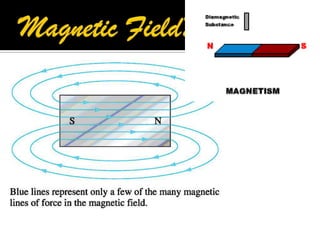
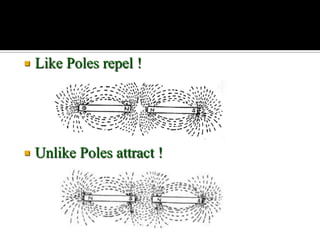
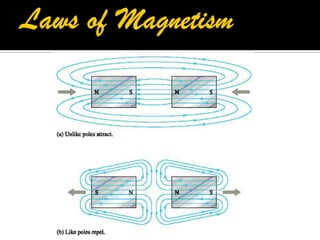
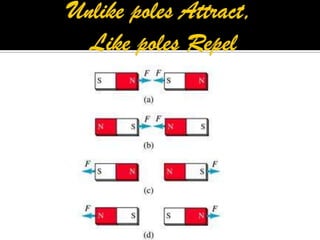
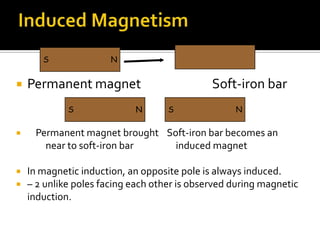
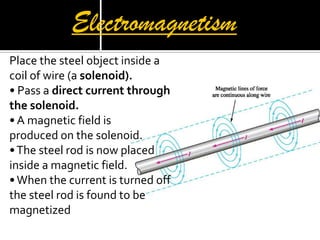
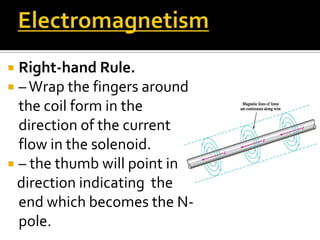
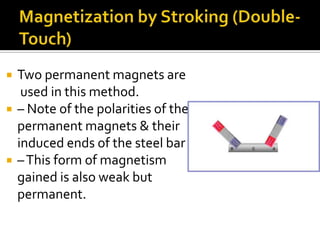
This document defines key terms related to magnets and magnetism. It explains that magnets have north and south poles and attract iron, cobalt, and nickel. The magnetic field lines run from the north to south pole. There are natural and artificial magnets. Electromagnets are created when electric current passes through a coil of wire wrapped around an iron core, inducing magnetism. The Earth's magnetic field is believed to originate from circulating currents in its iron-rich liquid outer core.