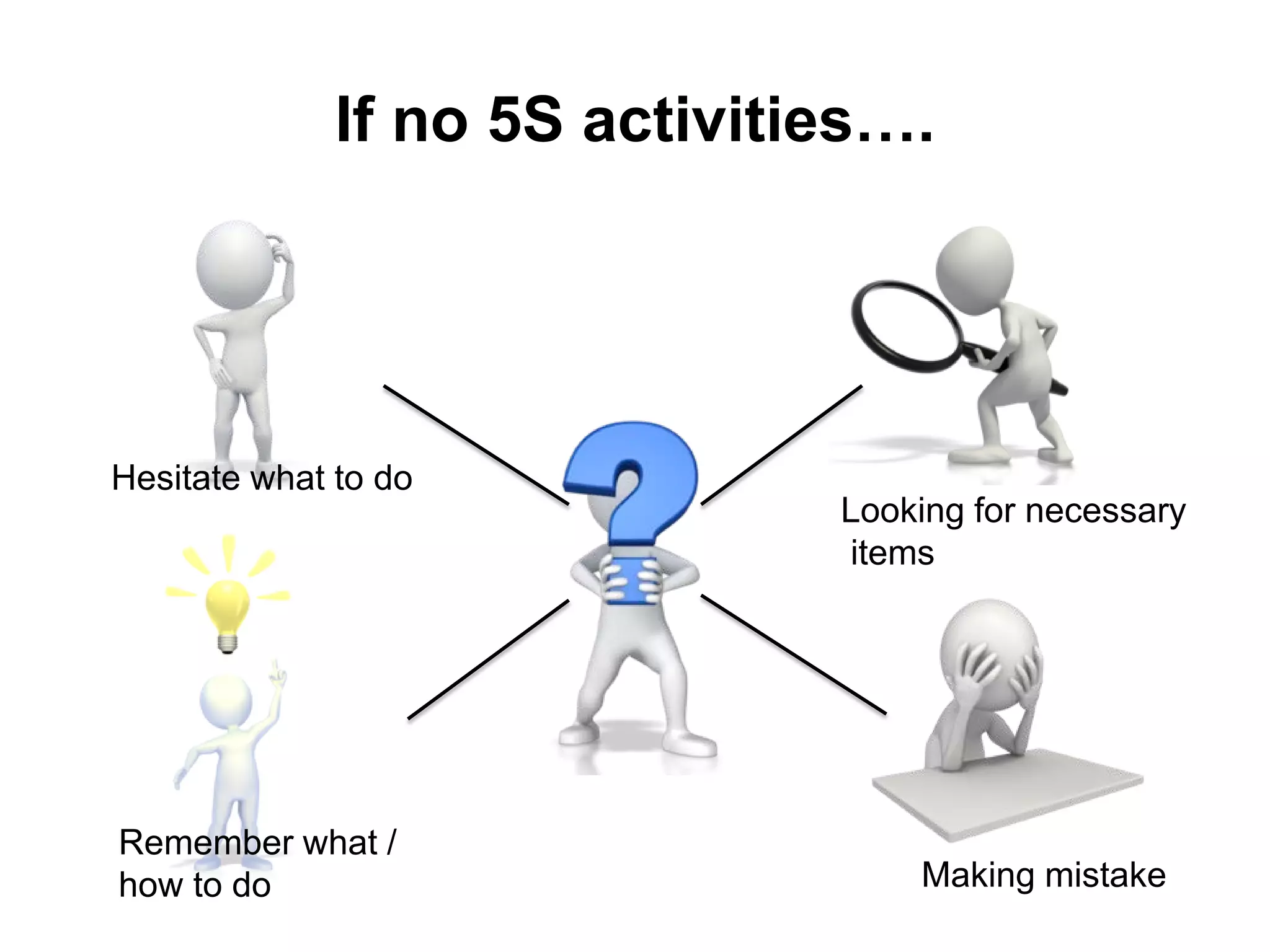
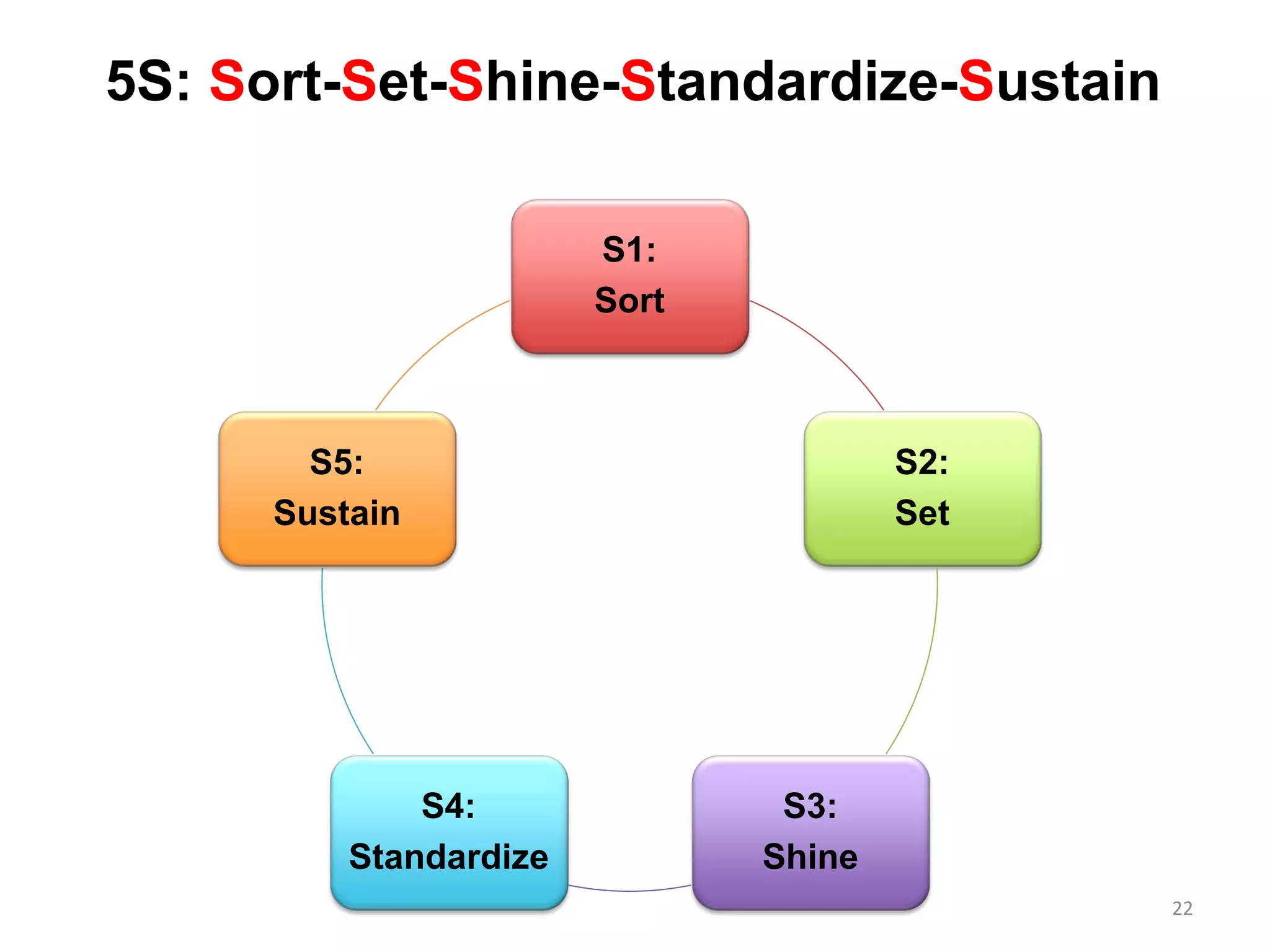
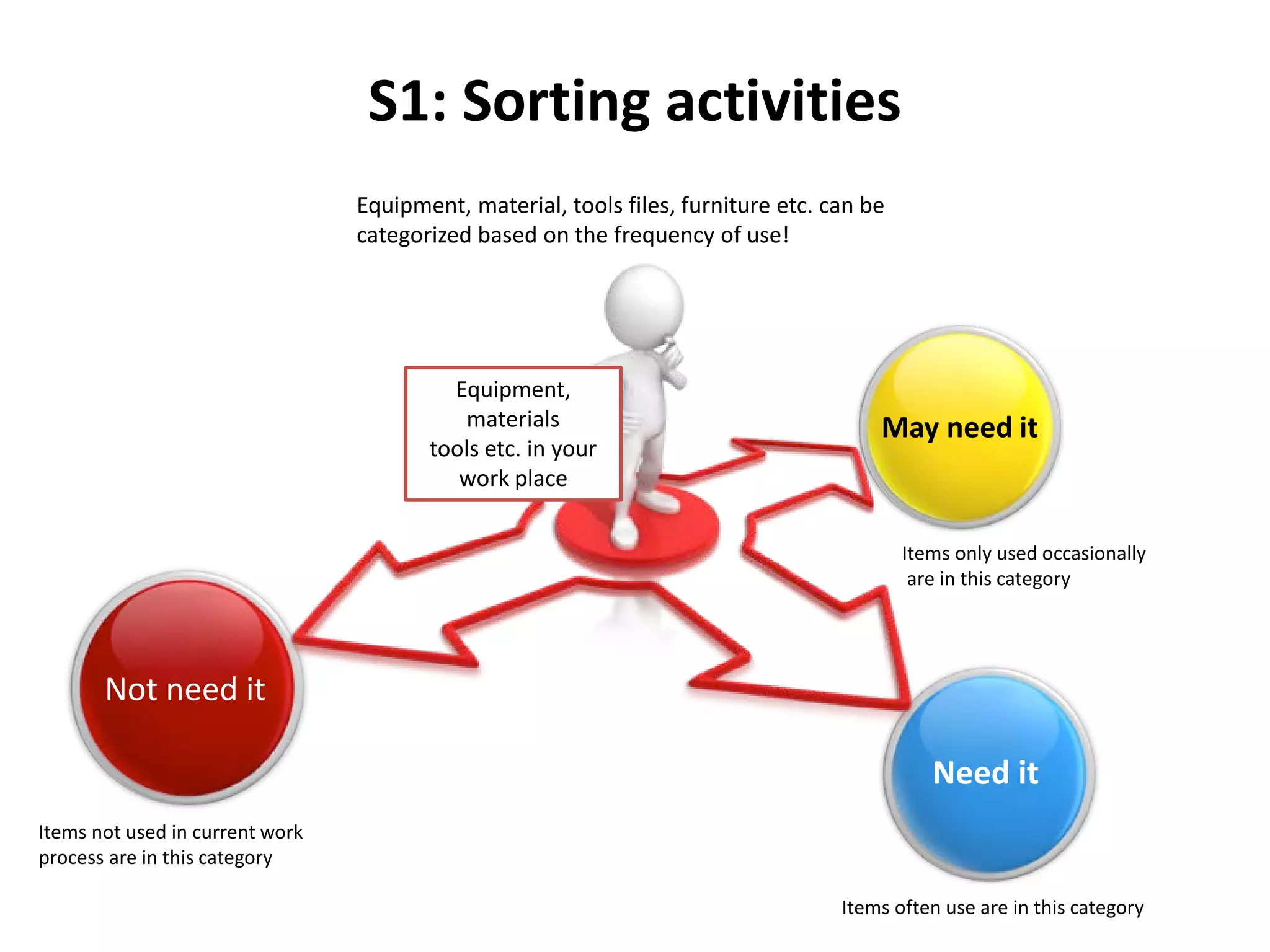
