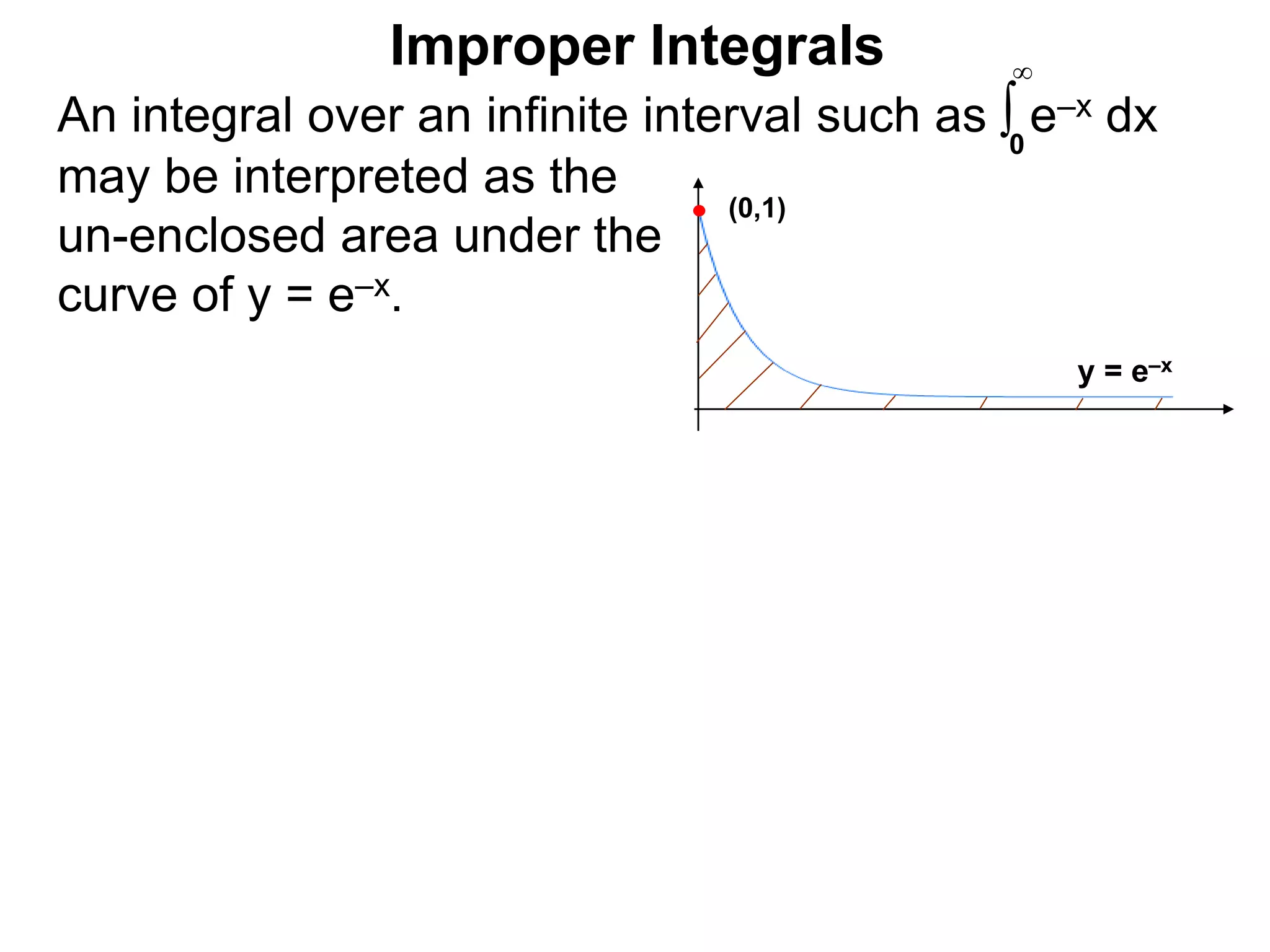
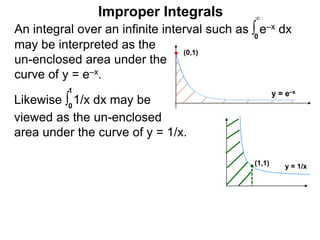
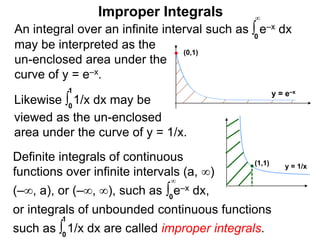
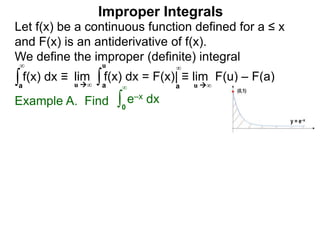
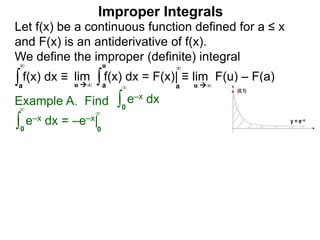
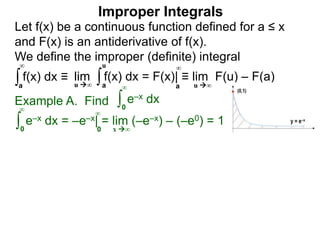
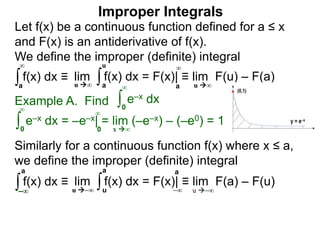
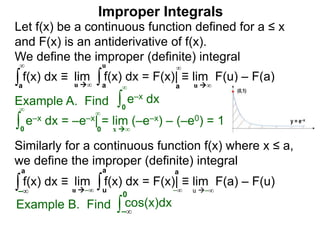
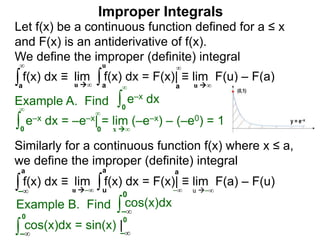
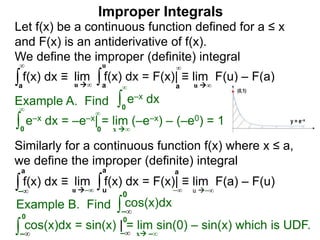
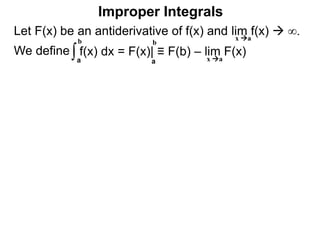
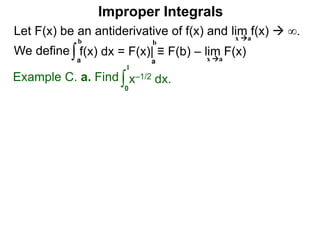
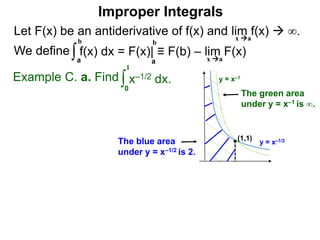
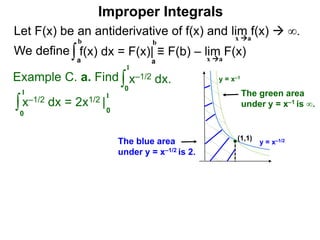
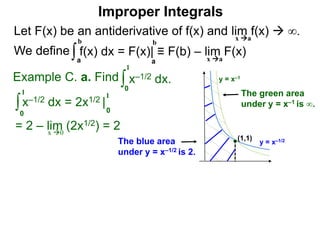
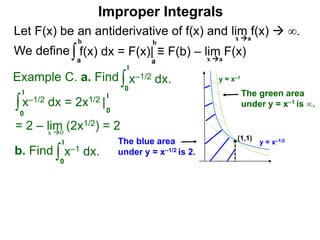
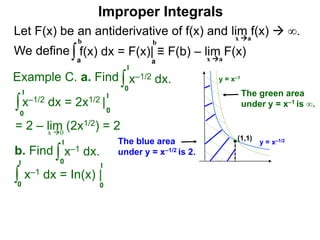
