Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX
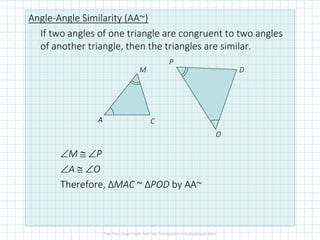
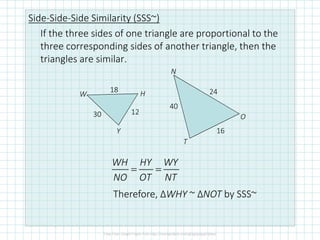
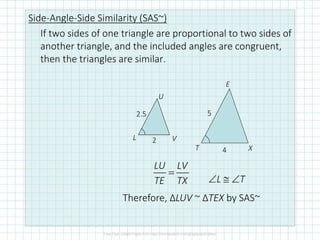
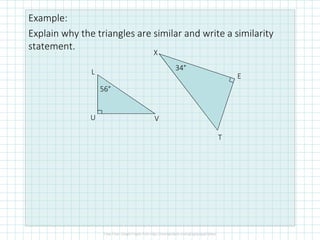
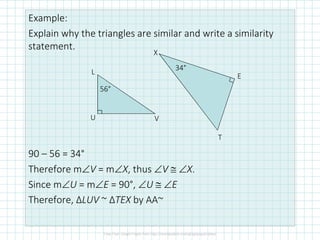
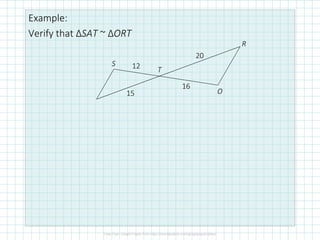
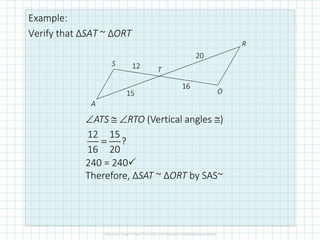
This document discusses properties of similar triangles. It defines three ways triangles can be similar: angle-angle similarity (AA~) if two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another; side-side-side similarity (SSS~) if the three sides of one triangle are proportional to the three sides of another; and side-angle-side similarity (SAS~) if two sides of one triangle are proportional to two sides of another and the included angles are congruent. Examples are provided to demonstrate applying these properties to determine if triangles are similar and write similarity statements.