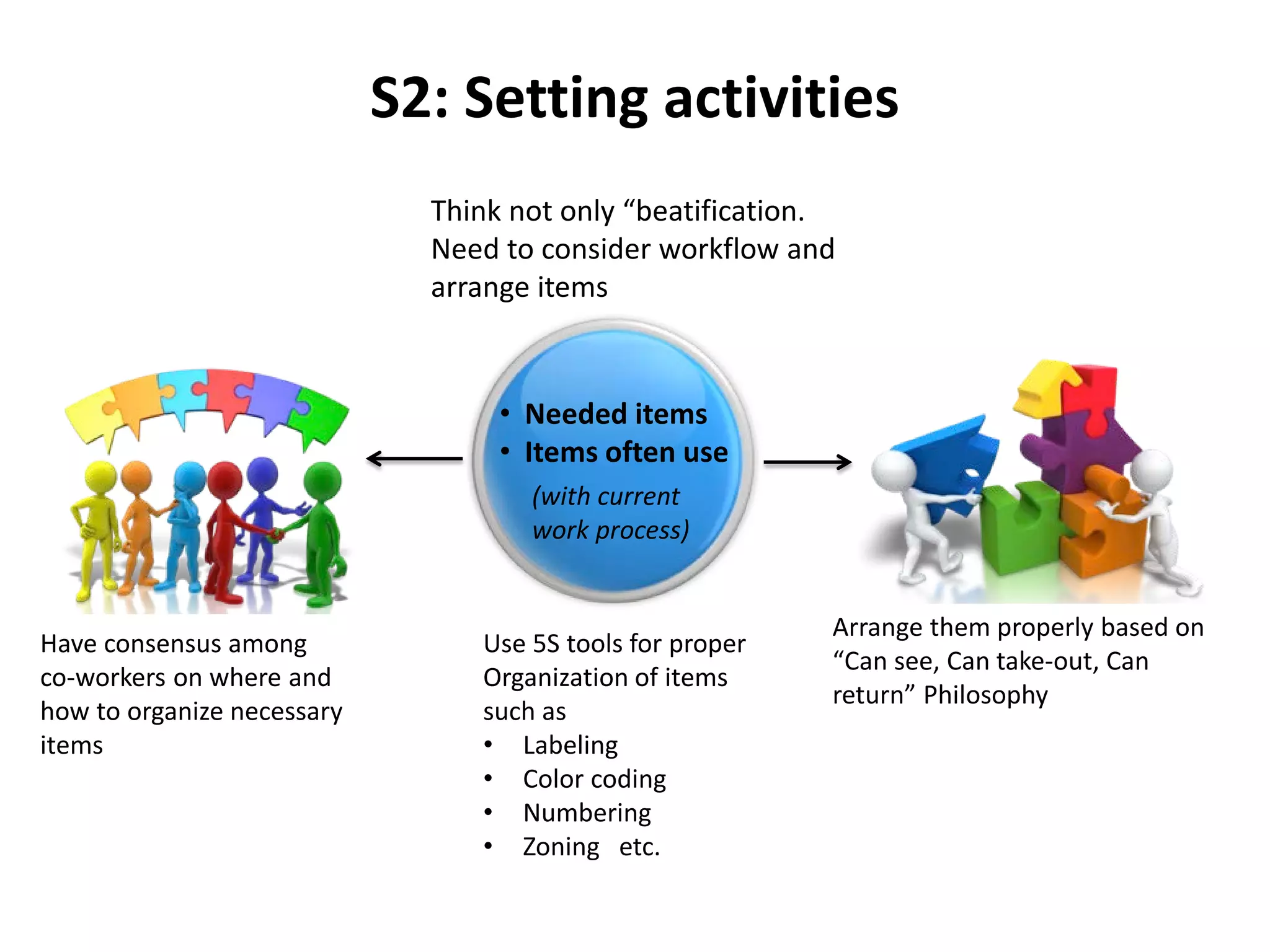
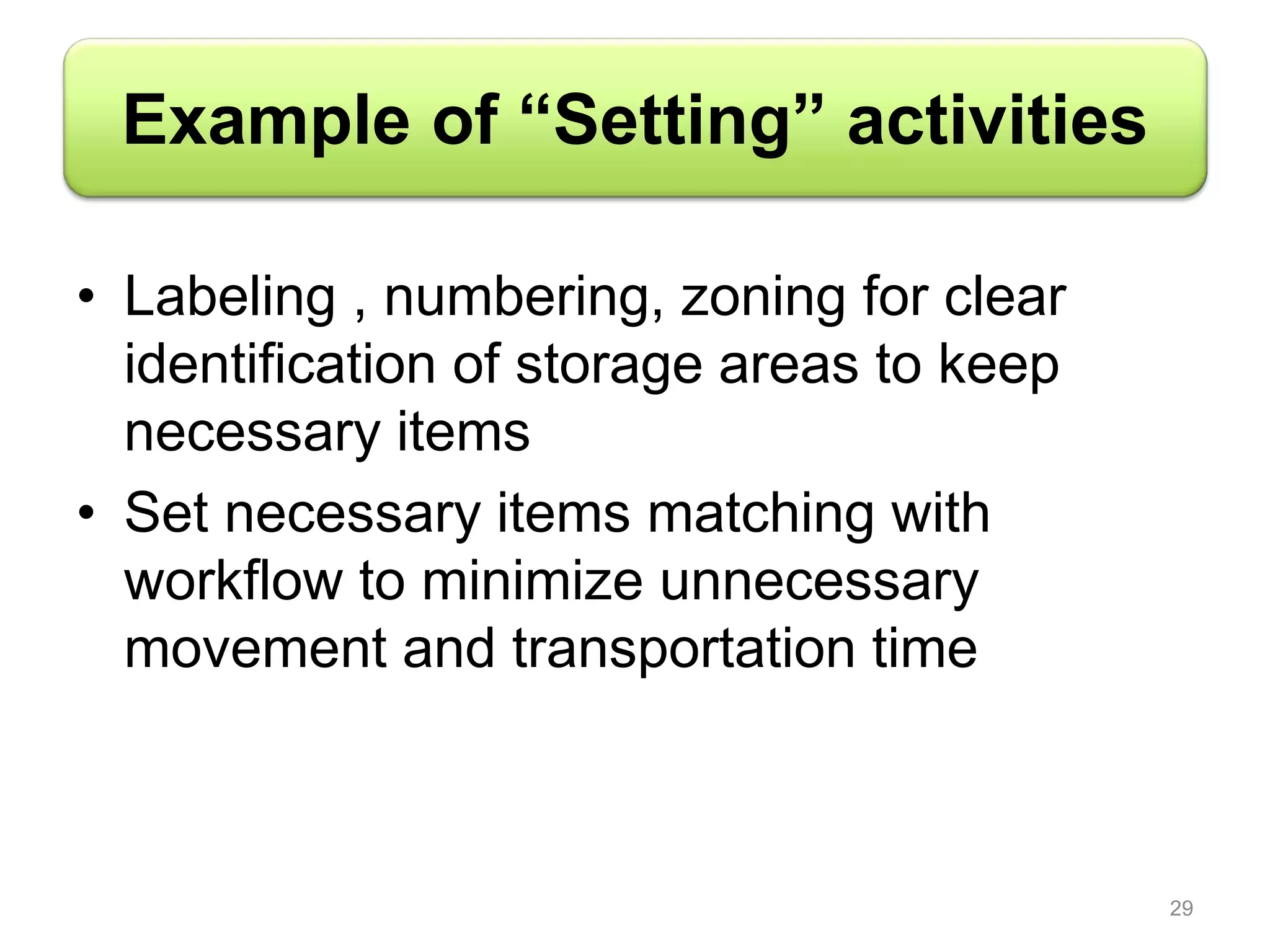
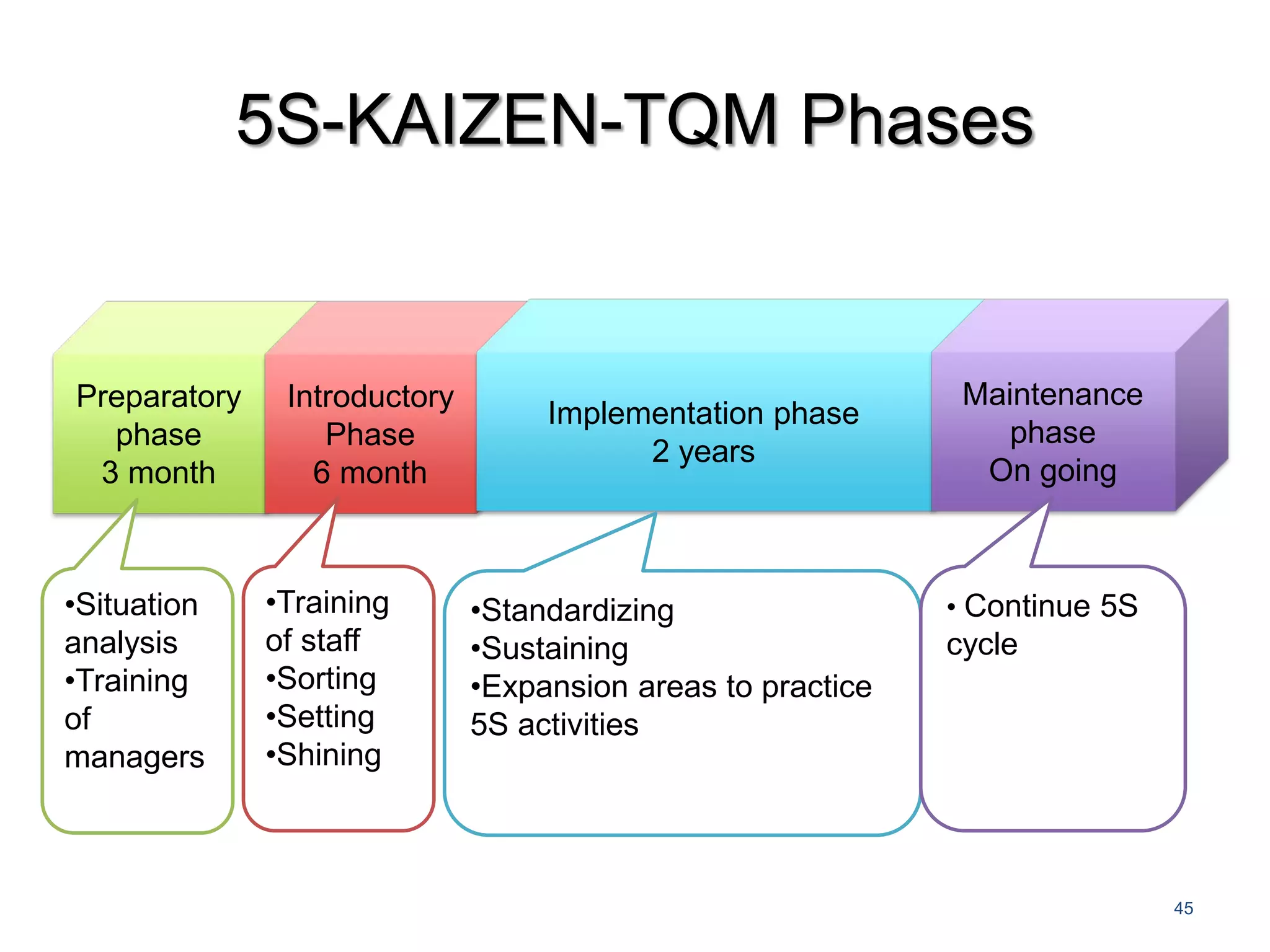
