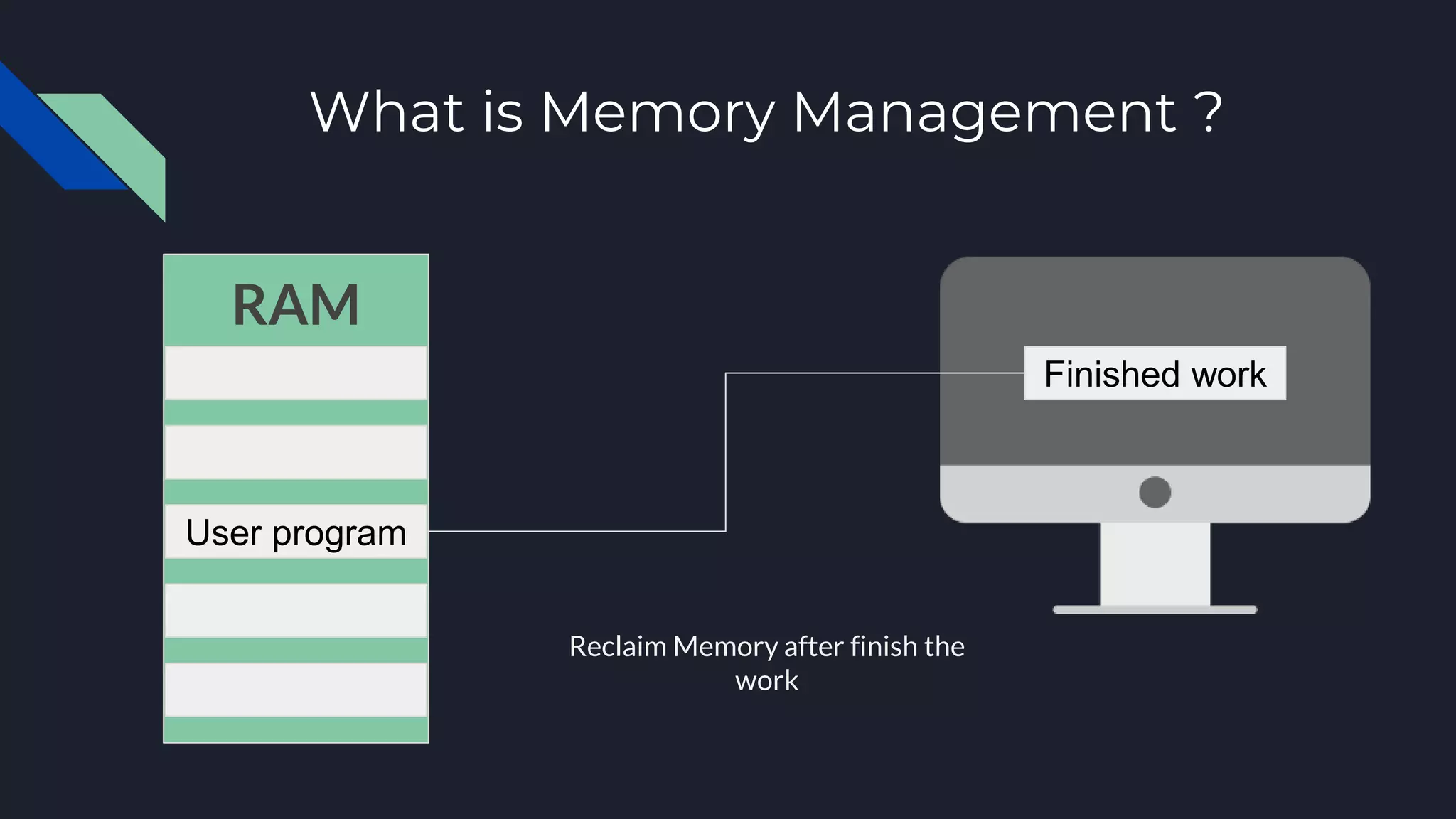
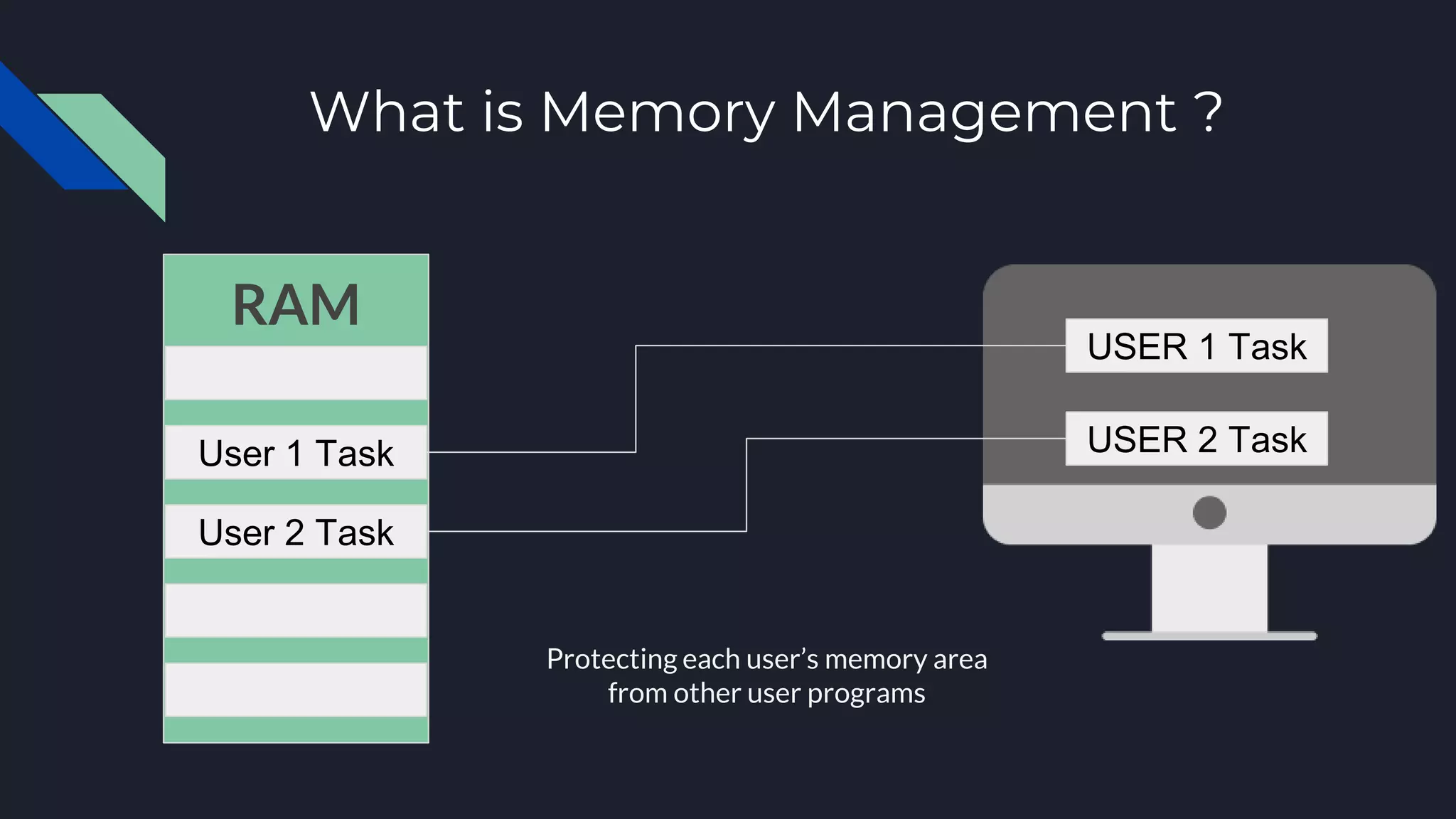
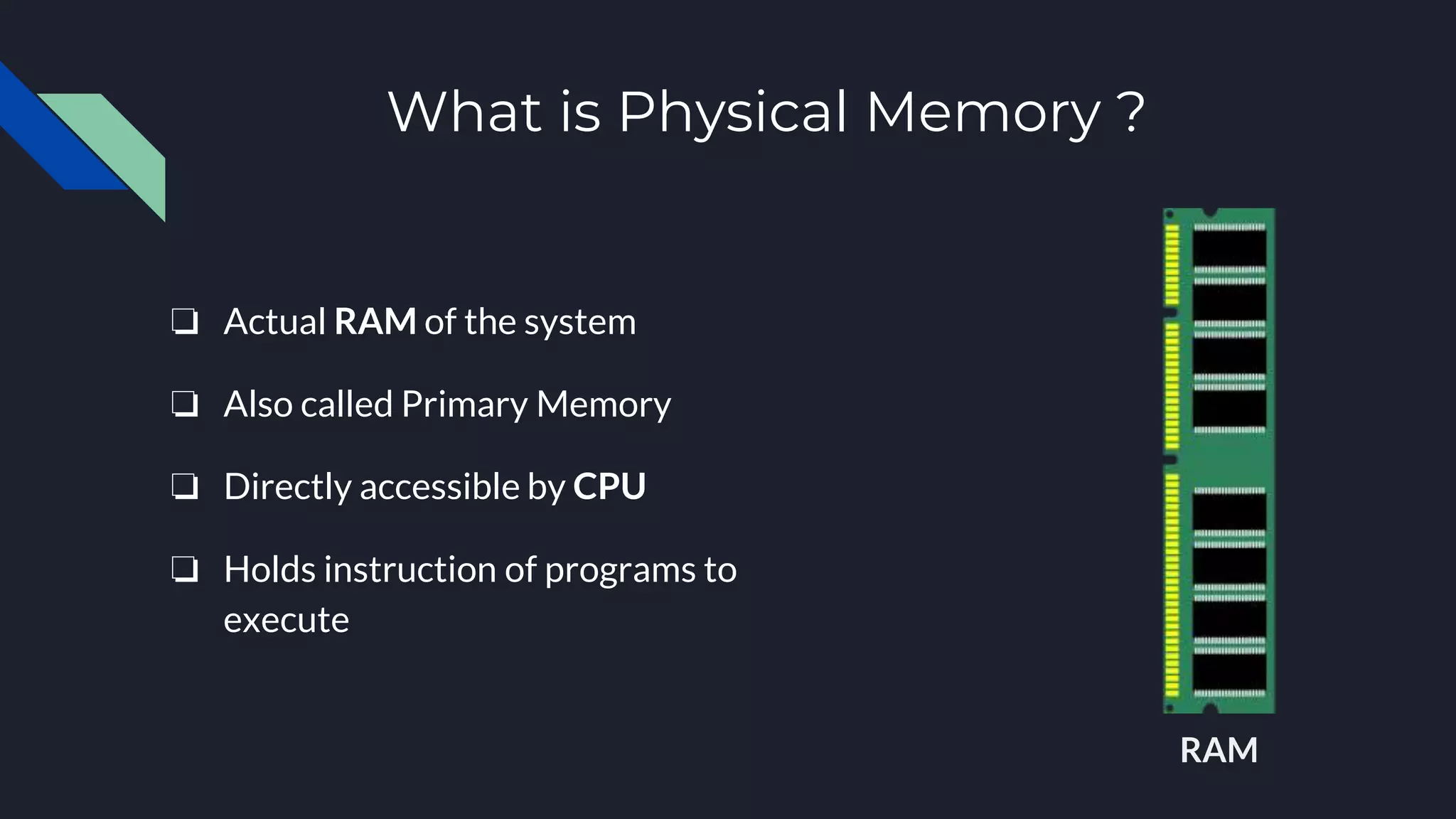
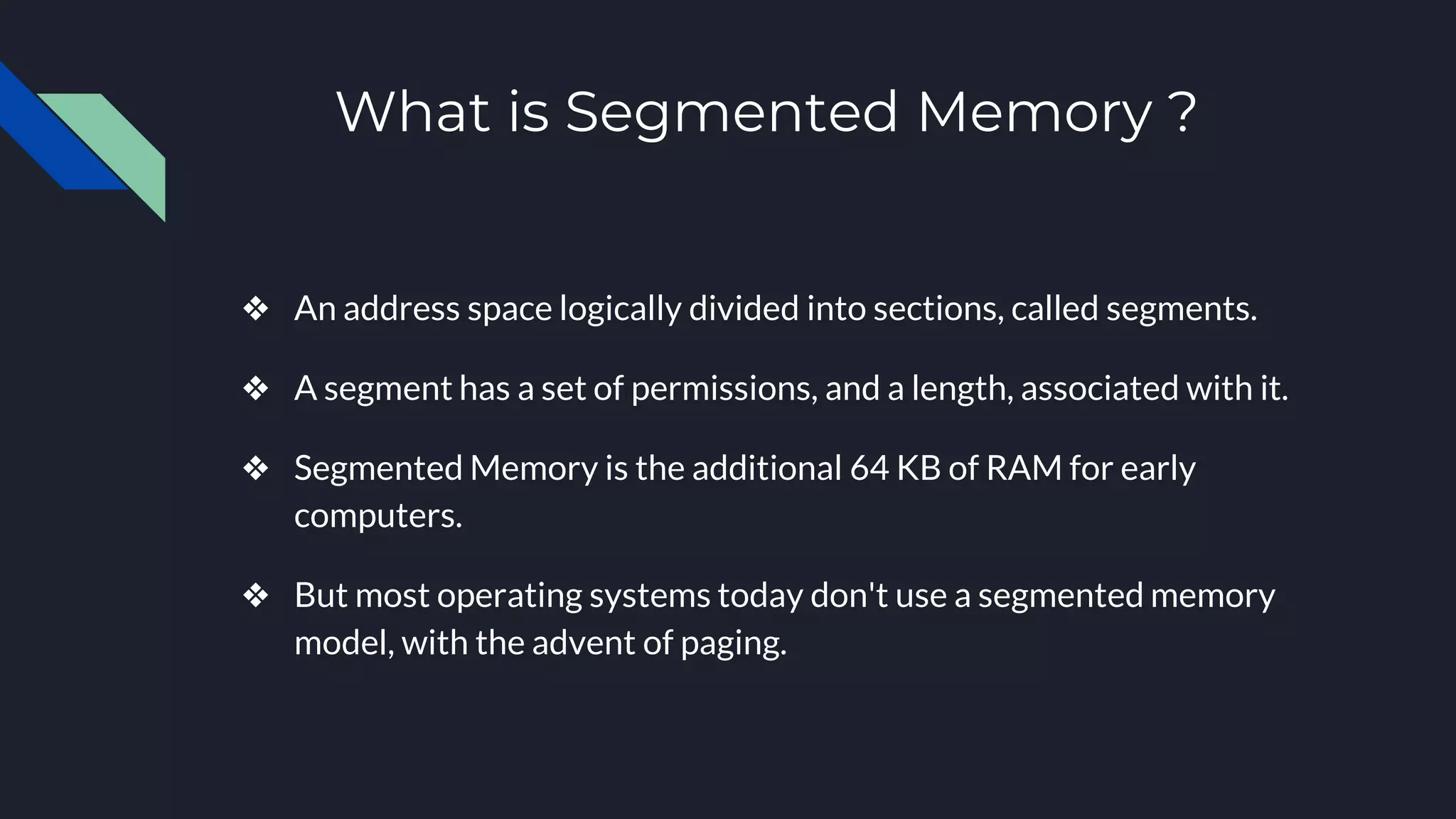
