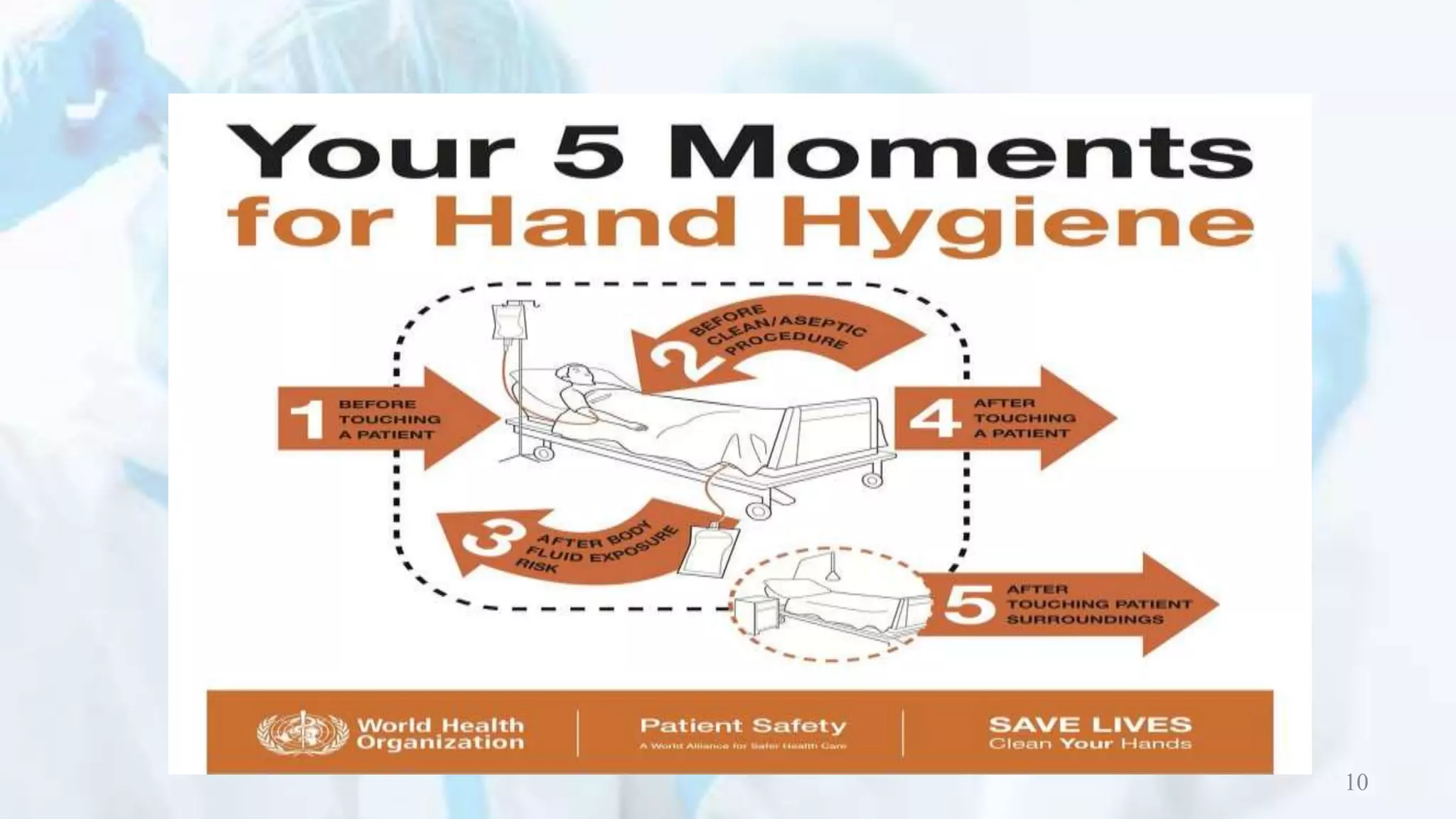
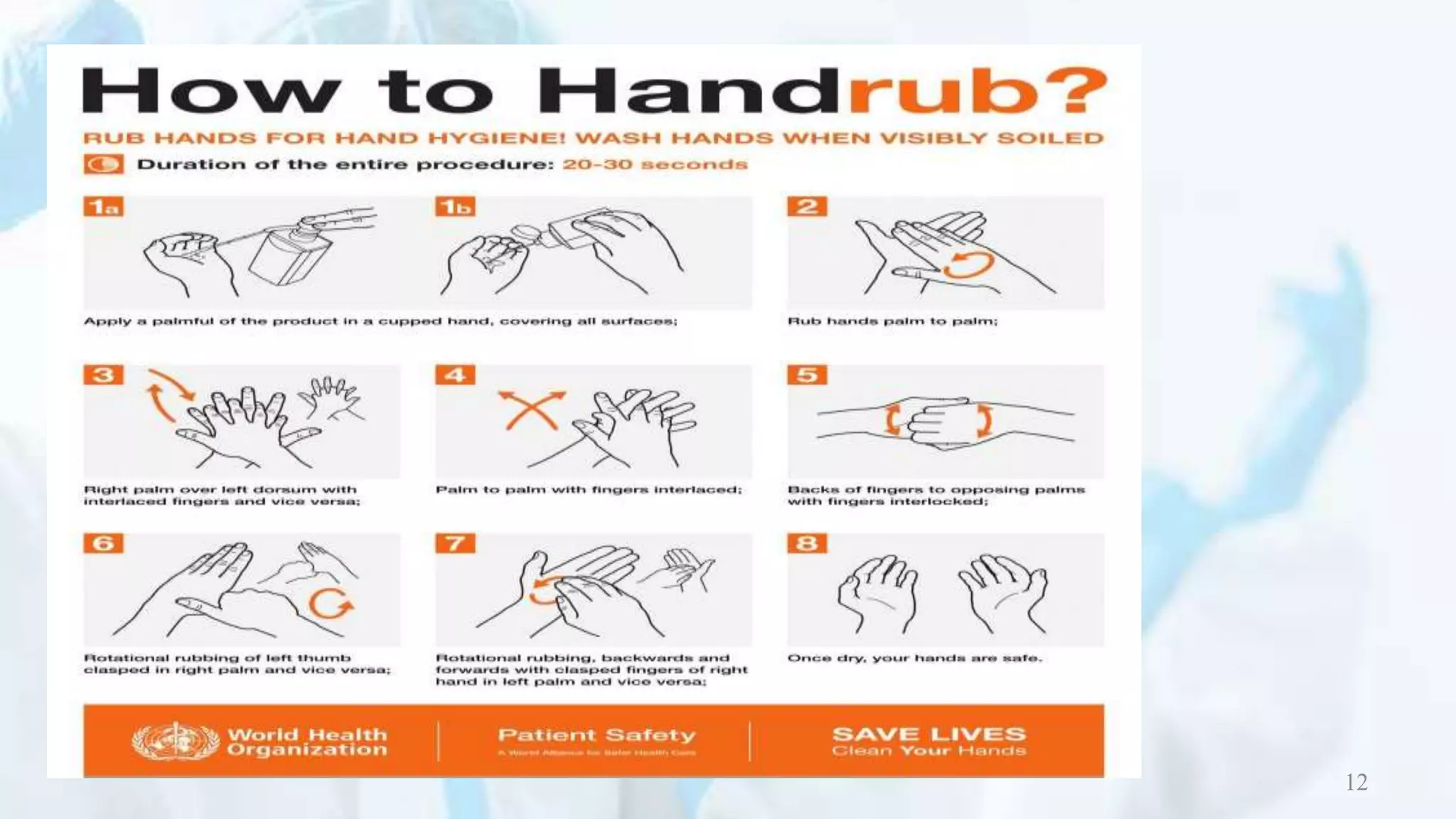
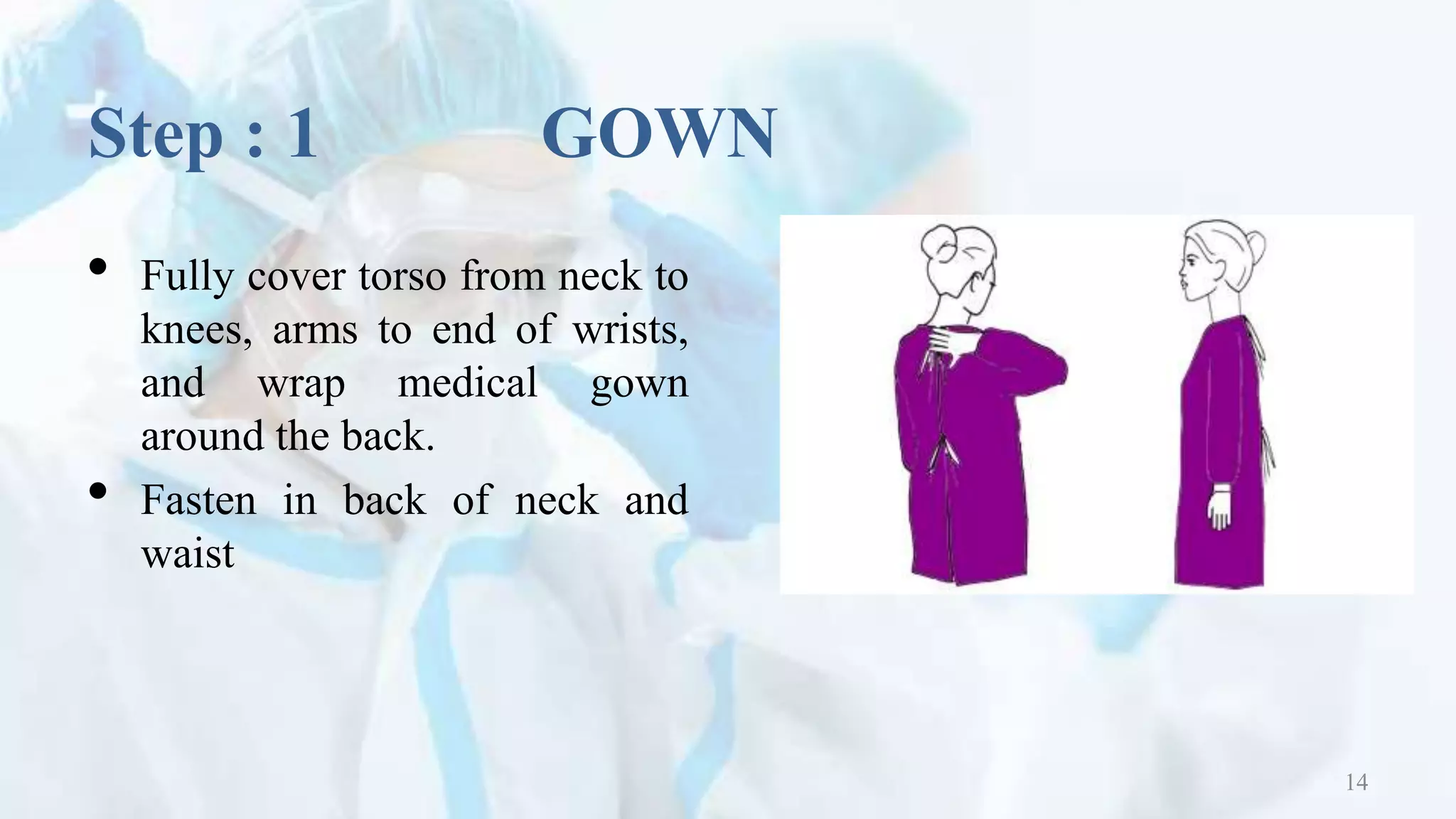
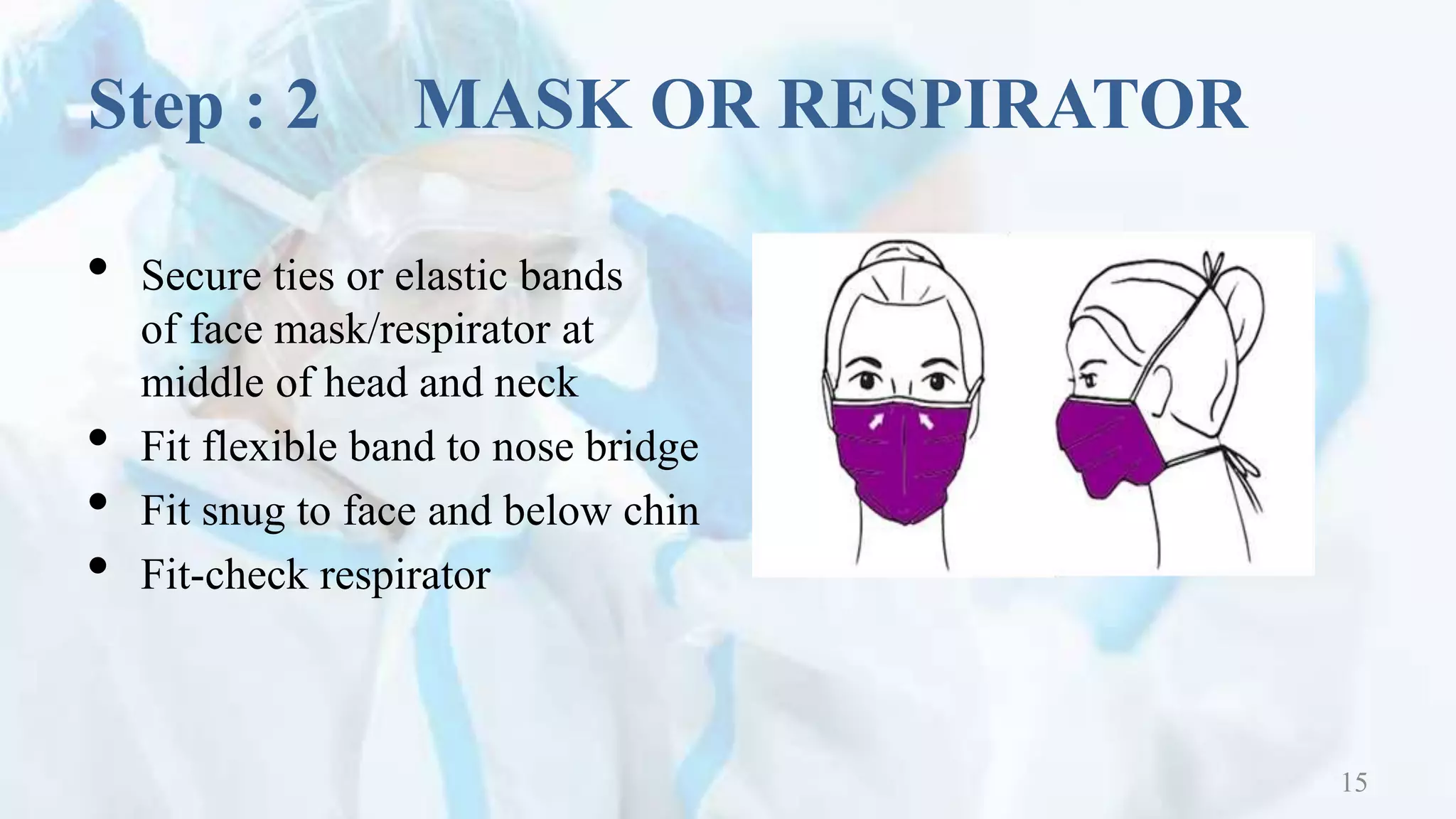
This document outlines the proper procedures for donning and doffing personal protective equipment (PPE). It describes the 4 steps to donning PPE, which are to first put on a gown, then a mask or respirator, followed by goggles or a face shield, and lastly gloves. The 4 steps to doffing PPE are removing gloves first, then goggles or face shield, followed by removing the gown, and lastly removing the mask or respirator. The document emphasizes the importance of hand hygiene and outlines the proper steps for hand rubbing.

















![REFERENCES
• World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF. Joint Monitoring
Program (JMP) 2017 2. Health care without avoidable infections. The
critical role of infection prevention and control 3. Burden of endemic
health-care-associated infection in developing countries: systematic
review and meta-analysis.
24
• Molloy J. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Donning and
Removal of PPE. St. John's: Eastern Health Infection Prevention and
Control; 2017. Eastern Health Infection Prevention and Control.
Policy: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) - Donning and Removal
of PPE. [Google Scholar]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/donninganddoffing1-3-221201010233-7e506309/75/Donning-and-doffing-1-3-pptx-24-2048.jpg)
