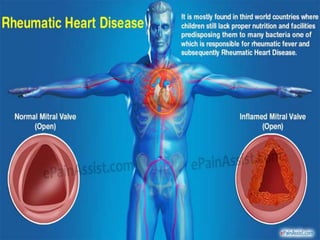
Rheumatic heart disease is a chronic condition caused by rheumatic fever, which is an inflammatory response to a streptococcal infection. It often involves damage to the heart valves that causes them to not open and close properly, restricting blood flow. Common symptoms include chest pain, breathlessness, and swelling. Diagnosis involves examining the patient history, performing tests like echocardiograms and electrocardiograms. Treatment depends on severity but may include antibiotics, surgery to repair or replace valves, and managing symptoms like heart failure. Nursing care focuses on monitoring the patient's condition, administering medications, providing respiratory support, and addressing psychological needs.