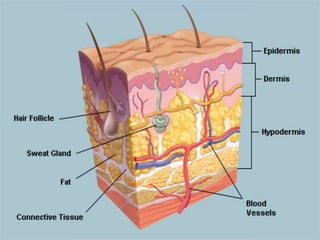
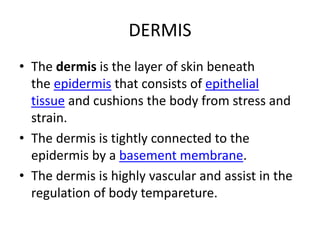
The skin is the largest organ of the body and has three layers - the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. The epidermis is the outermost waterproof layer that protects against microbes. The dermis lies beneath the epidermis, contains connective tissue, hair follicles, and sweat glands. The deepest layer, the hypodermis, is made of fat and connective tissue. Assessment of the integumentary system involves history, physical exam, and diagnostic tests like biopsies, cultures, and patch tests to identify skin conditions.