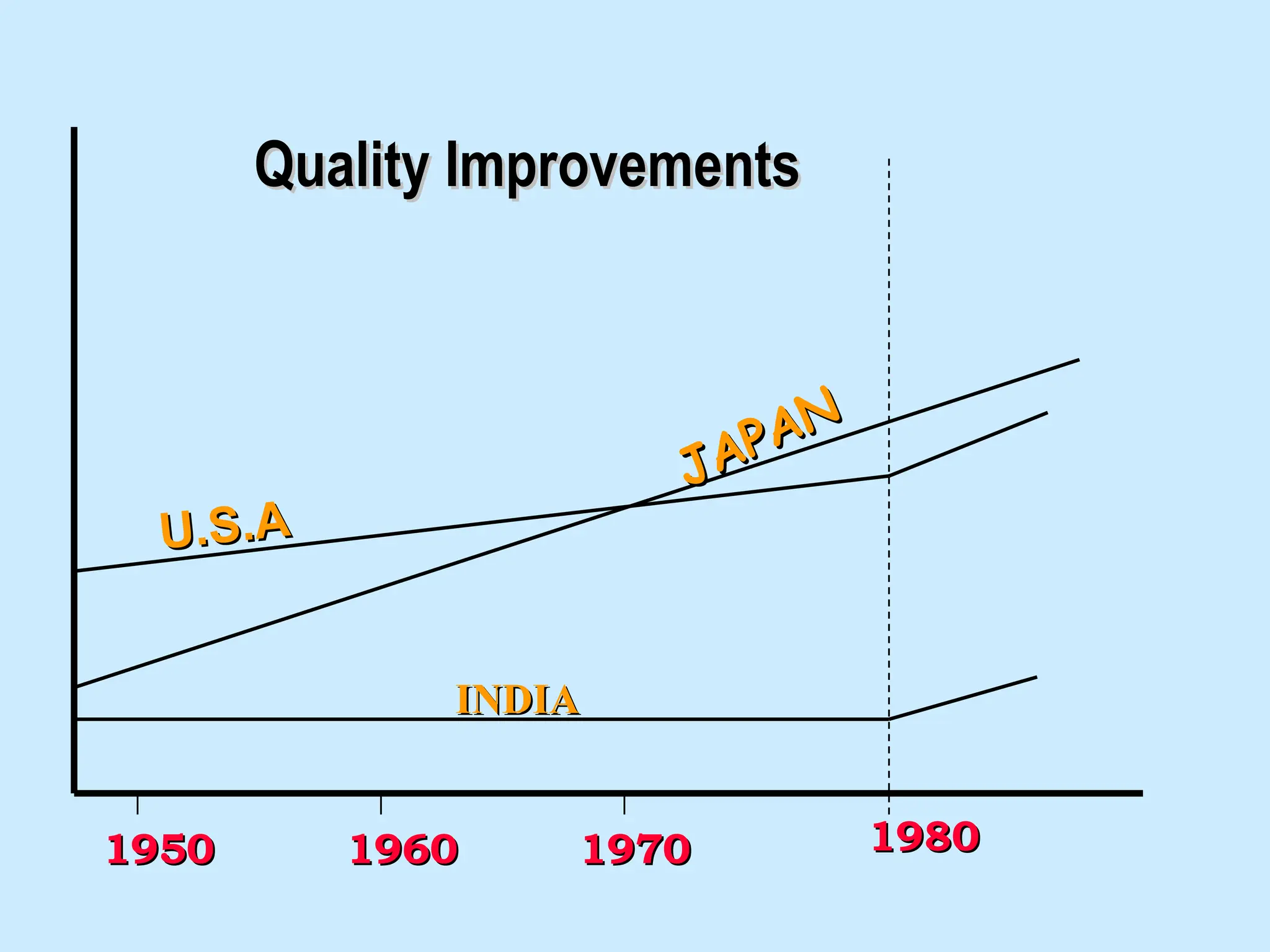
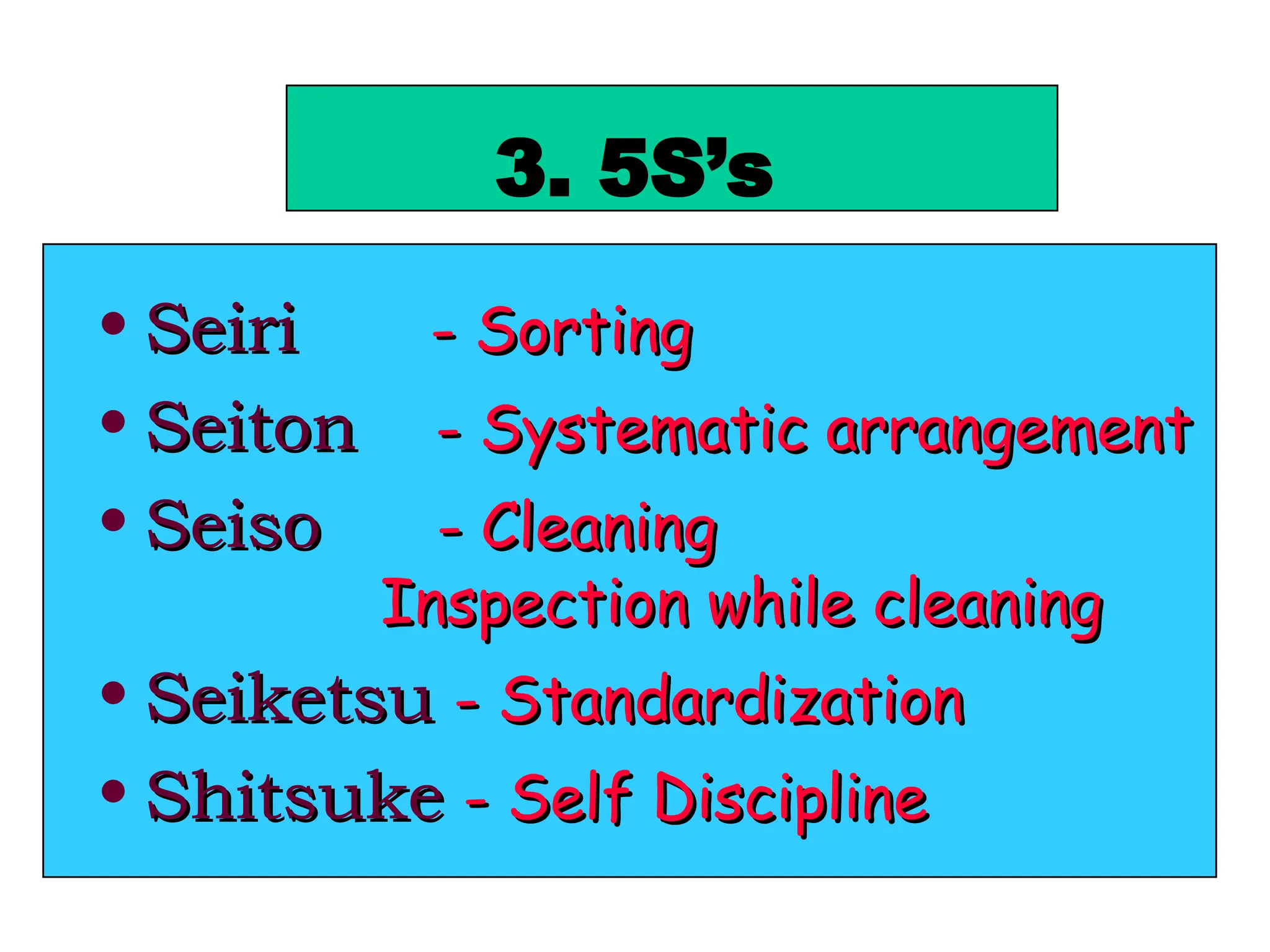
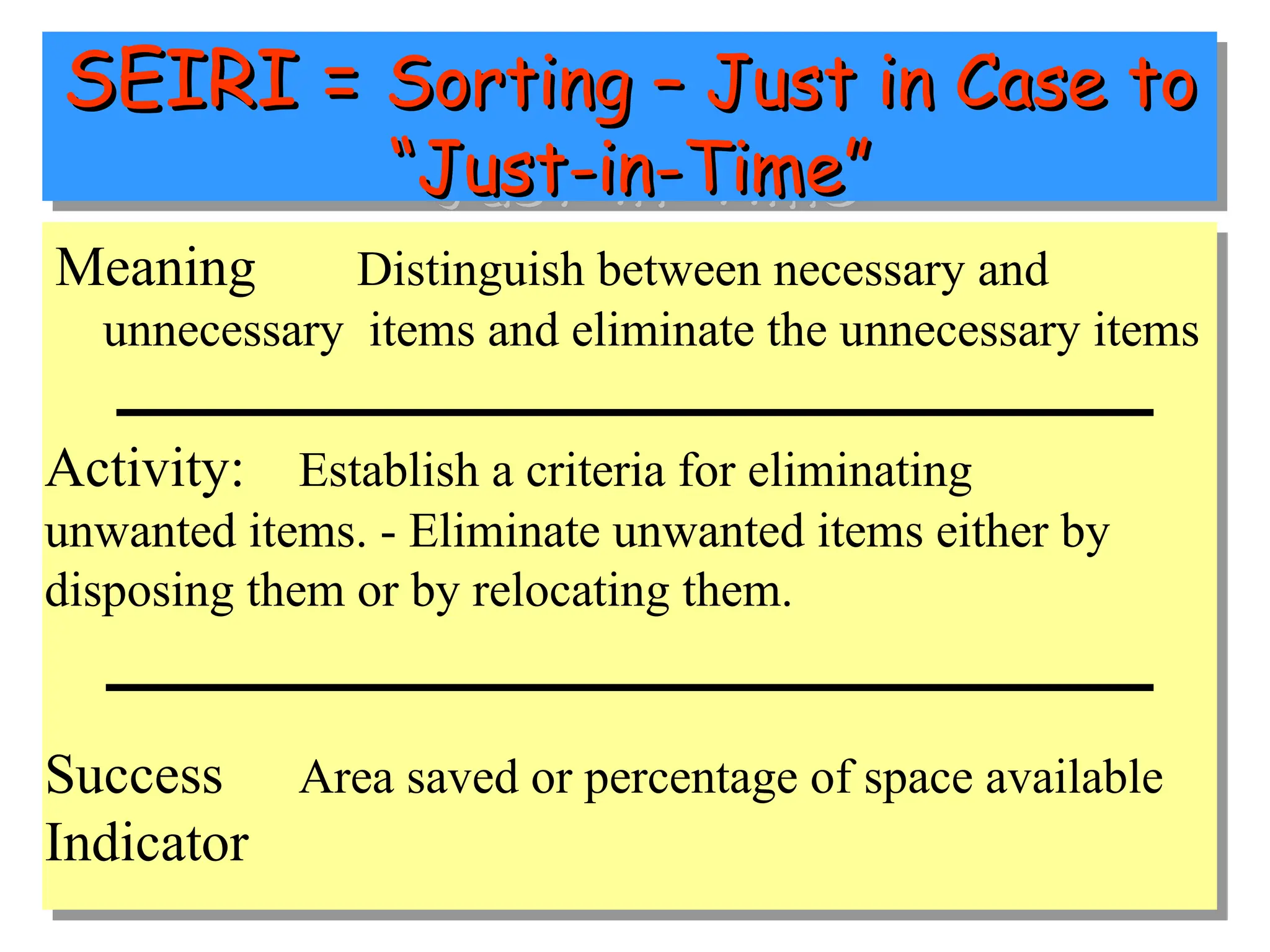
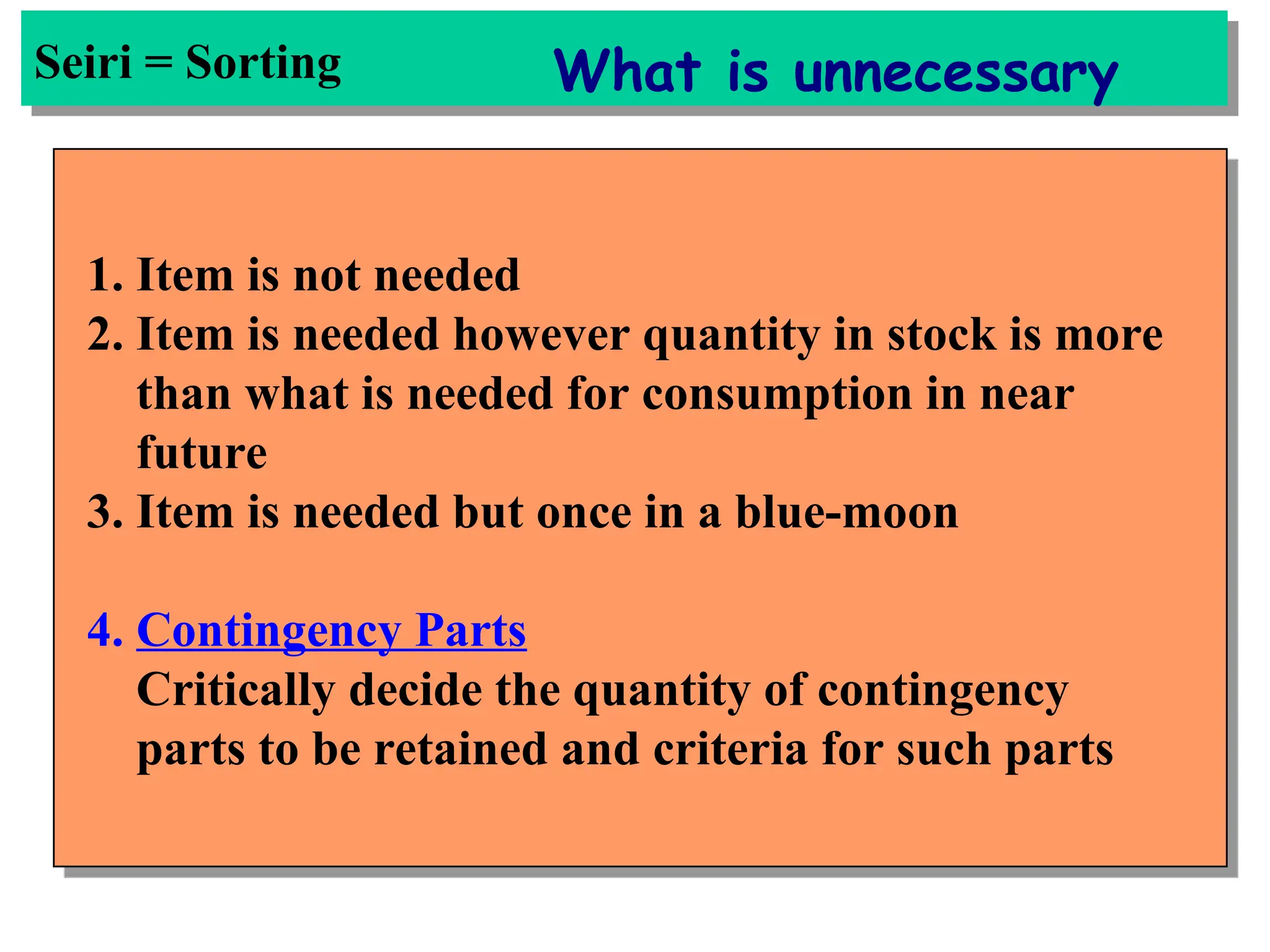
