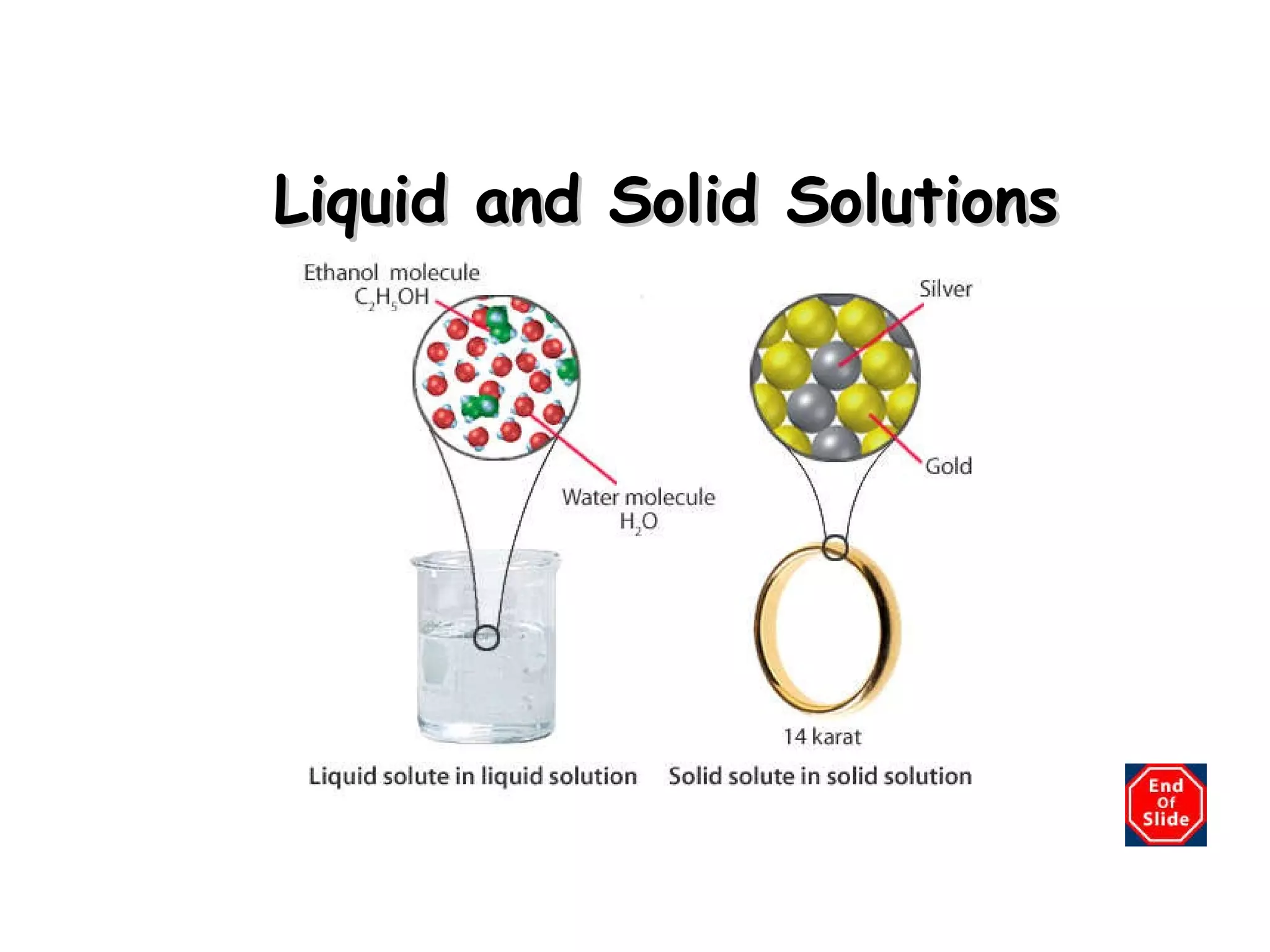
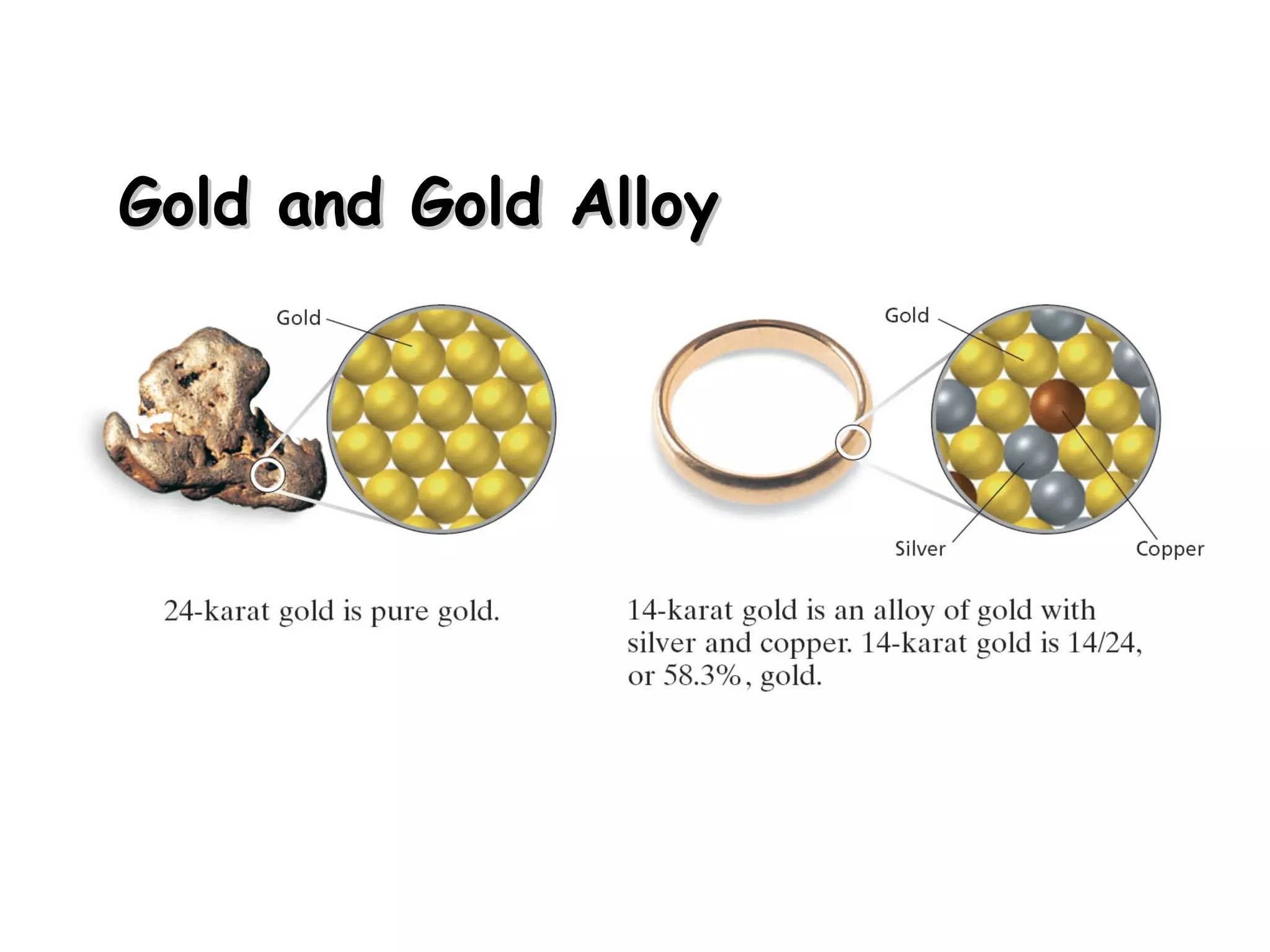
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances uniformly dispersed throughout a single phase. A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture where particles remain mixed while being stirred but later settle to the bottom. A colloid is a middle-sized mixture that is stable and homogeneous like a solution but contains particles that can be seen with a light microscope.