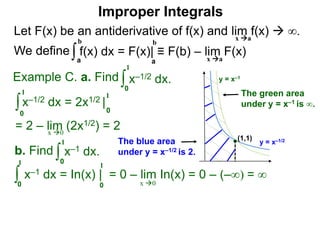
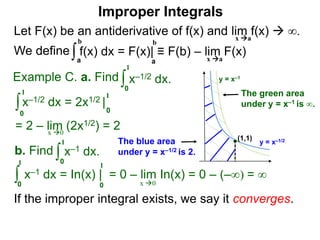
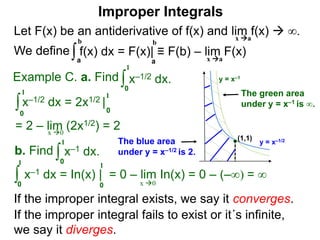
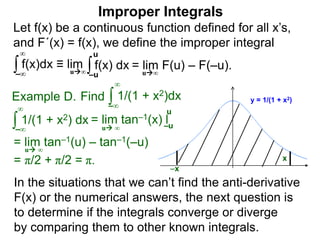
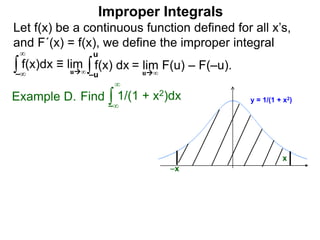
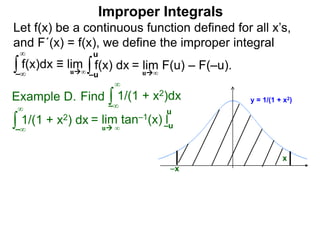
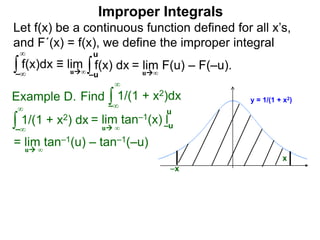
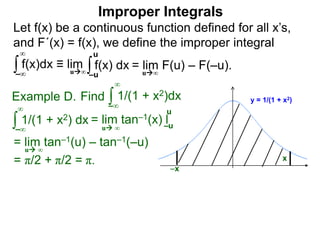
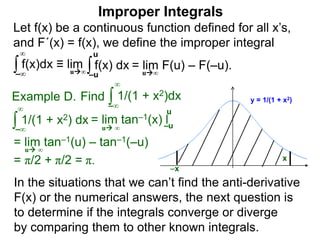
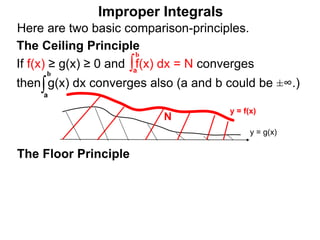
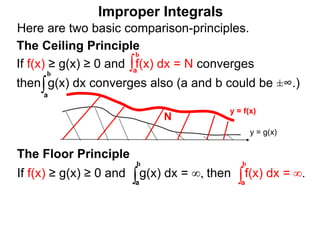
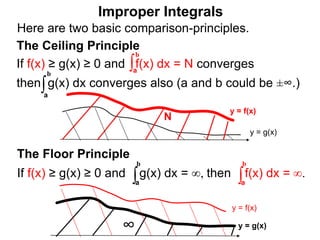
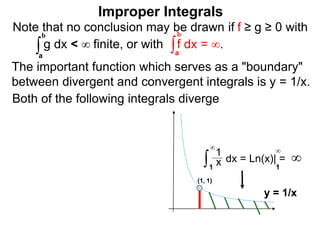
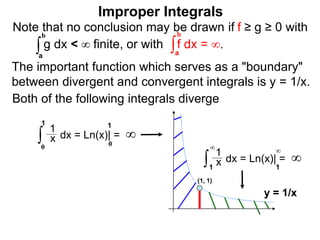
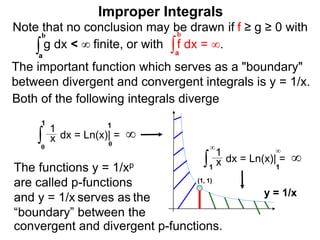
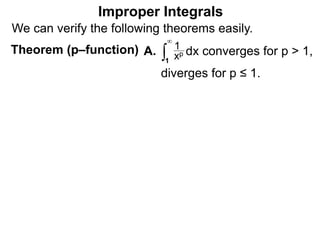
