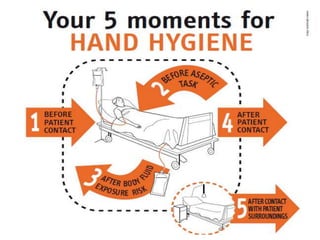
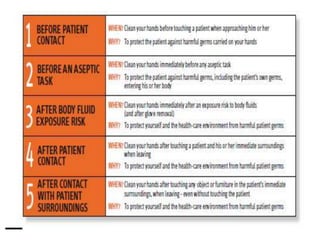
This document discusses proper hand hygiene techniques, including the 5 moments when hand hygiene should be performed and the steps for handwashing with soap and water or using a hand sanitizer. It emphasizes that handwashing helps remove microorganisms to prevent the spread of disease. The 7 steps for handwashing with soap and water and the 7 steps for using hand sanitizer are presented. Videos demonstrating the techniques are referenced. Recommended soaps, sanitizers, and the proper use of sanitizers are also described.