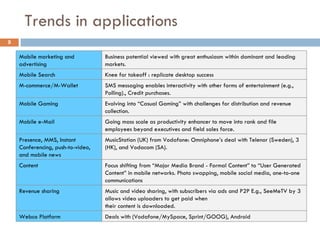
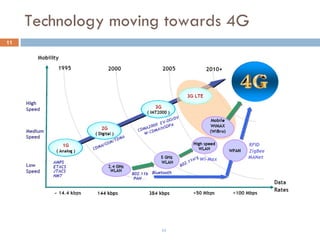
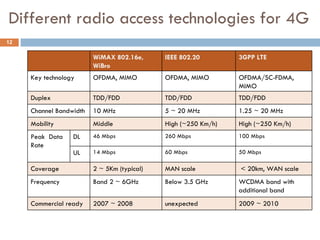
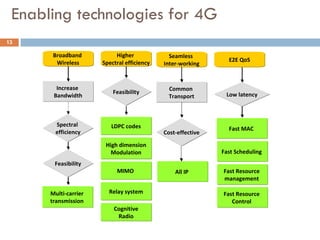
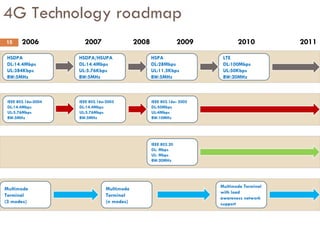
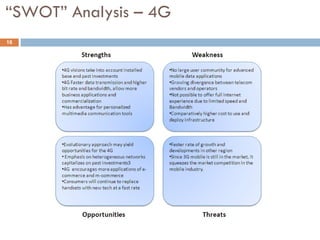
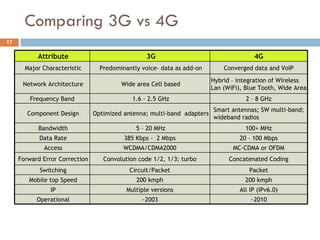
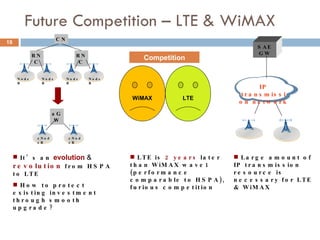
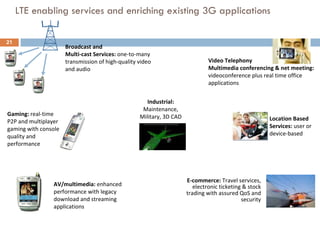
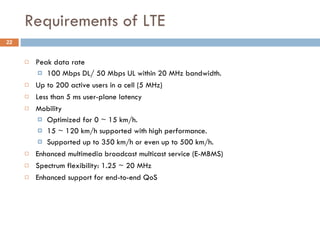
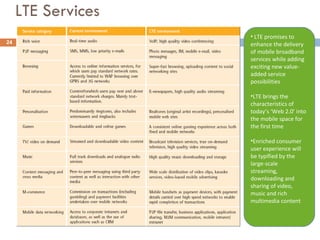
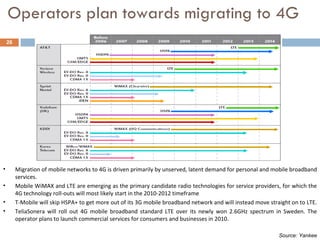
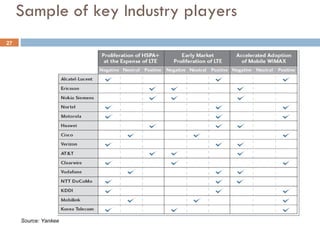
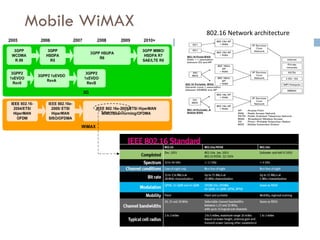
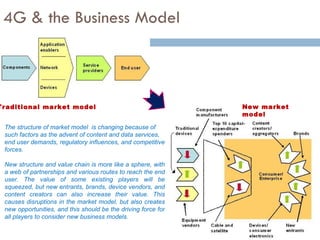
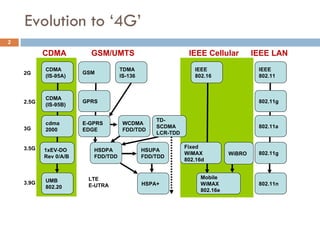
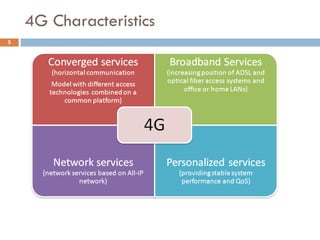
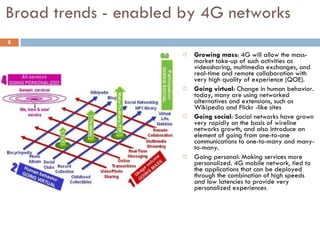
4G wireless networks will provide significantly higher data rates and an improved quality of experience for users. The two main competing 4G standards are 3GPP LTE, being developed by 3GPP, and Mobile WiMAX, being developed by IEEE. LTE aims to provide peak data rates of 100 Mbps for downlink and 50 Mbps for uplink. Many mobile network operators plan to migrate to 4G LTE networks starting in 2010. The transition to 4G will change the mobile broadband market and business models.



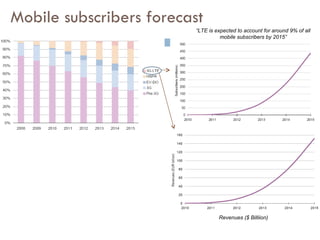
![Key business trends Global Telecom Spending Patterns Realigning Early growth in international capex, US capex lag Rise in Mobile Data Revenues Internationally ARPUs up by 25% CAGR, US [< 5% CAGR] 50% Rise in Mobile Voice Subscribers [+1.4B] International +100%, US +15% Emerging markets to remain unsaturated through 2012 Mobile broadband subscribers up 275% [+750M] New Mobile Services Taking Hold – SK/Japan/Nordics Provide impetus to mobile data services Operators Consolidating Domestically While Expanding Overseas Total number of 4G subscribers worldwide, including both LTE & WiMAX is expected to exceed 90 million in 2013 (ABI Research)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4gwireless-100512064142-phpapp02/85/4G-wireless-8-320.jpg)