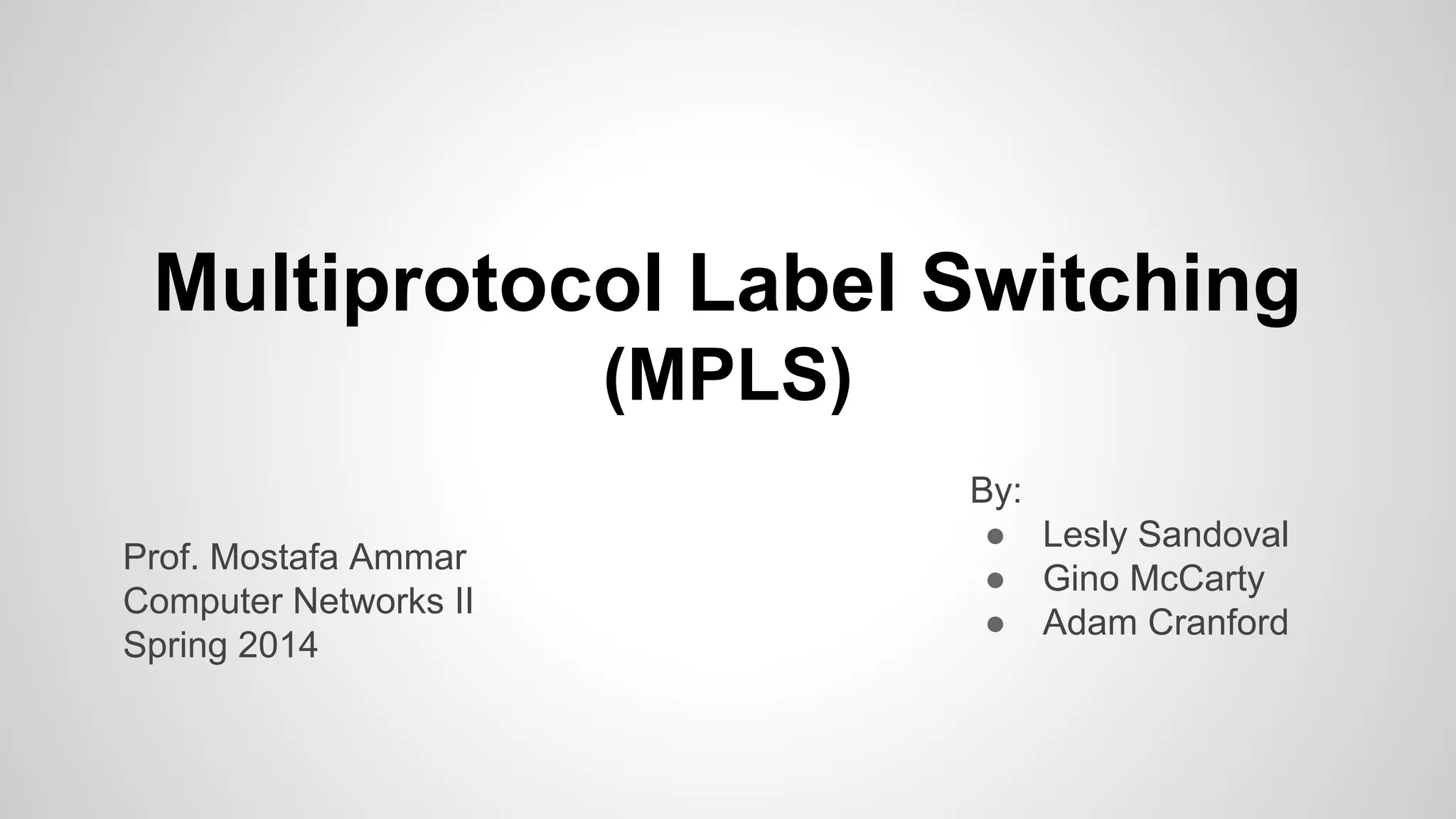
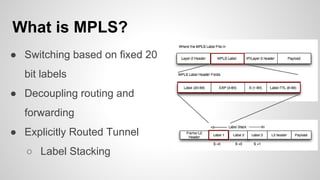
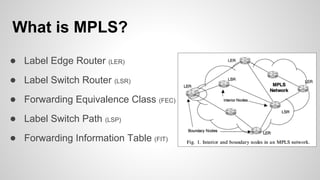
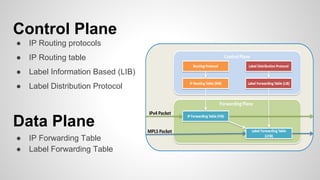
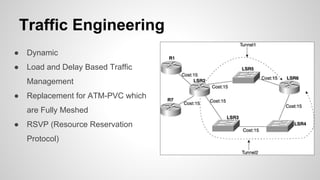
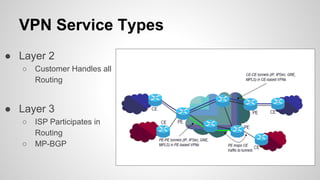
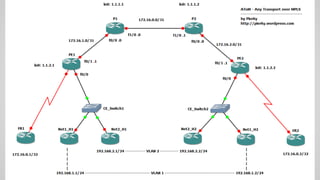
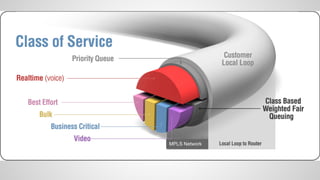
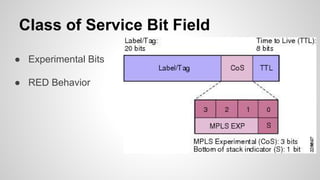
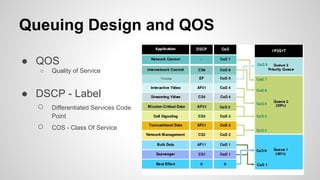
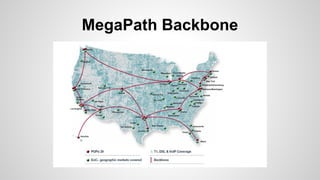
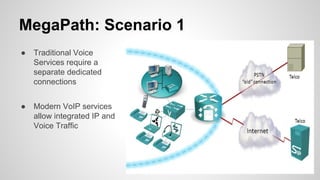
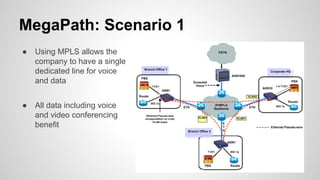
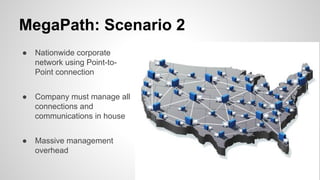
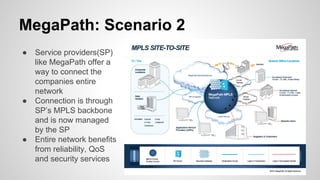
This document provides an overview of Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), including its history, key concepts, applications, and use by service providers. MPLS was developed in the late 1990s to meet the needs of scalable routing and quality of service on the growing internet. It works by assigning fixed length labels to data packets, allowing routers to forward based on these labels rather than long network addresses. Major applications of MPLS include traffic engineering, virtual private networks, and bandwidth management. The document discusses how service providers like MegaPath use MPLS in their backbones to provide integrated data and voice services, and nationwide networking solutions for corporate customers.