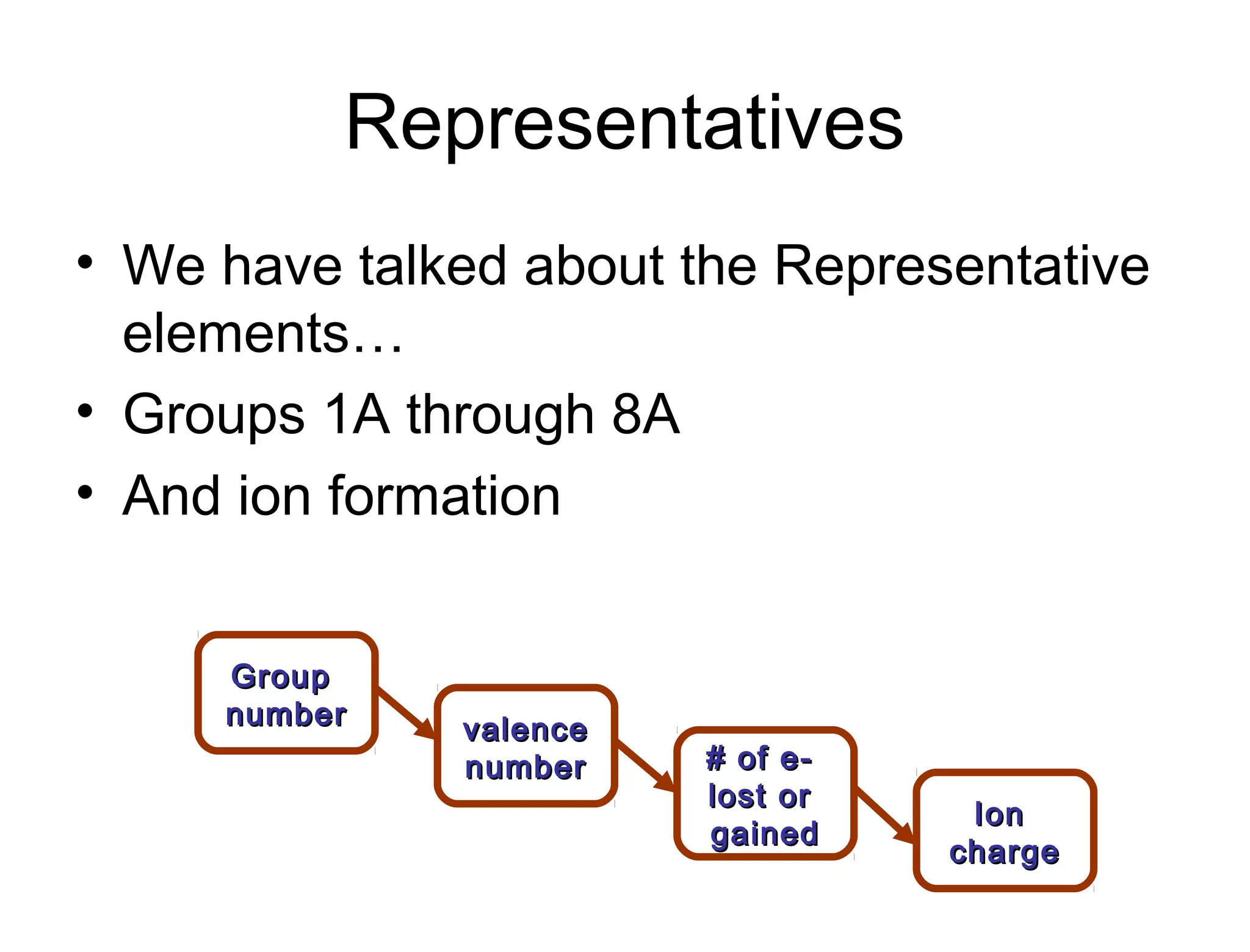
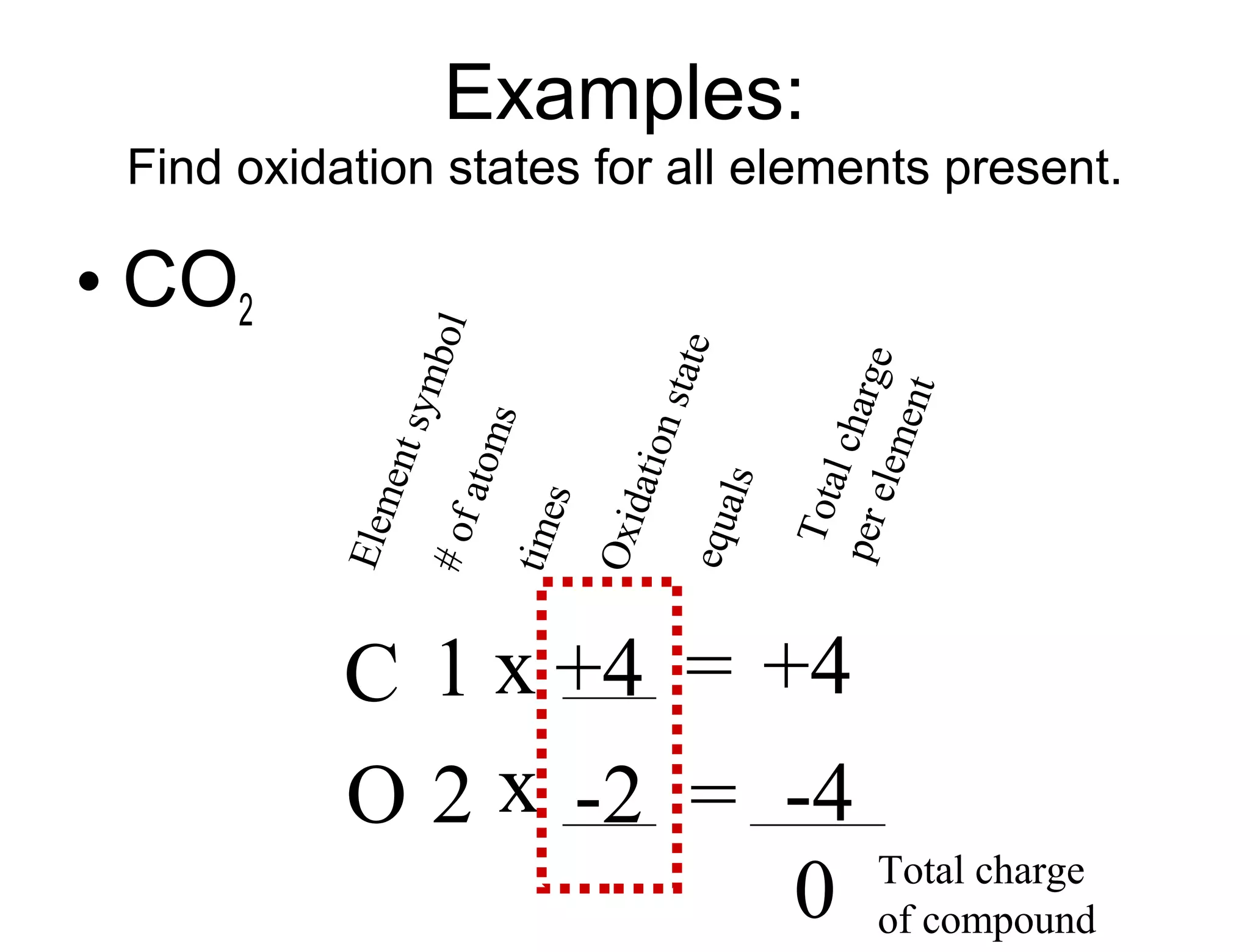
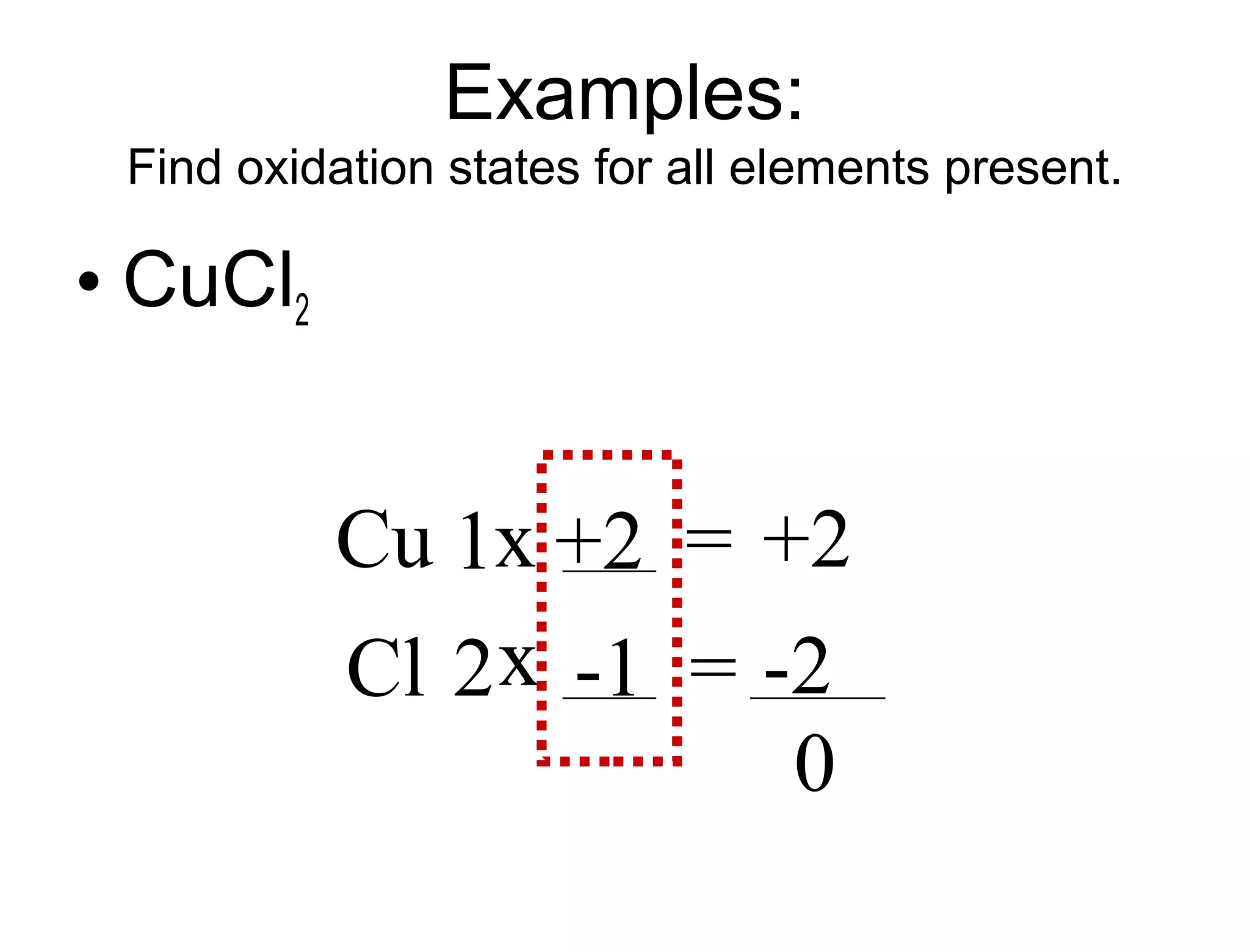
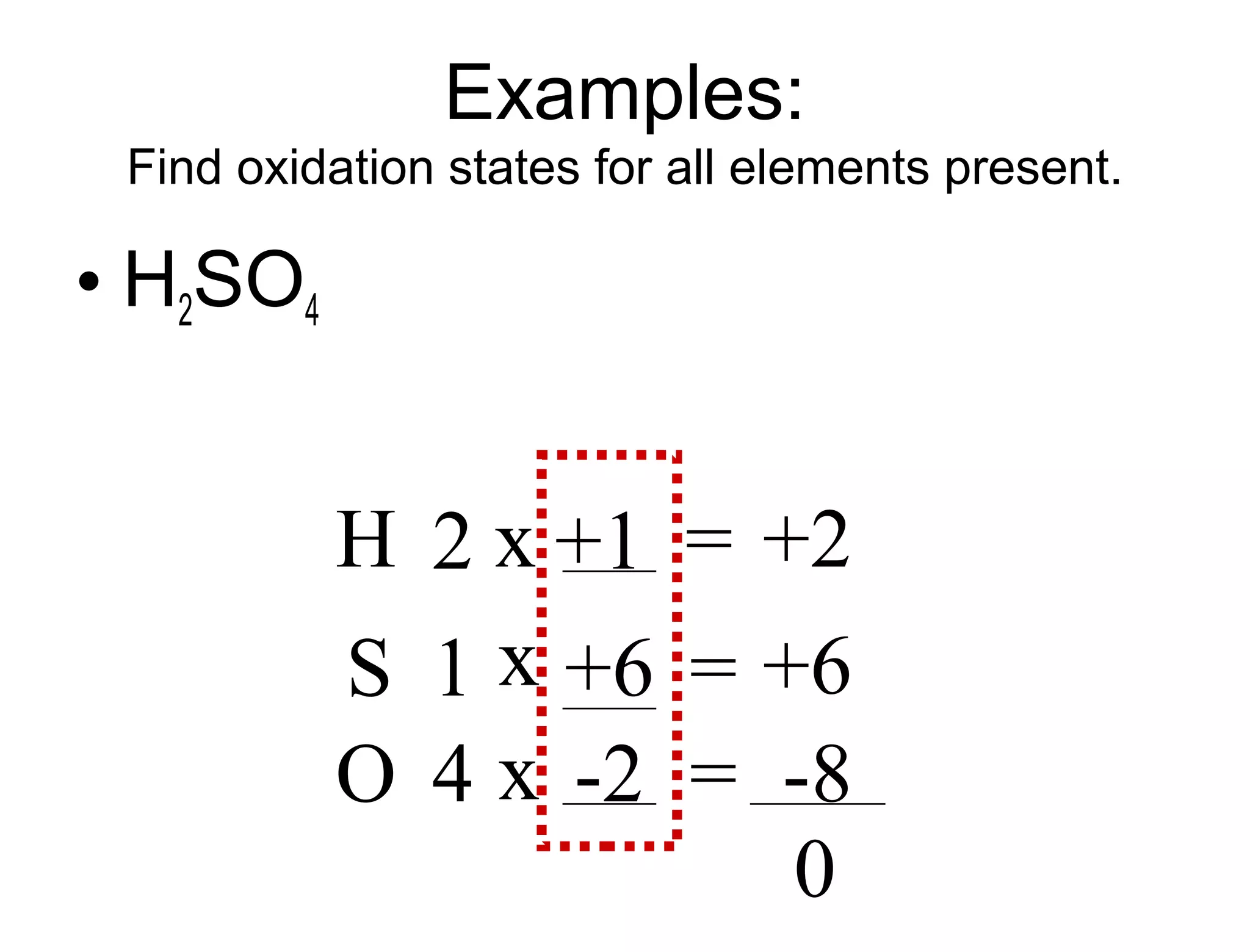
