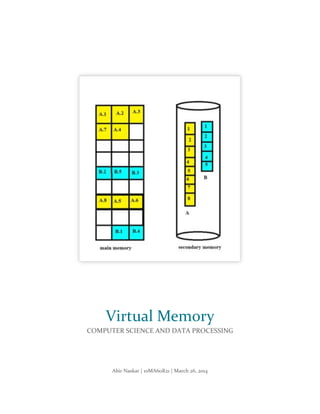
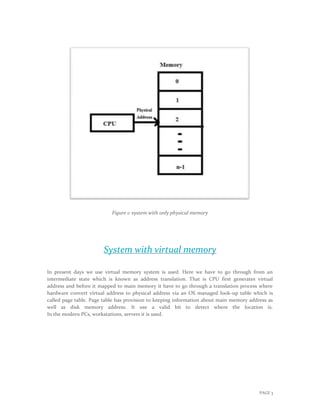
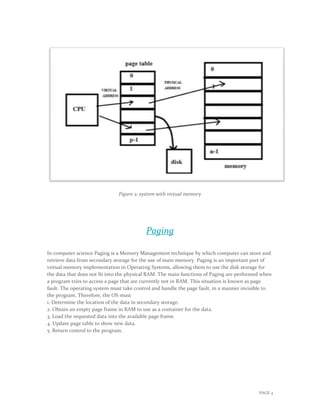
Virtual memory is a memory management technique that allows programs to access memory addresses beyond their actual physical RAM size. It maps virtual addresses to physical addresses stored in RAM or on a hard disk using page tables and a translation process. When a program requests a page not in RAM, a page fault occurs and the OS moves a page from disk to RAM, suspending the program until the page is loaded. Page replacement algorithms like LRU then select pages to remove from RAM and write to disk when RAM is full to make space for new pages. This allows for larger memory sizes, more efficient memory usage, and multitasking.