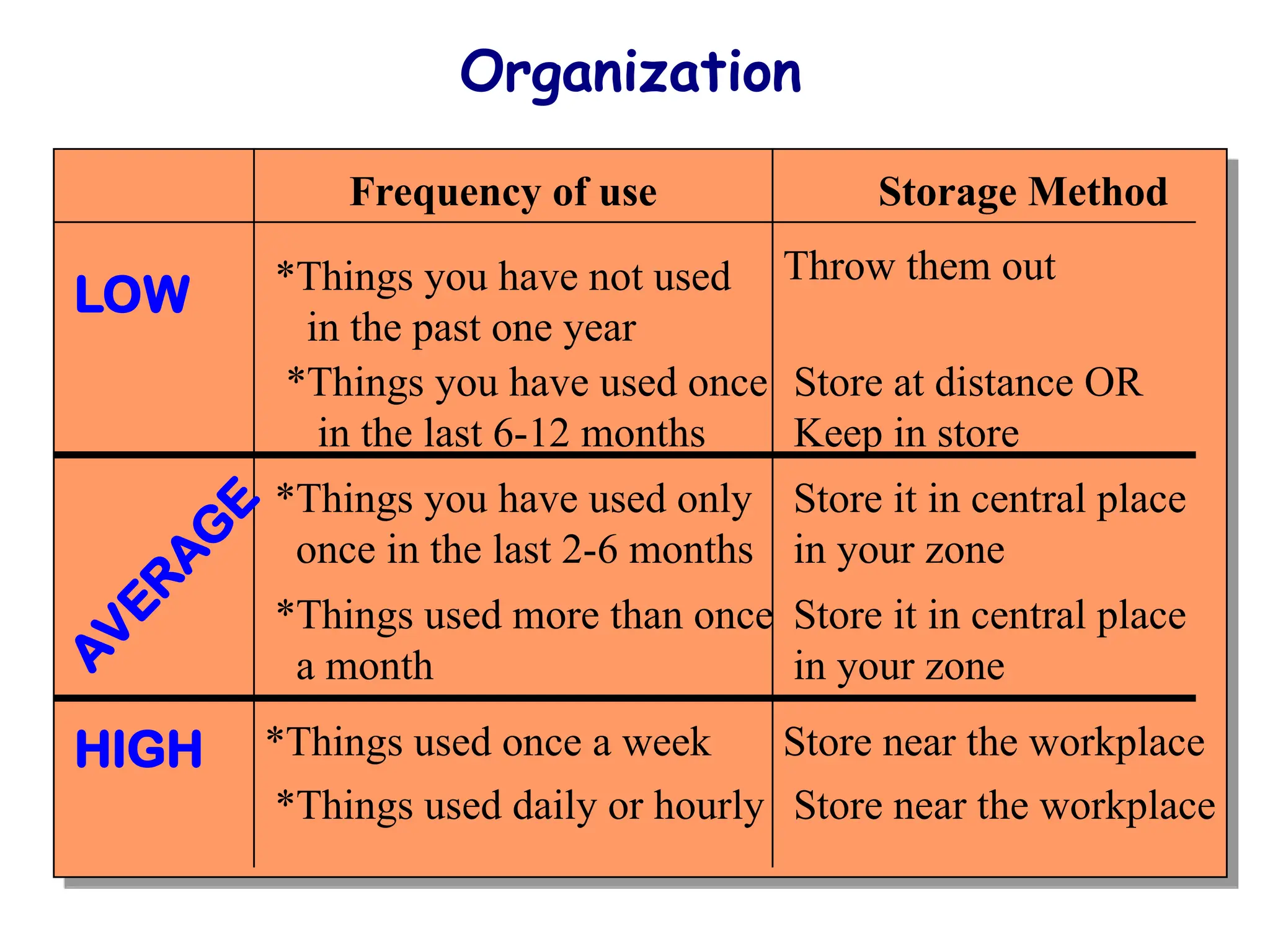
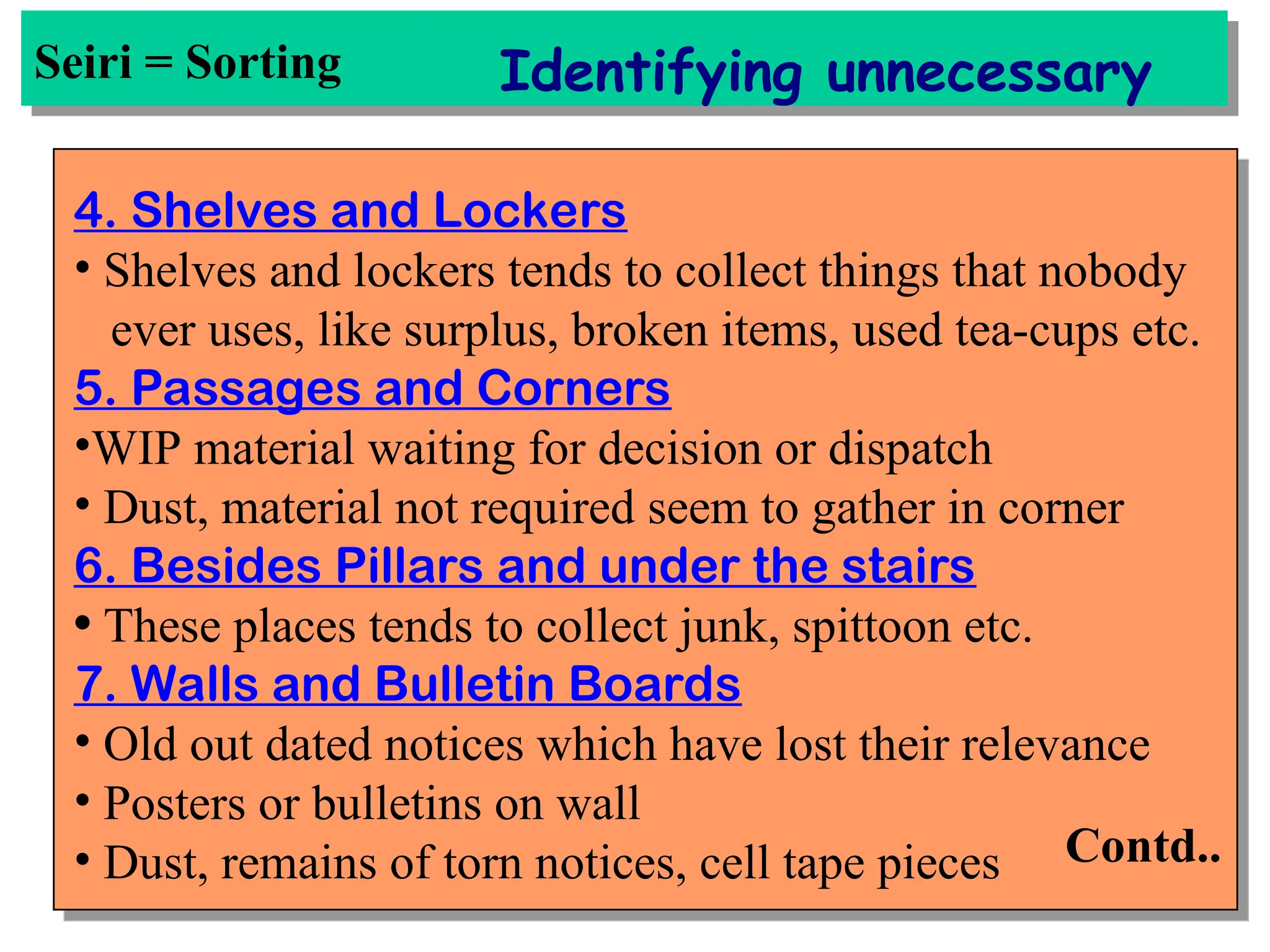
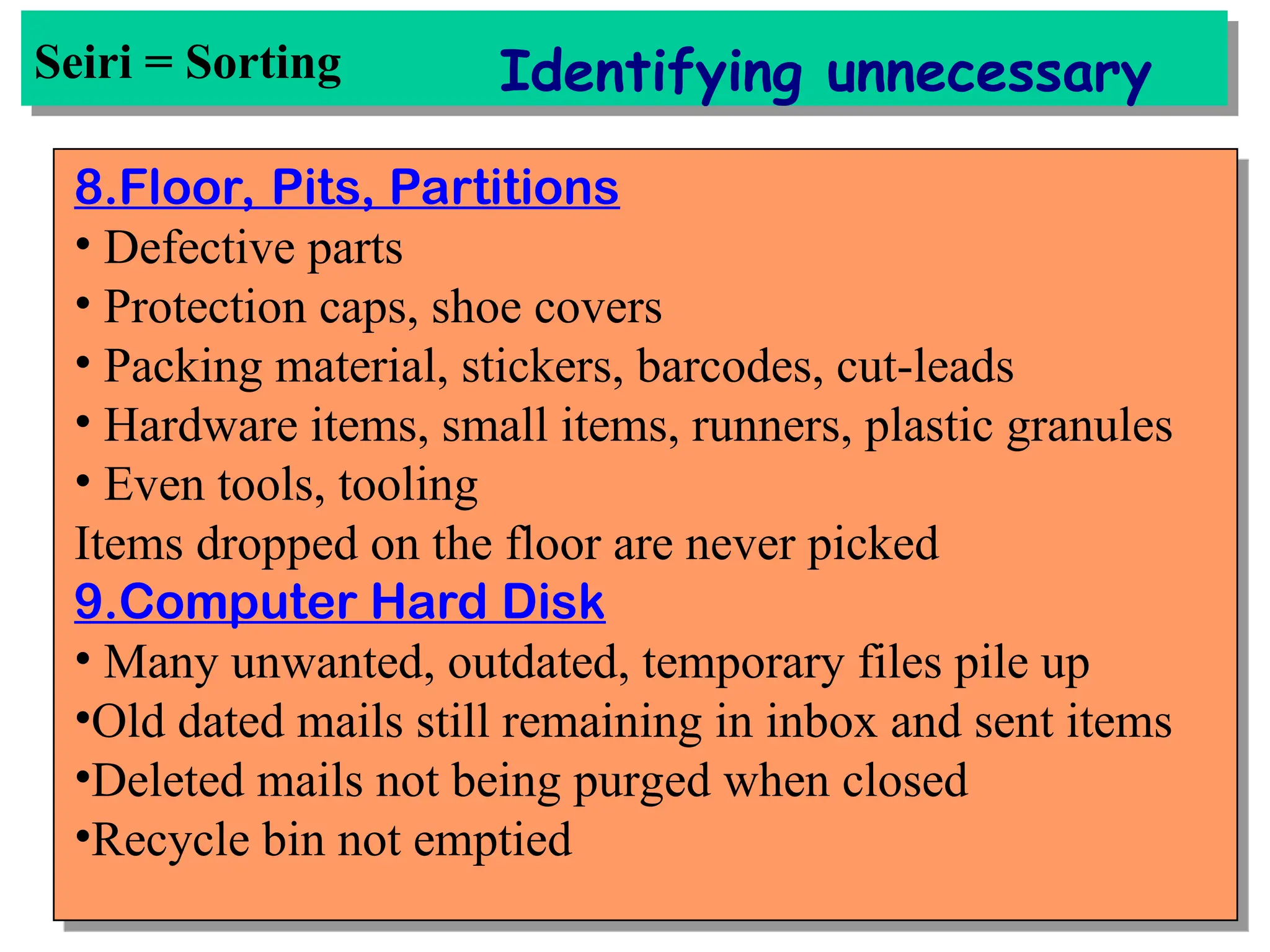
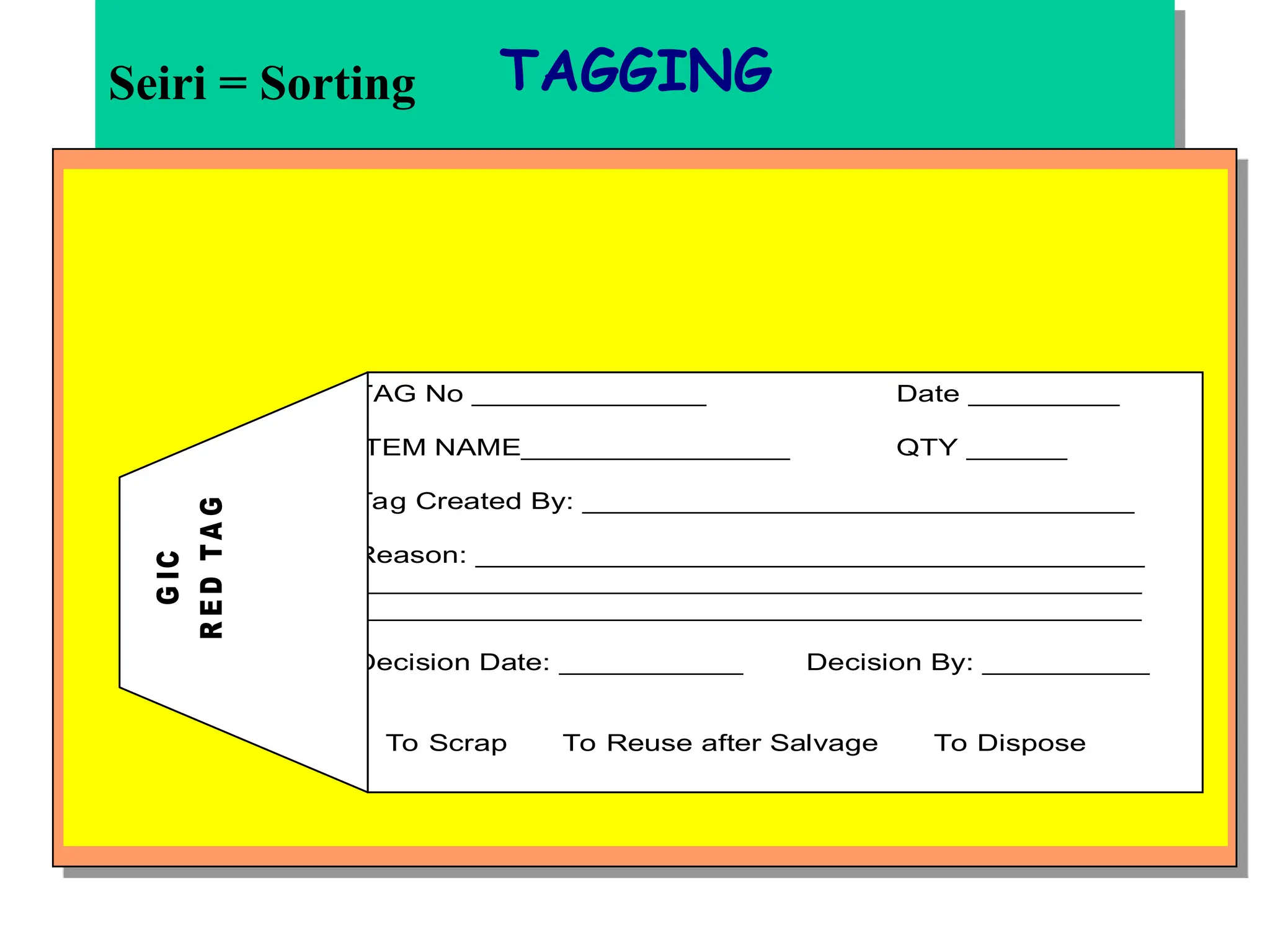