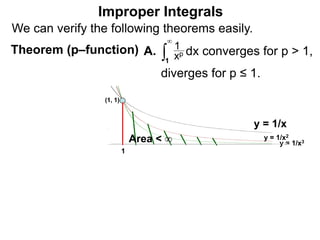
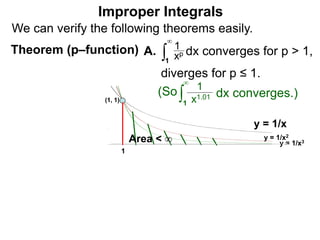
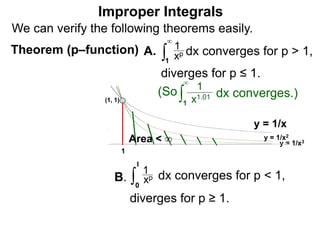
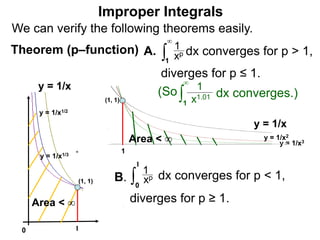
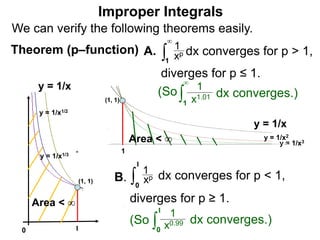
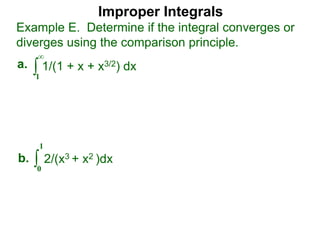
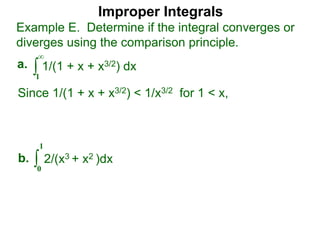
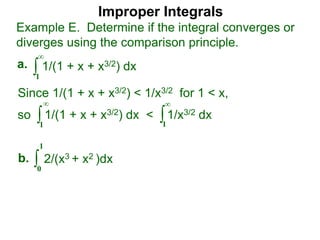
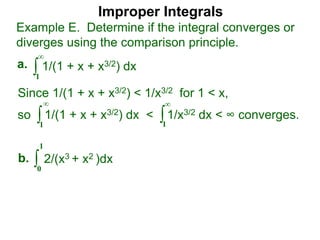
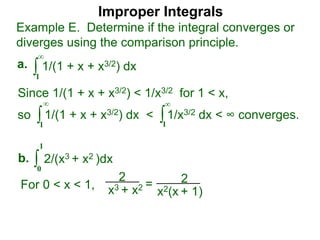
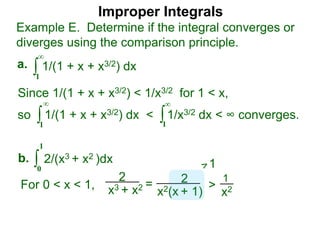
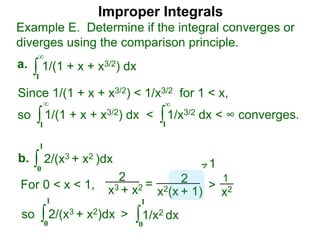
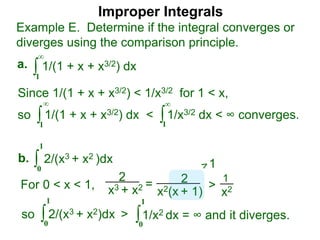
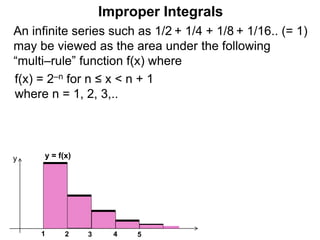
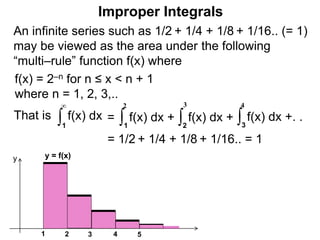
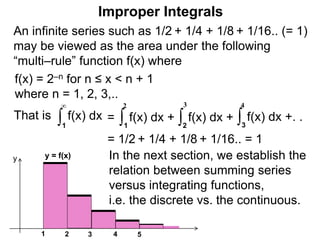
The document discusses improper integrals, which are definite integrals with infinite intervals. An improper integral of a continuous function over an infinite interval, such as ∫ e-x dx from 0 to ∞, or an integral of an unbounded continuous function, such as ∫ 1/x dx from 0 to 1, are called improper integrals. Improper integrals are evaluated by taking the limit of the integral as the interval approaches infinity or by taking the limit of the antiderivative. If the limit exists and is finite, the improper integral converges; if the limit fails to exist or is infinite, the improper integral diverges. Examples are provided to demonstrate the evaluation and convergence of improper integrals.