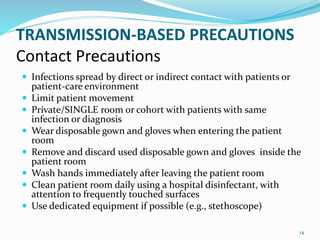
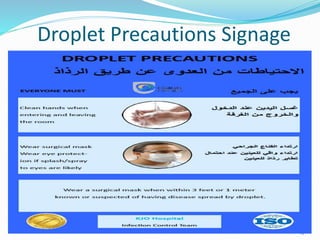
This document discusses isolation precautions in healthcare settings. It defines isolation precautions as special measures used to prevent the spread of contagious diseases. The document outlines the different modes of disease transmission - contact, droplet, airborne, vector-borne, and common vehicles. It then describes the various types of isolation precautions, including standard, contact, droplet and airborne precautions. For each type of precaution, it provides details on patient placement, signs, personal protective equipment used, and other measures to prevent disease transmission.