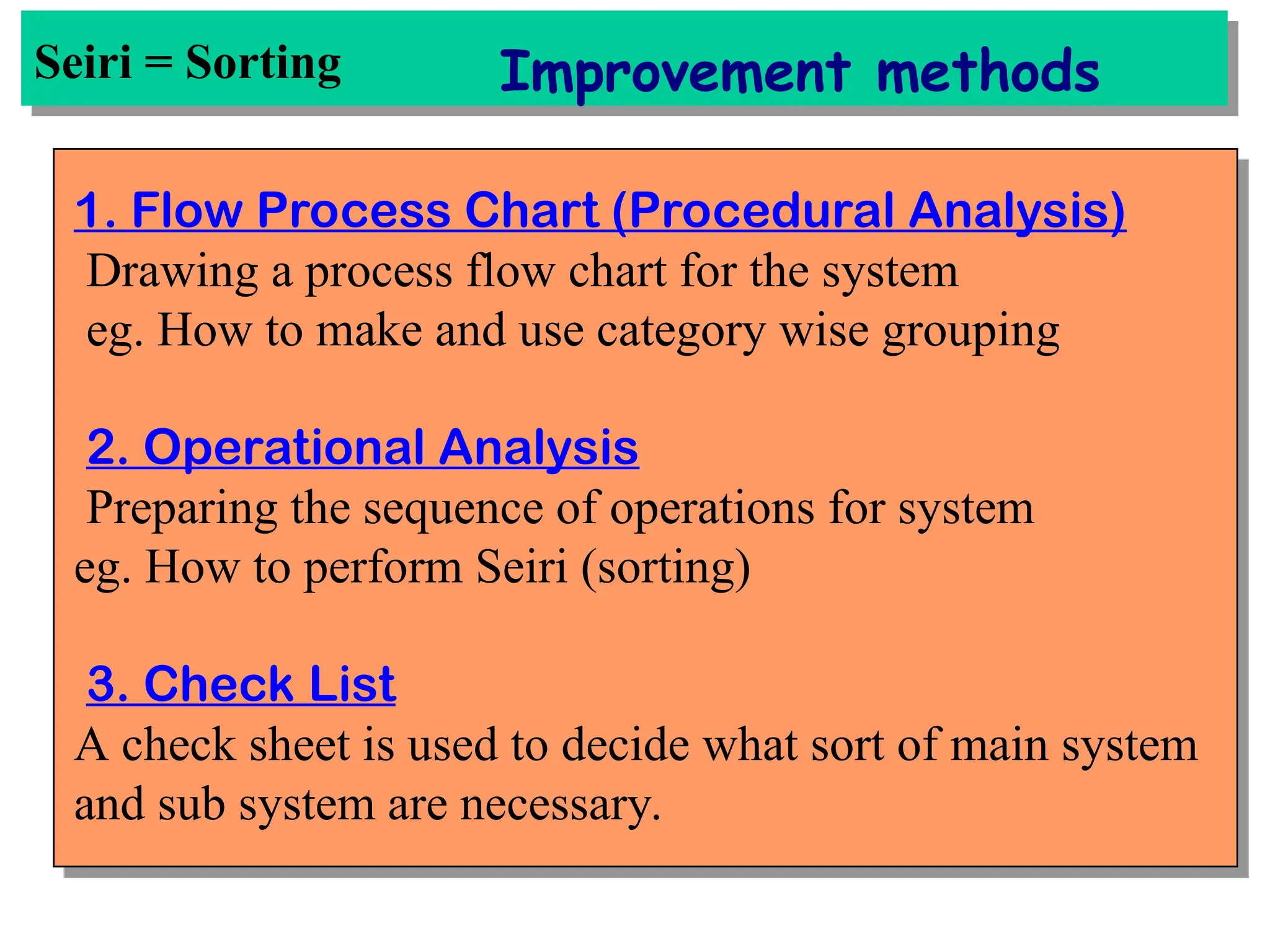
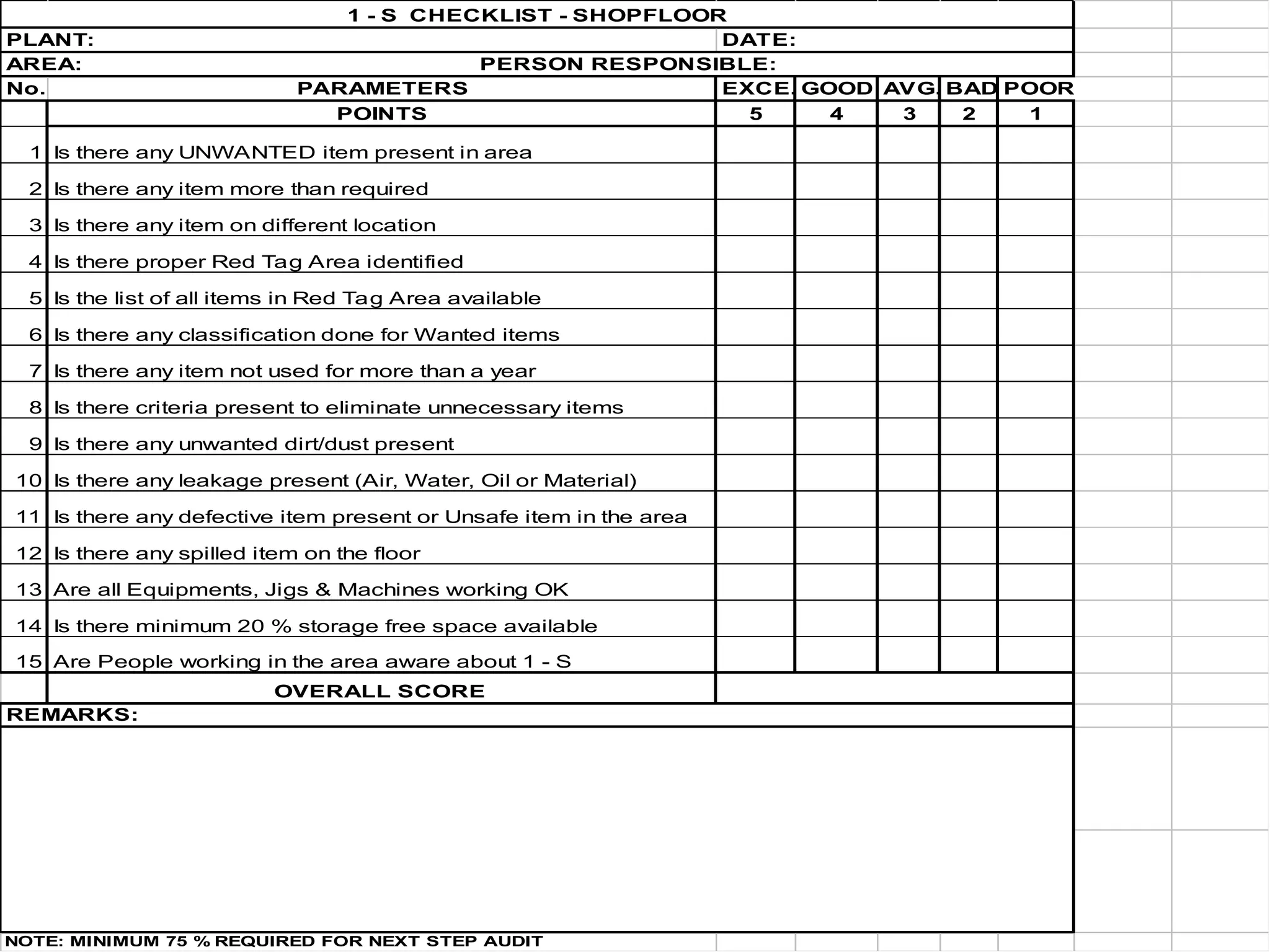
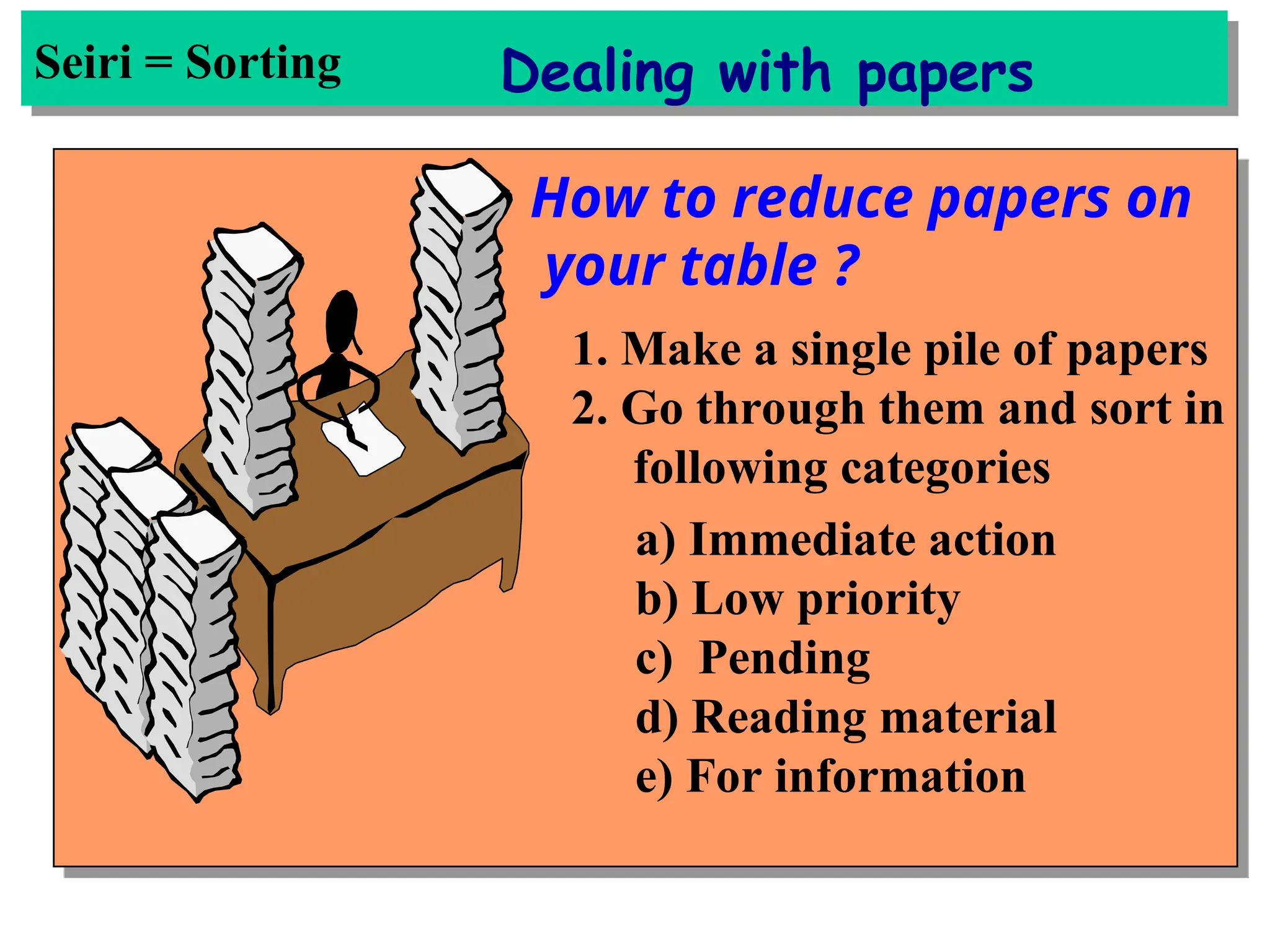
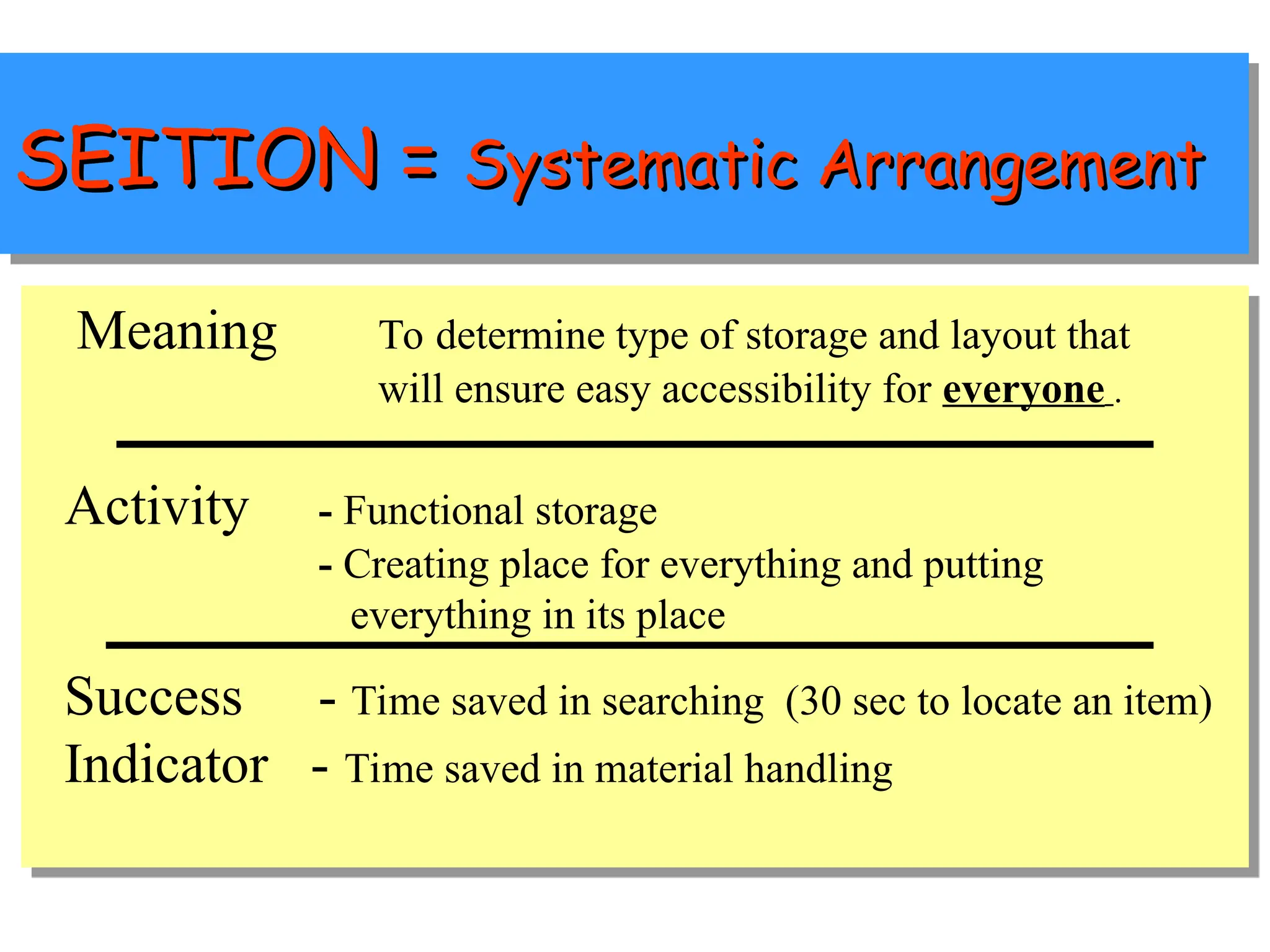
