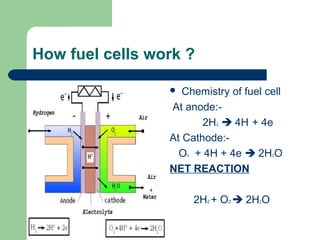
Fuel cells convert hydrogen and oxygen into water, producing electricity and heat in the process. Sir William Grove invented the first fuel cell in 1839, proving that electricity could be produced from reversing the electrolysis of water. There are several types of fuel cells including proton exchange membrane, phosphoric acid, solid oxide, alkaline, direct methanol, and molten carbonate. Fuel cells provide an efficient and non-polluting alternative power source without noise or moving parts. Applications include powering vehicles, buses, portable devices, telecommunications equipment, and someday powering homes. Major challenges include higher initial costs compared to conventional energy sources, though organizations worldwide are working to develop fuel cells further.