Embed presentation
Downloaded 106 times
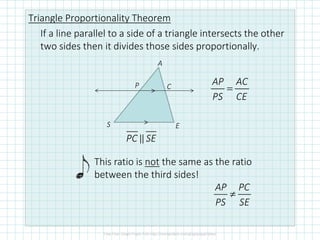
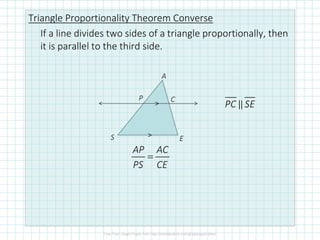
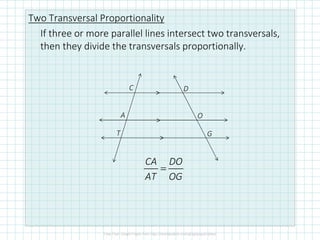
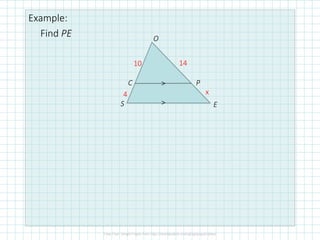
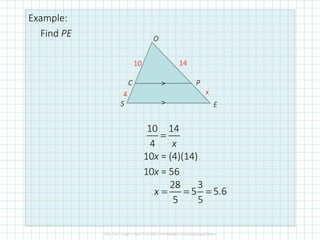
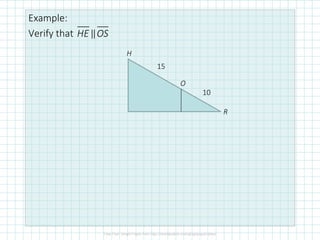
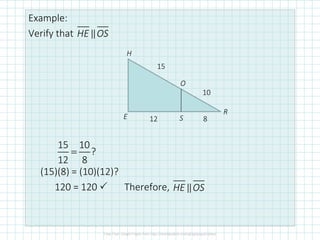
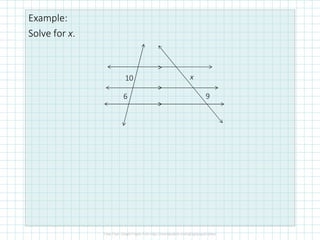
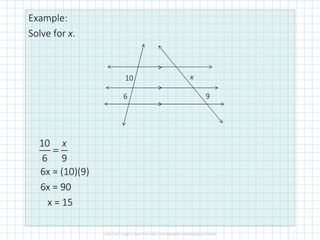
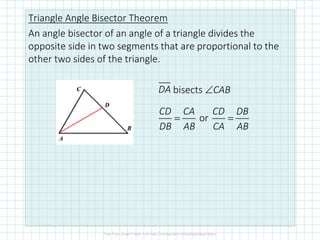
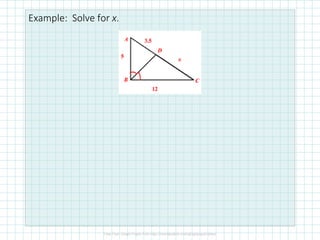
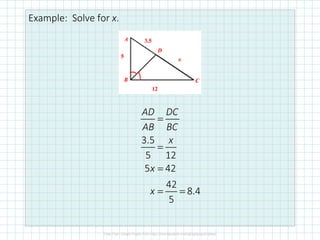
This document discusses proportionality theorems in triangles. It defines the triangle proportionality theorem and its converse, which state that if a line parallel to one side of a triangle intersects the other two sides, it divides them proportionally. It also discusses the two transversal proportionality theorem and the triangle angle bisector theorem. Examples are provided to illustrate using these theorems to find unknown side lengths and verify proportions.