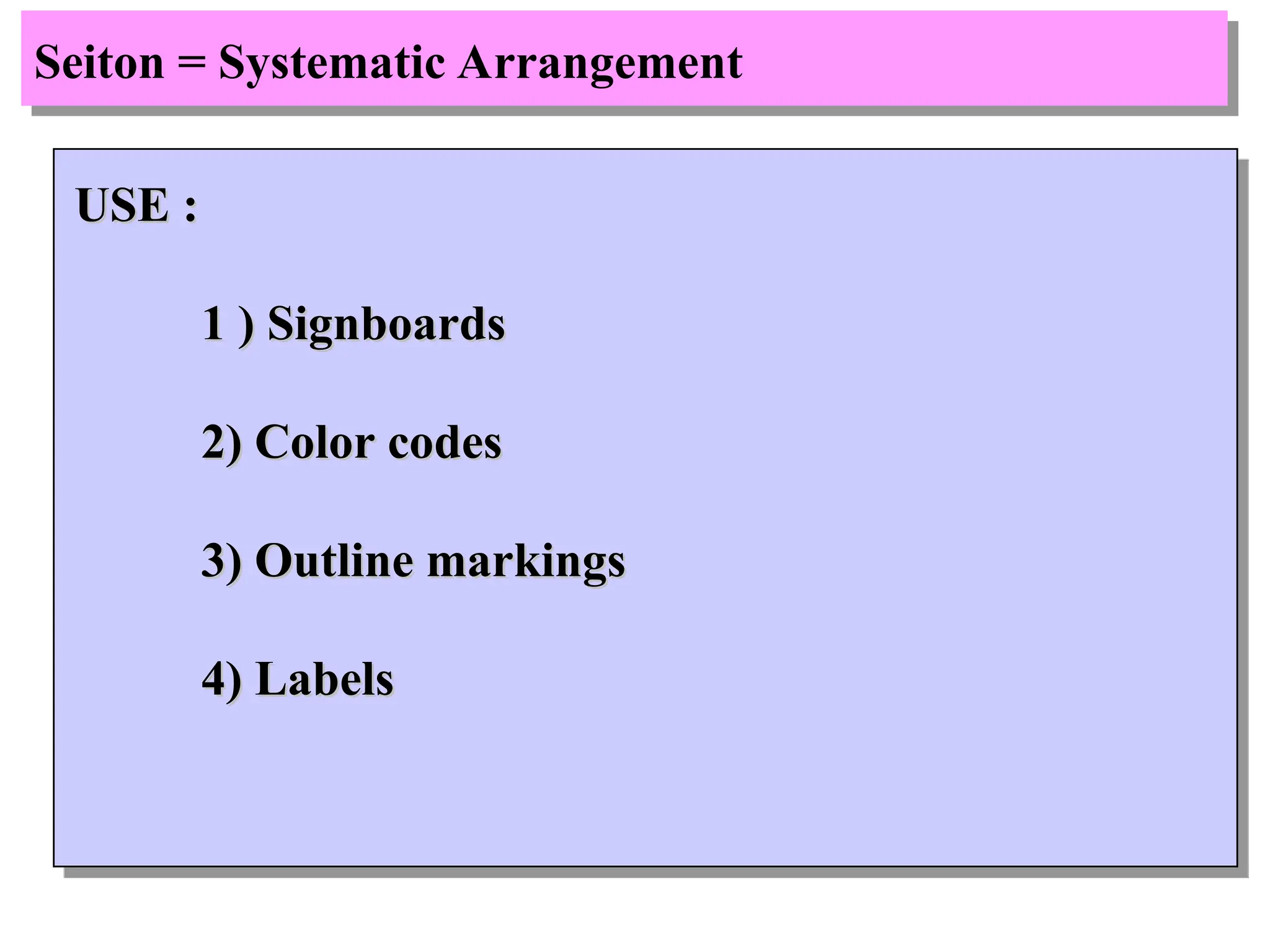
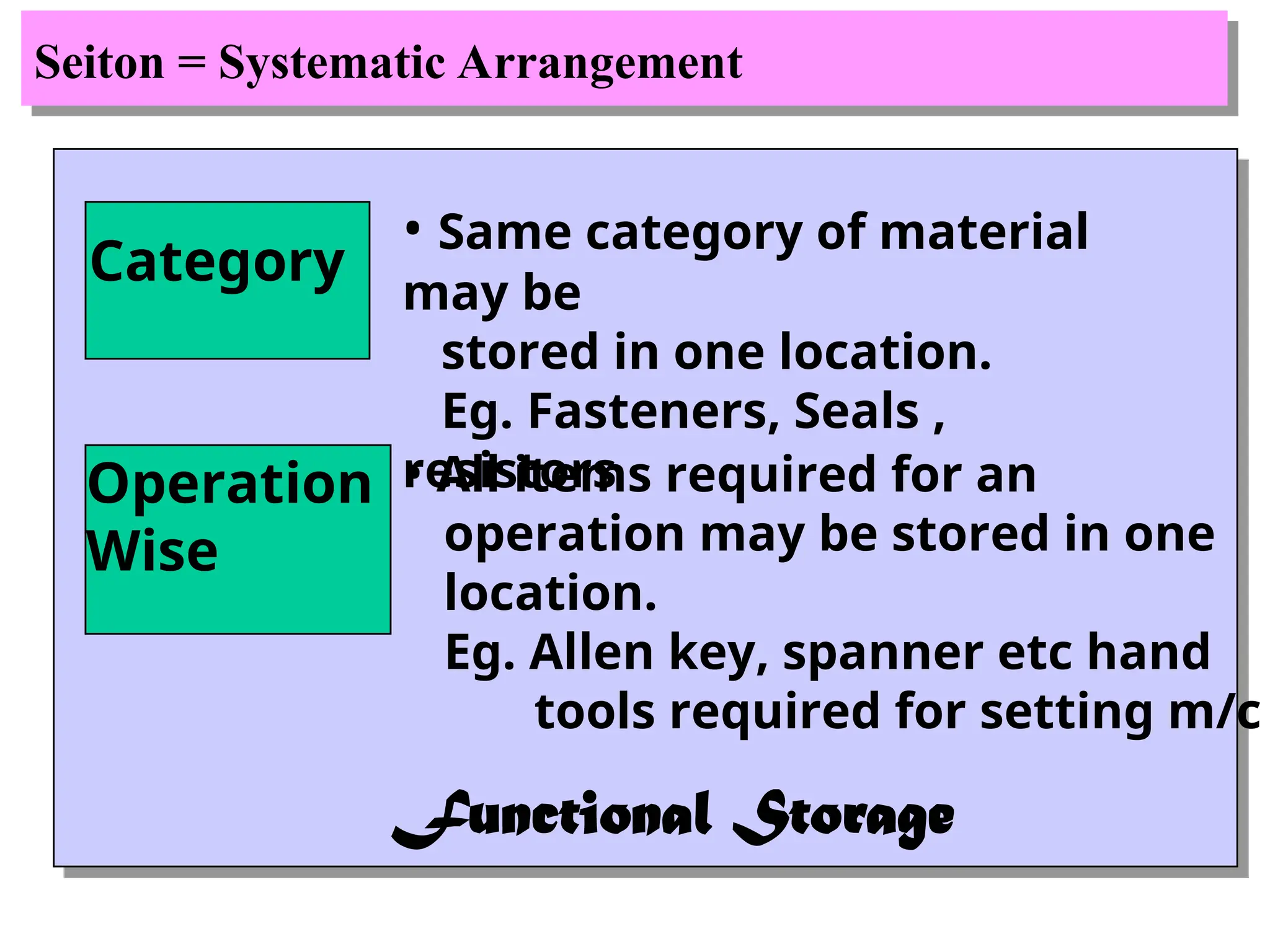
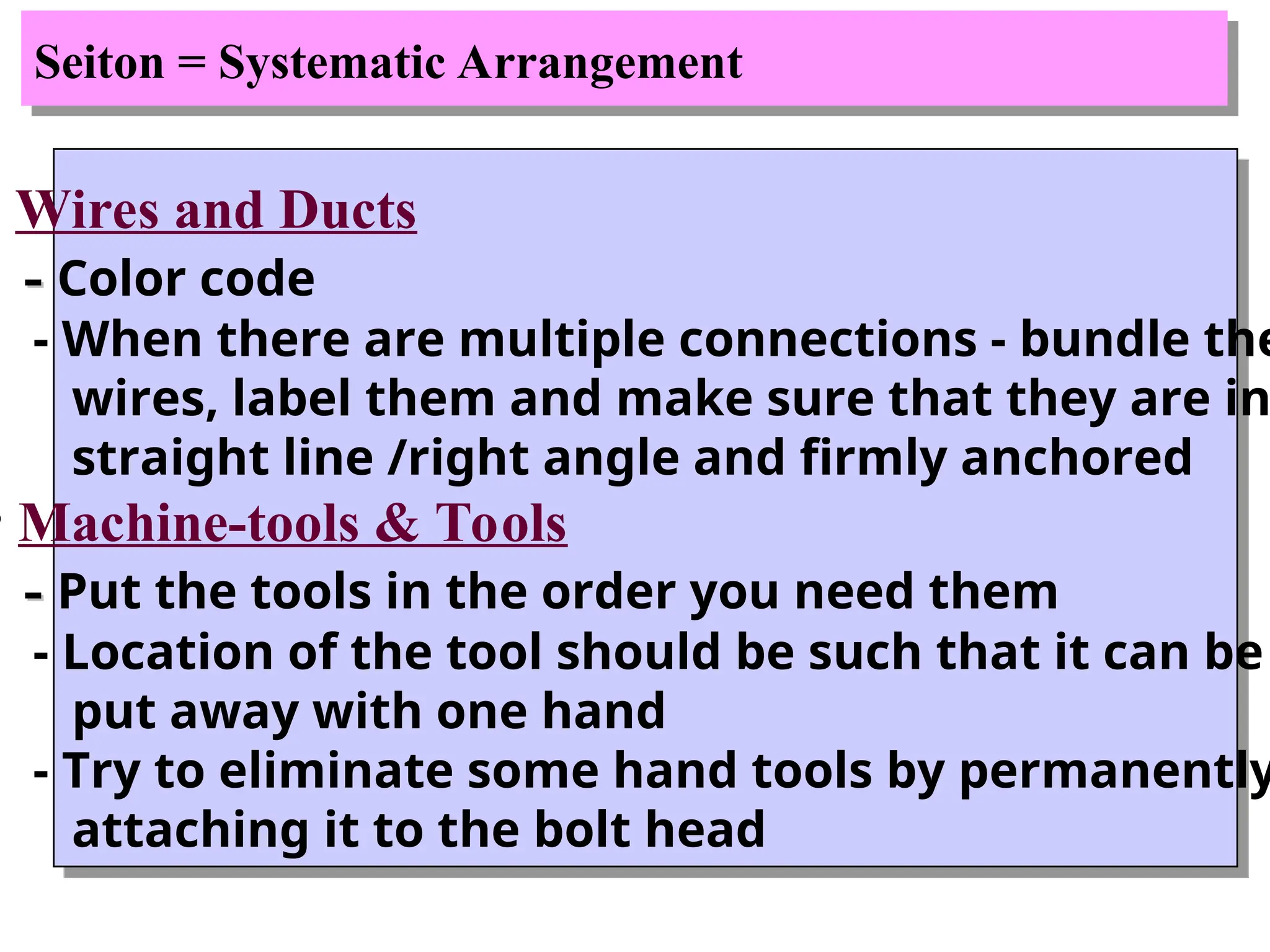
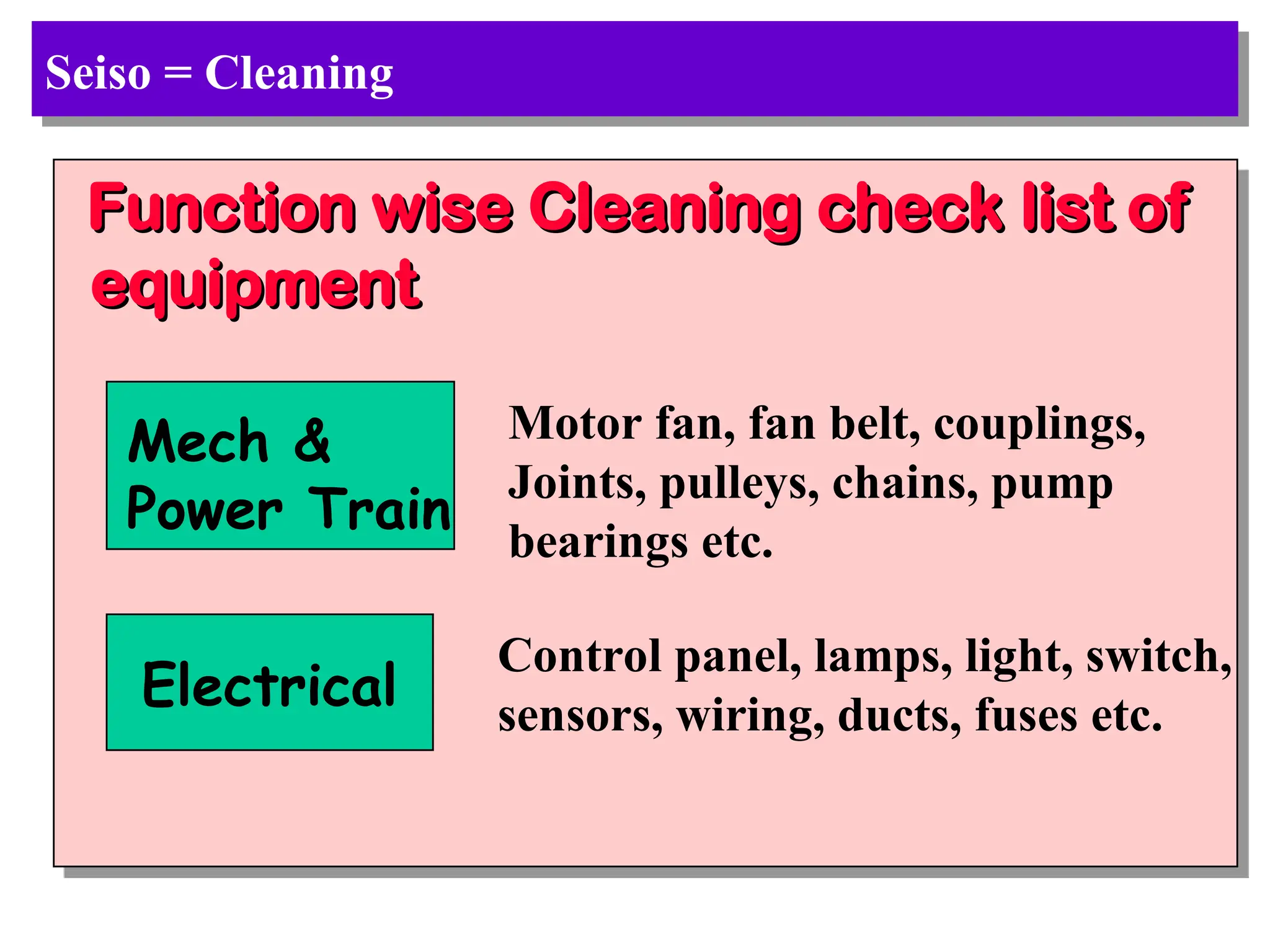