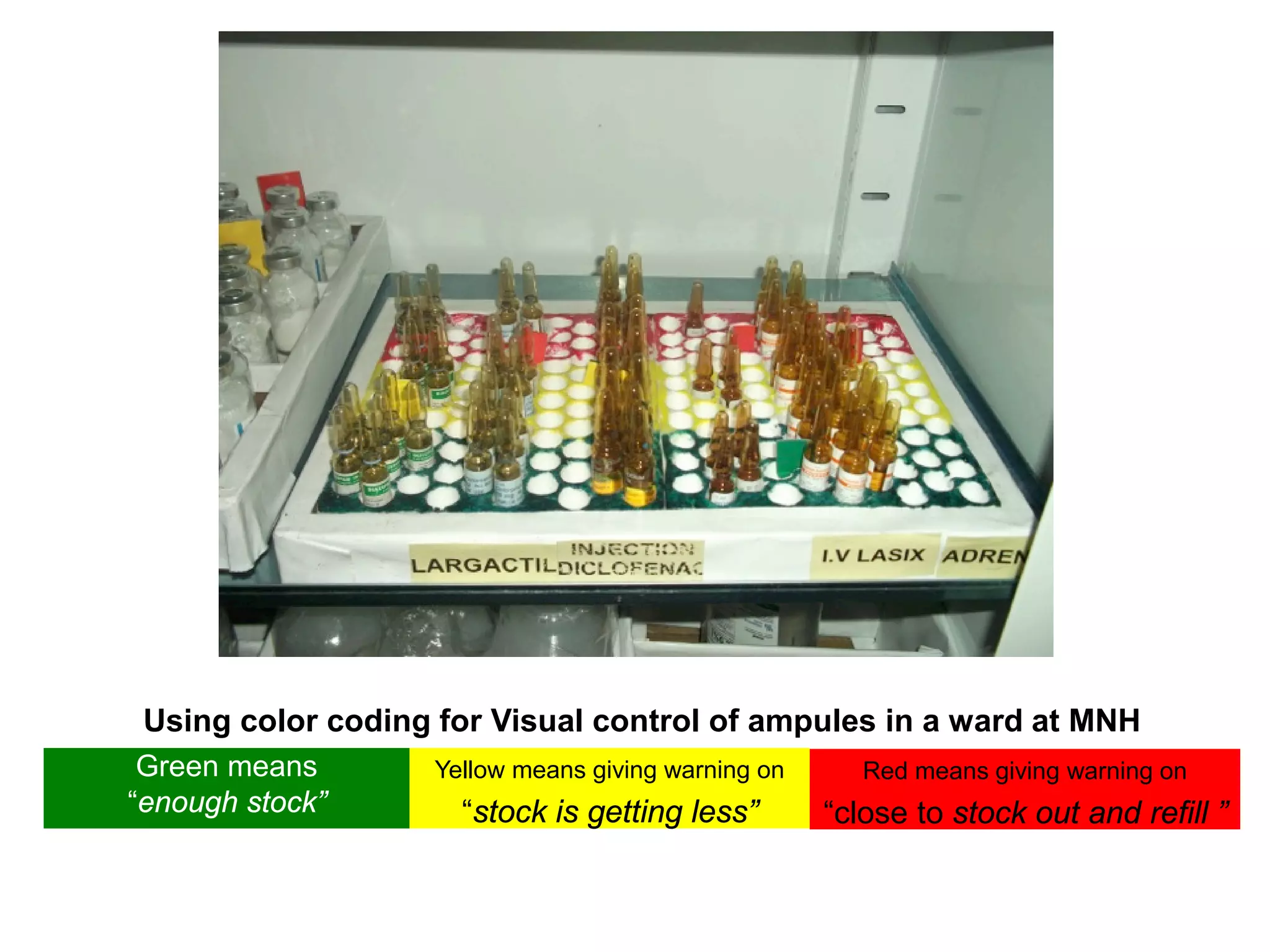
5S is a philosophy and methodology for organizing and managing workspaces using five principles: Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain. The document discusses each of the 5S principles in detail, providing examples of activities for each. Implementing 5S aims to create a more efficient work environment by reducing waste, improving workflow, and building organization. It has benefits like improving teamwork, safety, and productivity while identifying issues and abnormalities. The 5S methodology originated in manufacturing in Japan and has since been adopted by various industries worldwide.