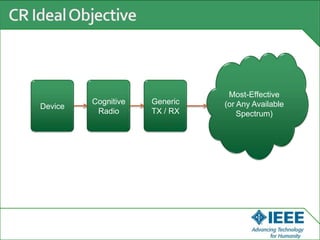
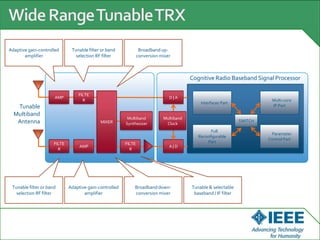
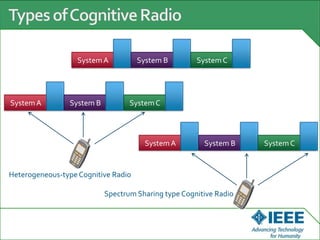
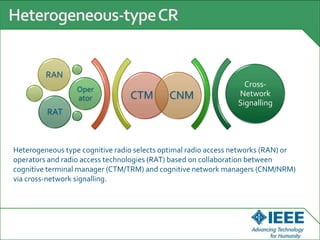
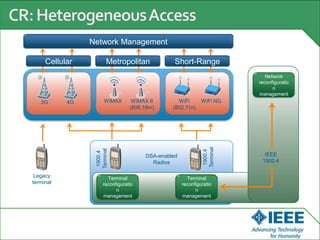
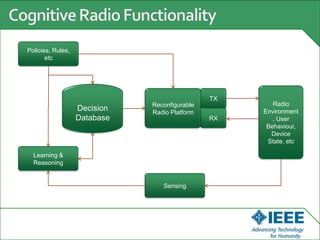
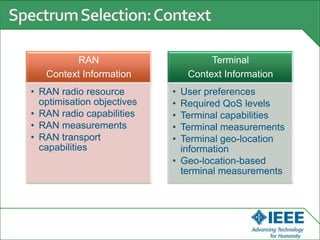
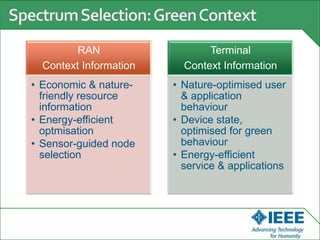
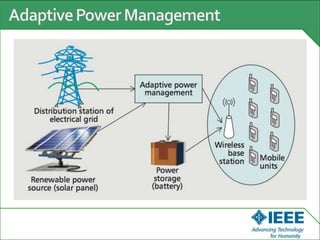
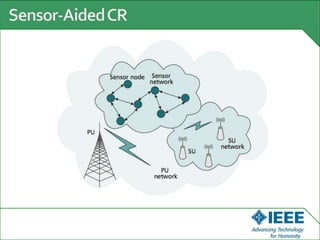
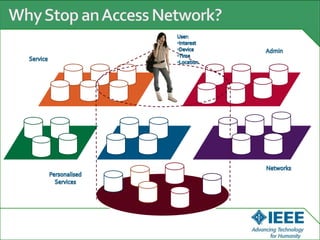
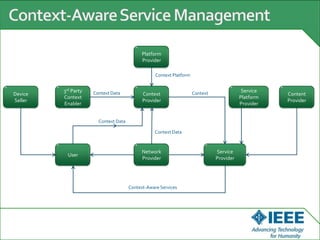
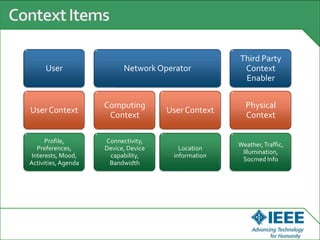
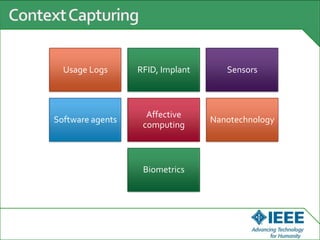
The keynote speech at the National Electrical Engineering Seminar in Indonesia outlined IEEE's mission to promote technological innovation for humanity and its vast network of over 425,000 members worldwide. Key topics included sustainability in ICT, advancements in various technology fields such as cloud computing, electric vehicles, and cognitive radio, as well as the need for energy-efficient resource management in cognitive networks. The speech emphasized the importance of collaboration and context-aware technologies for achieving a green lifestyle and enhancing user experiences.