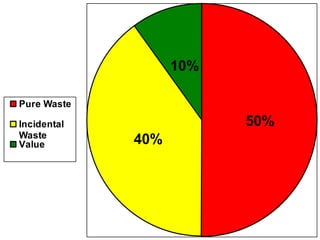
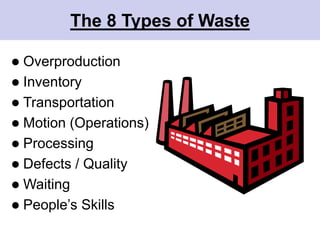
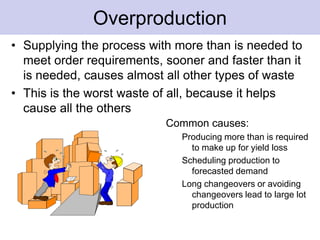
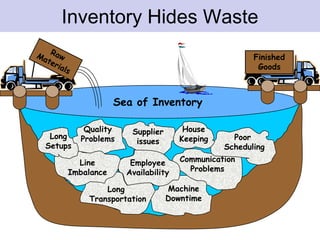
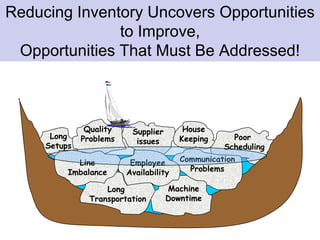
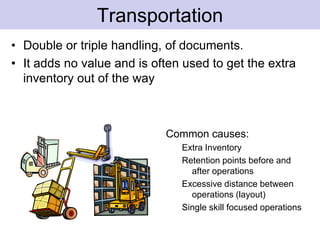
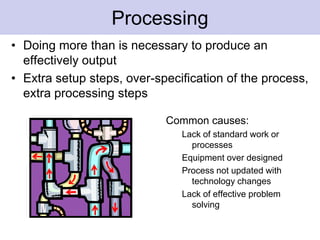
The document discusses the concept of waste in processes, emphasizing the eight types of waste, which include overproduction, inventory, transportation, motion, processing, defects, waiting, and people's skills. It explains that waste adds costs and time without contributing value, and outlines methods to identify and eliminate waste using lean tools and employee engagement. Understanding customer value is crucial to differentiate value-added activities from waste, and a proactive attitude is necessary for effective waste removal.