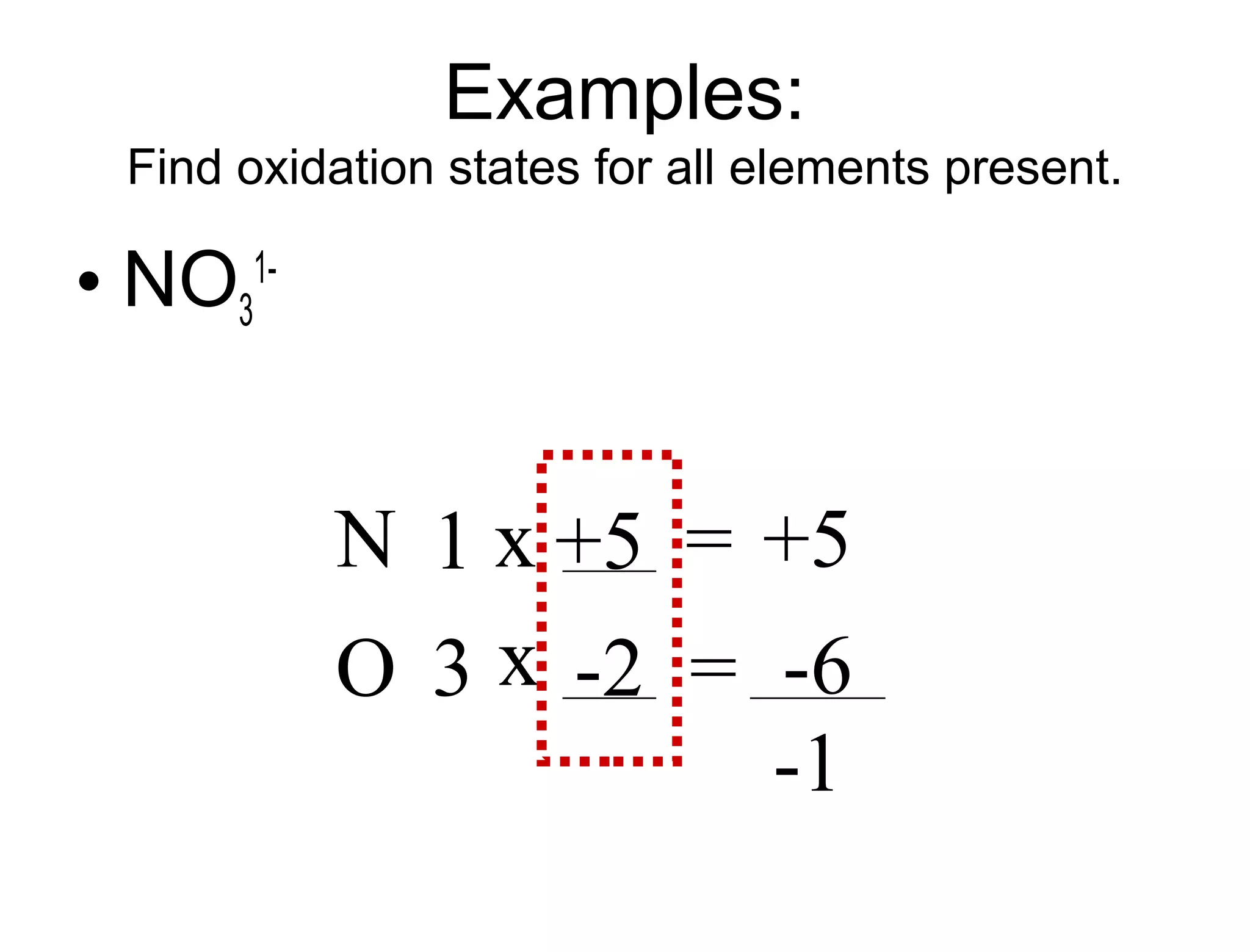
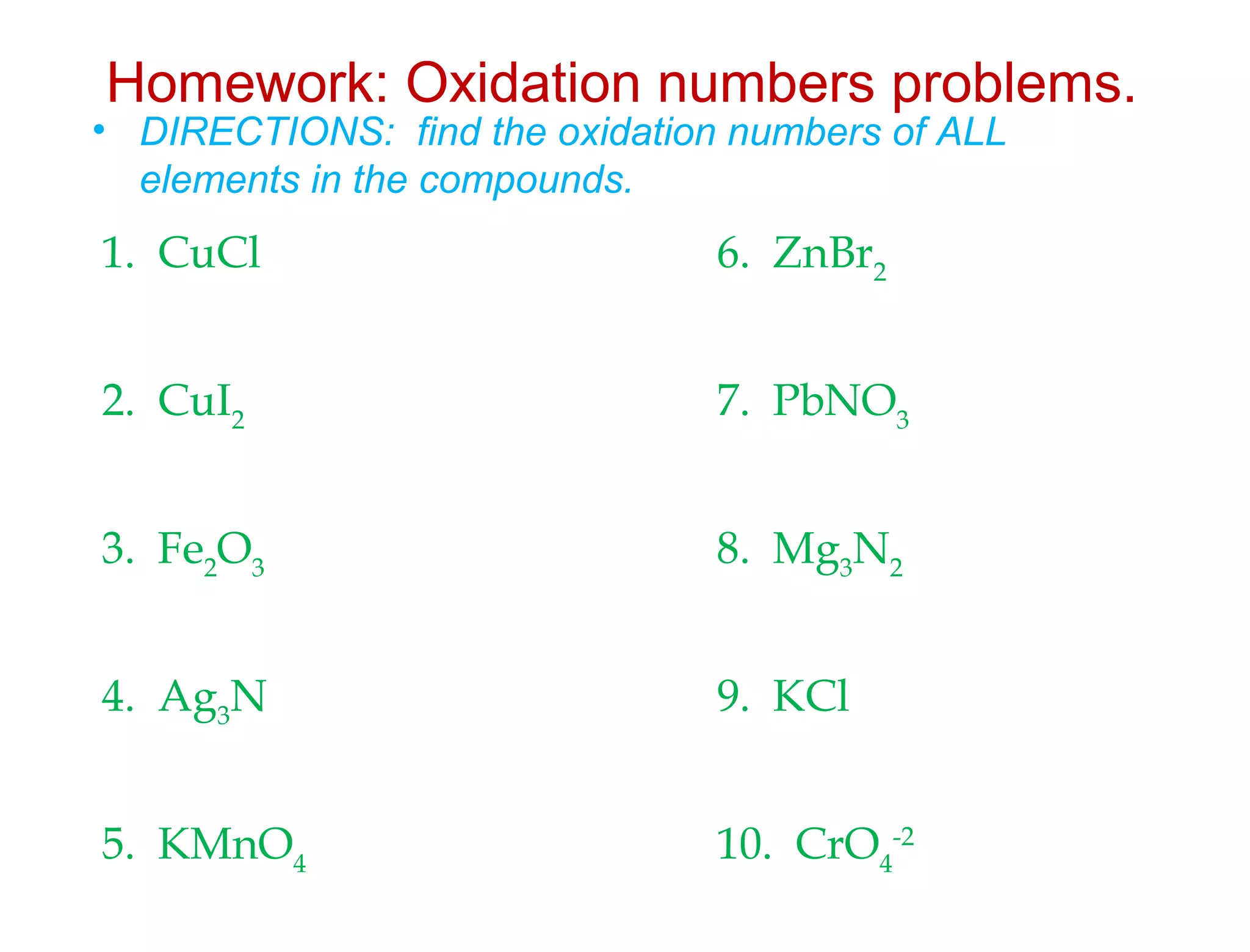
This document discusses transition metals and their ionic charges. Transition metals are found in the middle of the periodic table and are called the B group elements. Unlike representative elements whose ionic charge is equal to their group number, transition metals can exist in multiple oxidation states by gaining or losing electrons. Examples given are iron (Fe2+ and Fe3+) and tungsten (W2+ through W7+). To predict the ionic charge of a transition metal, you must examine how it reacts with other elements and determine its oxidation state, which represents the charge of an atom in a compound. Rules for determining oxidation states are provided.