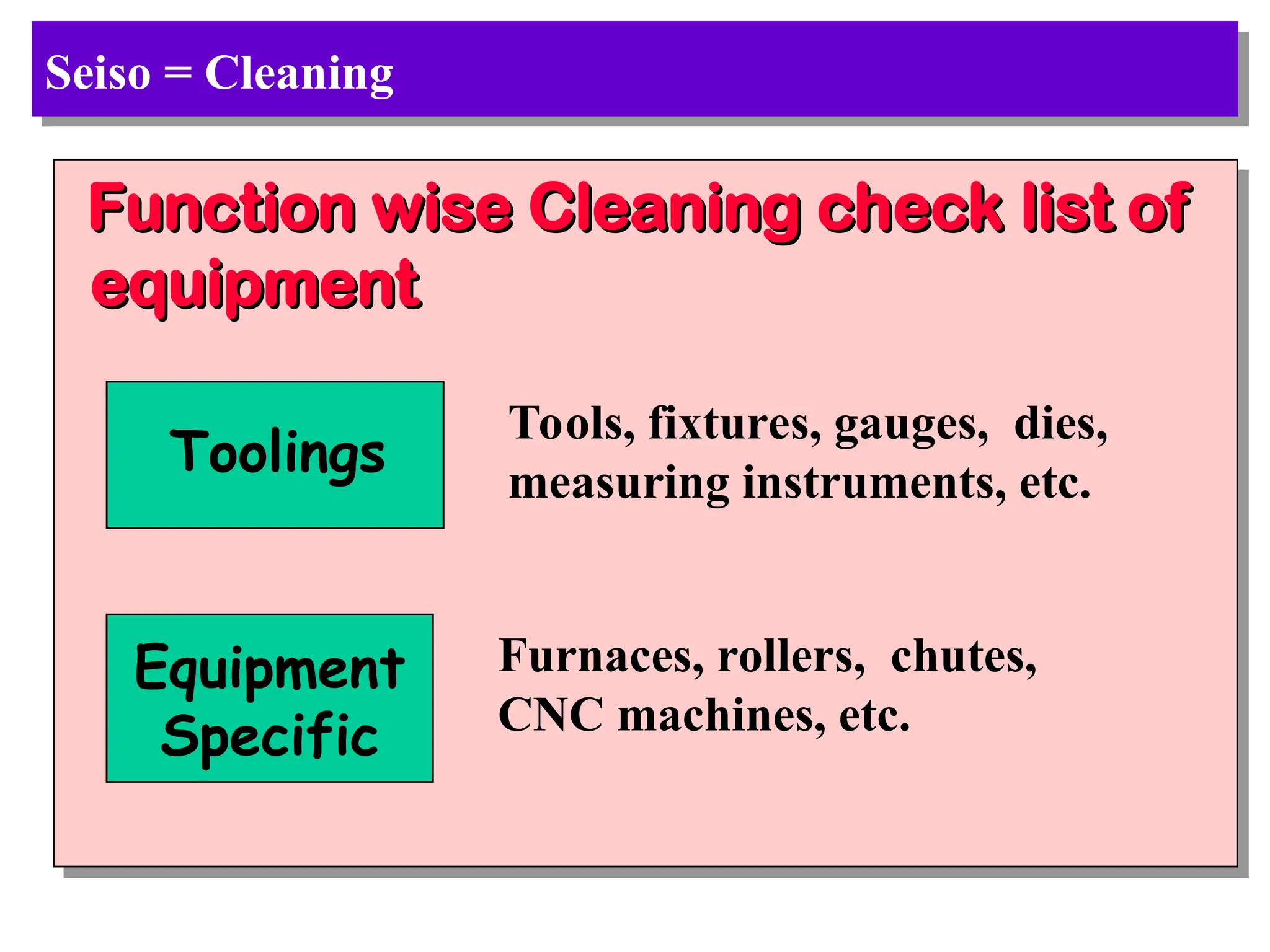
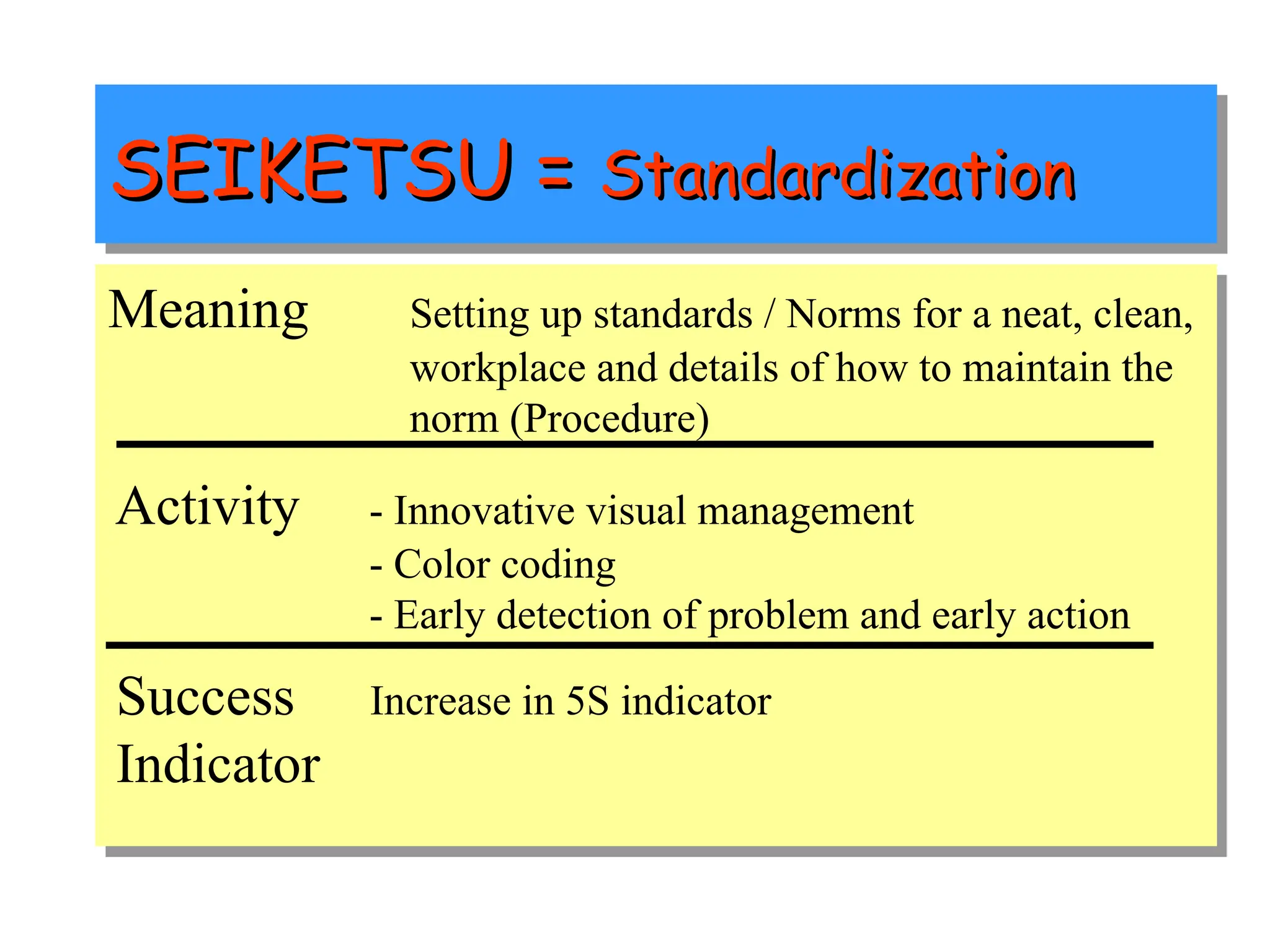
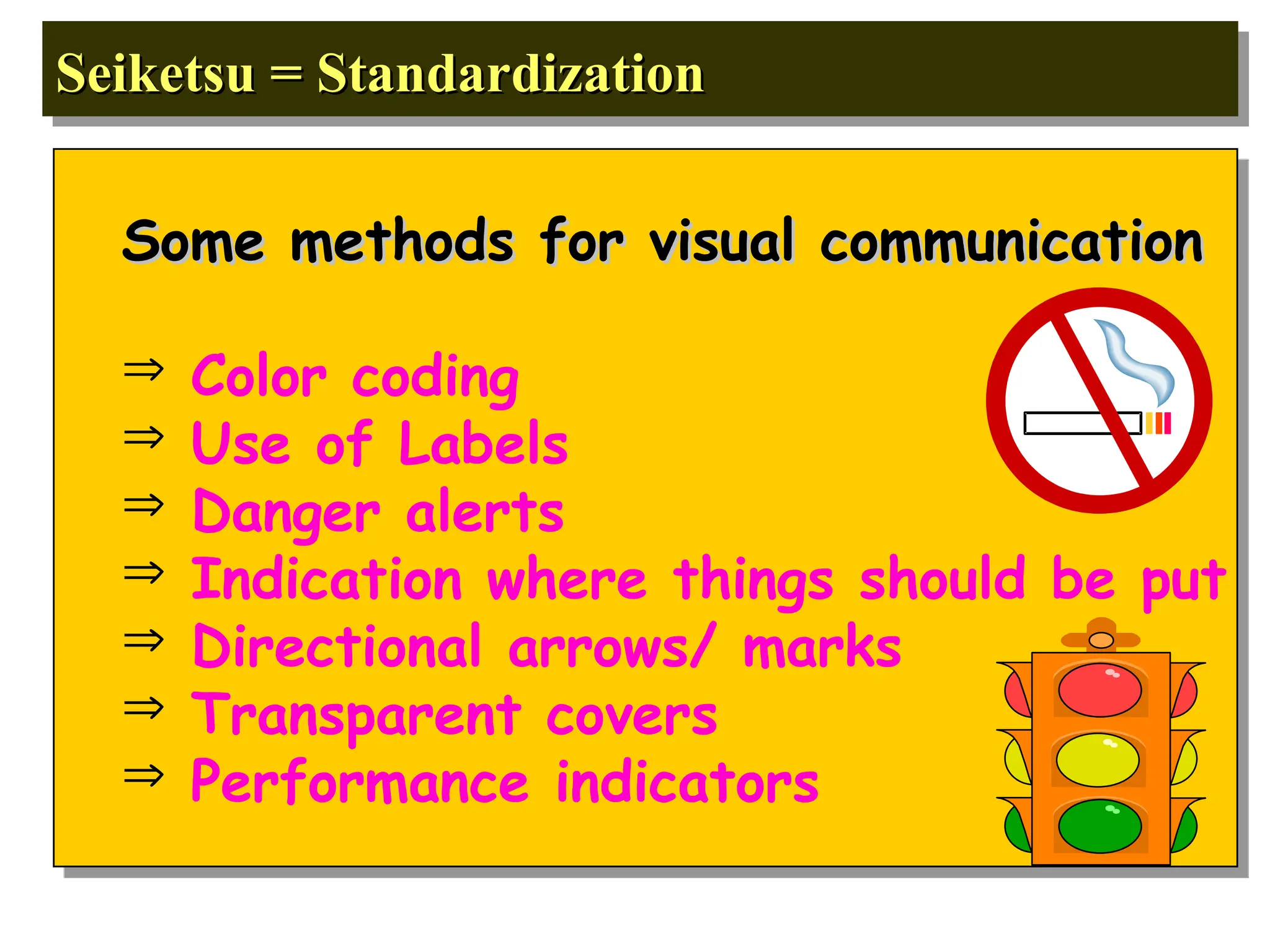
The document discusses the 5S principles (Seiri, Seiton, Seiso, Seiketsu, Shitsuke) aimed at improving workplace organization and efficiency by eliminating waste, standardizing processes, and promoting discipline among employees. Each principle focuses on specific actions like sorting items, systematic arrangement, cleaning, and maintaining standards, with the ultimate goal of enhancing productivity and creating a safe, clean work environment. It also emphasizes the importance of participation from everyone in the organization to adopt and maintain these practices.