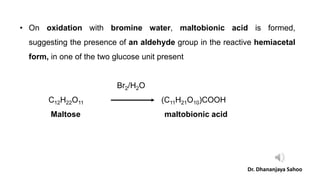
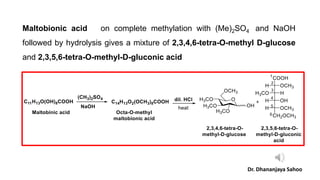
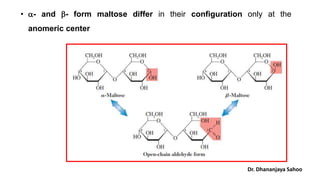
Maltose is a reducing sugar that is soluble in water but insoluble in ether. It reduces Tollen's reagent and Fehling's solution. Upon hydrolysis, maltose yields two molecules of glucose. Maltose is composed of two glucose units linked via an alpha-1,4-glycosidic bond between the anomeric carbon of one glucose and the C4 hydroxyl of the other. Oxidation of maltose forms maltobionic acid, indicating the presence of an aldehyde group in one of the glucose units. Complete methylation and hydrolysis of maltobionic acid produces 2,3,4,6-tetra-O-methyl-D-glucose