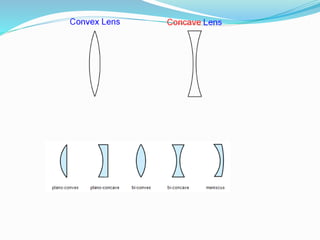
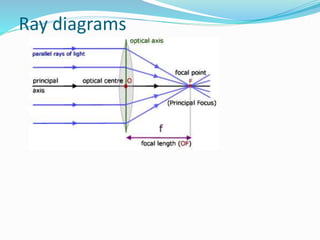
Lenses bend light to form images, either converging or diverging. Convex lenses are thick in the middle and thin at the edges, converging light, while concave lenses are thin in the middle and thick at the edges, diverging light. Ray diagrams illustrate the path of light through lenses using lines representing rays and key points like the optical center, principal axis, focal points, and images. Images can be magnified or diminished, inverted or upright, and real or virtual depending on their position relative to the lens and focal points. Magnification is calculated by comparing the size of the image to the object.