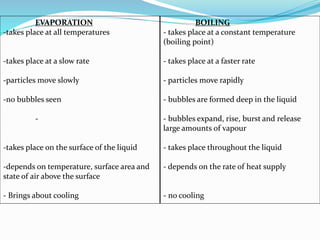
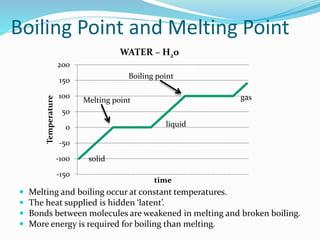
This document discusses melting and boiling. It defines melting as the change from solid to liquid that occurs at a specific melting point temperature for each substance. Ice melts at 0°C. Boiling is defined as the change from liquid to gas, which occurs at the boiling point temperature for each substance. Boiling involves particles gaining enough energy to break free of liquid form. Evaporation only occurs at the surface of a liquid, while boiling can occur below and above the surface as bubbles form and rise. Melting and boiling points are specific to each pure substance and involve heat being used to weaken or break molecular bonds without changing temperature.