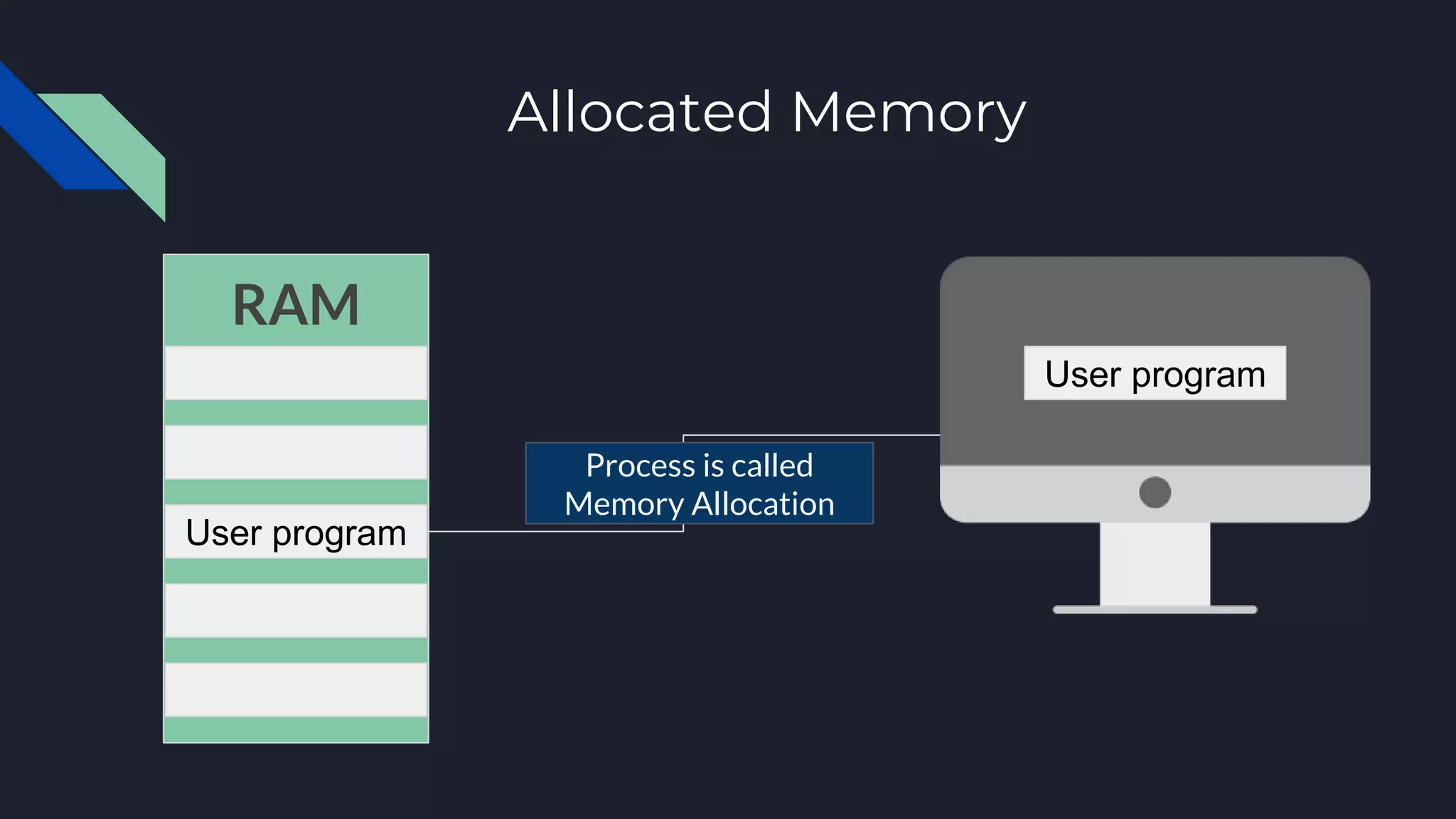
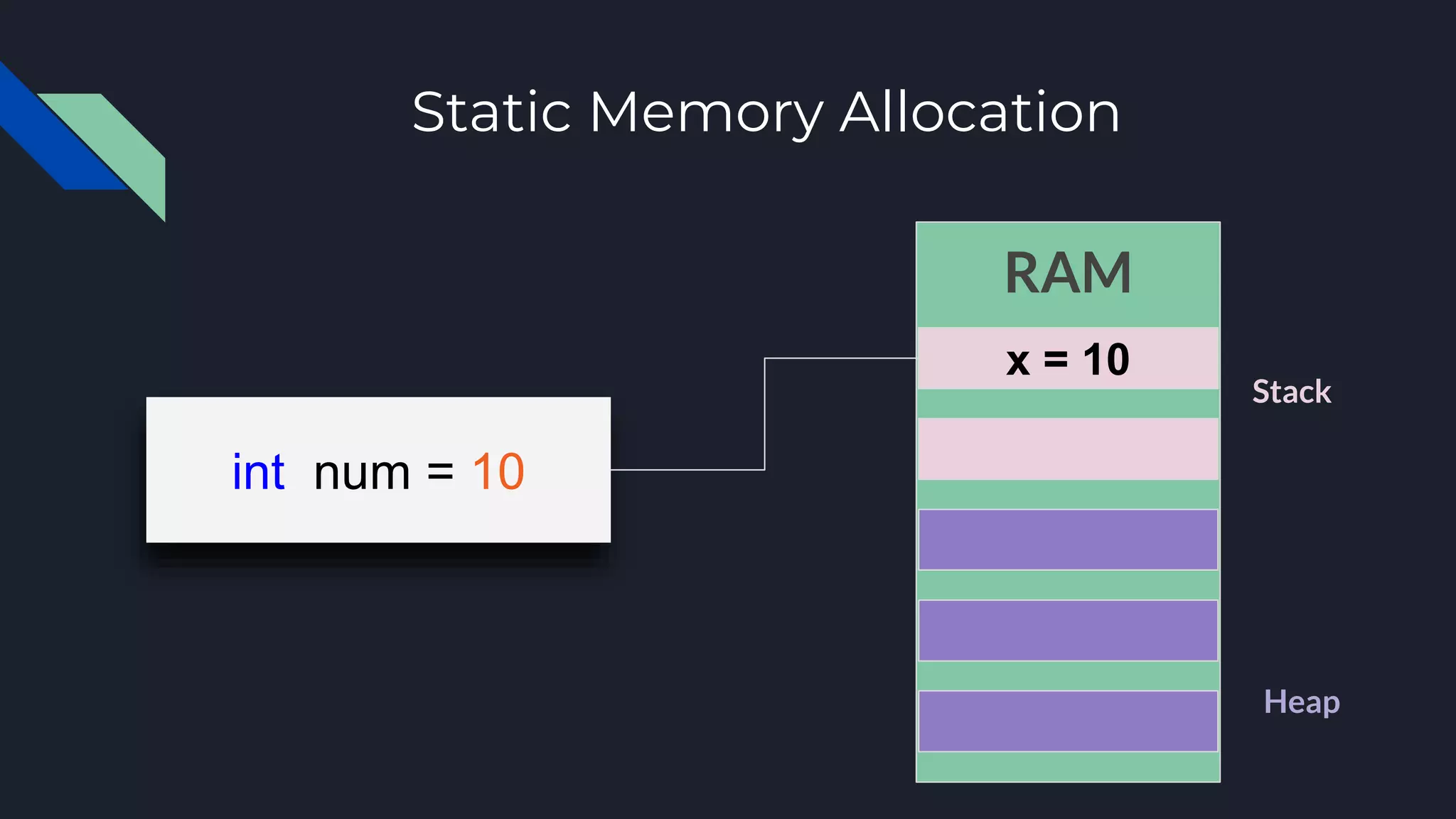
This document discusses memory management in operating systems. It defines memory management as allocating RAM to user programs and reclaiming memory after programs finish. It also describes protecting each user's memory from other programs. The document discusses physical and virtual memory, and types of virtual memory including paged, segmented, and swapped memory. It defines static and dynamic memory allocation, with static allocation assigning fixed memory at compile time and dynamic allocation assigning variable memory as needed from the heap.








![Dynamic Memory Allocation
char records [ ] = “Large
Data”
RAM
Large data
pointer
Heap
Stack](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memorymanagement-190620202515/75/Memory-management-15-2048.jpg)