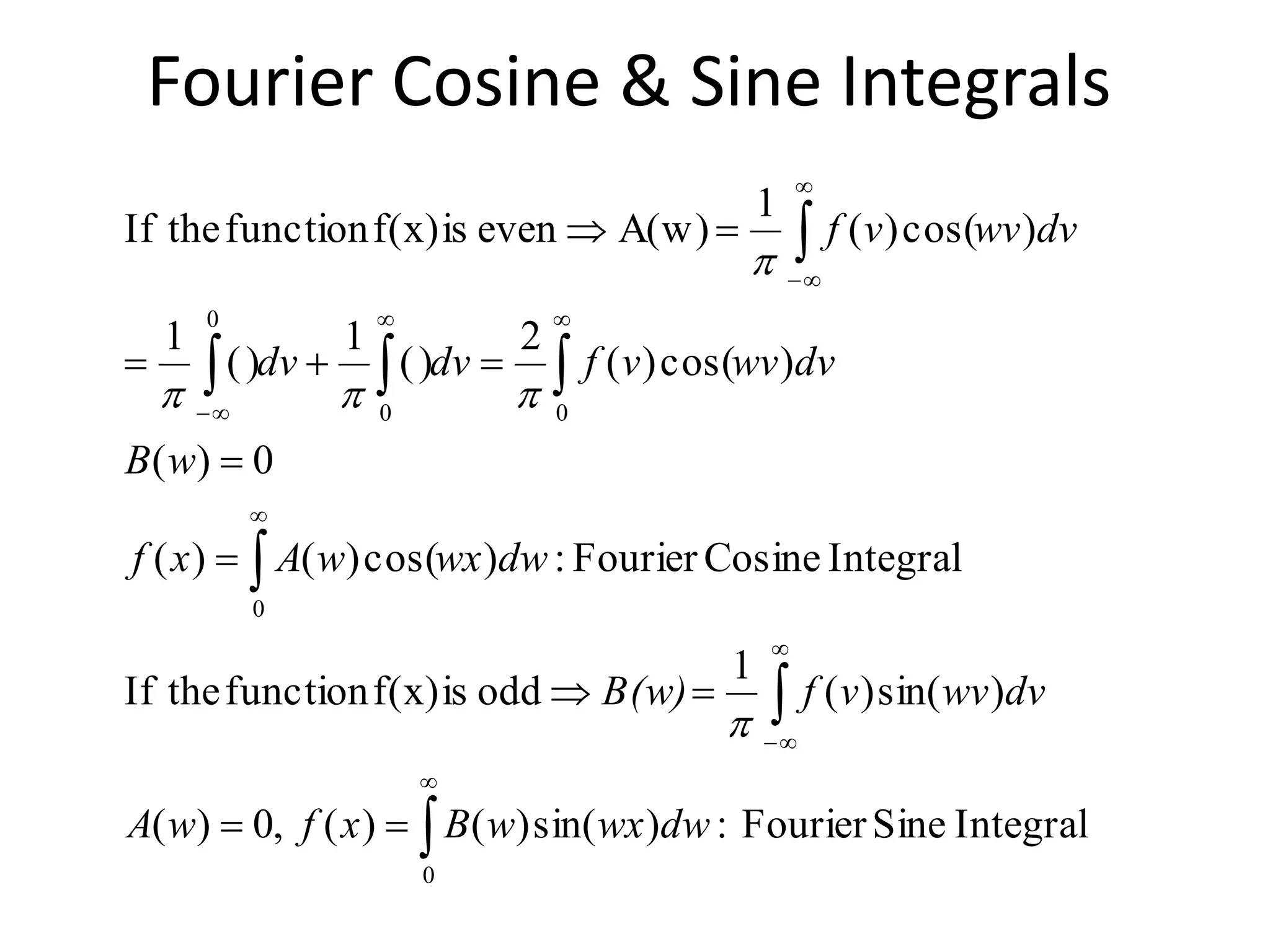
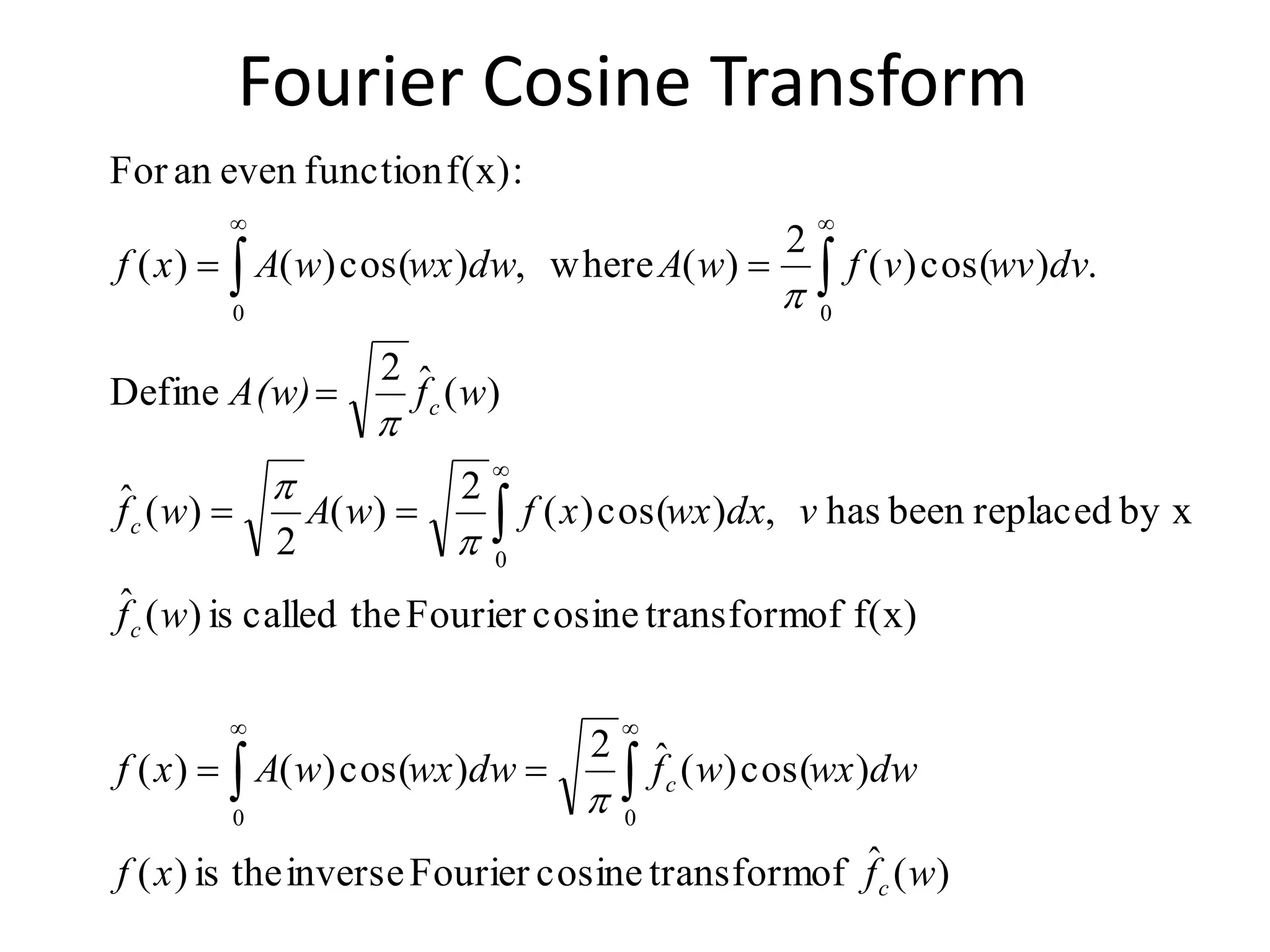
This document discusses Fourier cosine and sine integrals. It provides the definitions and formulas for the Fourier cosine transform, Fourier sine transform, and their inverses. It also discusses improper integrals of type 1 and 2, including definitions and convergence conditions. Examples are provided to illustrate the concepts. The physical interpretation of the Fourier integrals is that higher integration limits include more higher frequency sinusoidal components in the approximation of the real function.





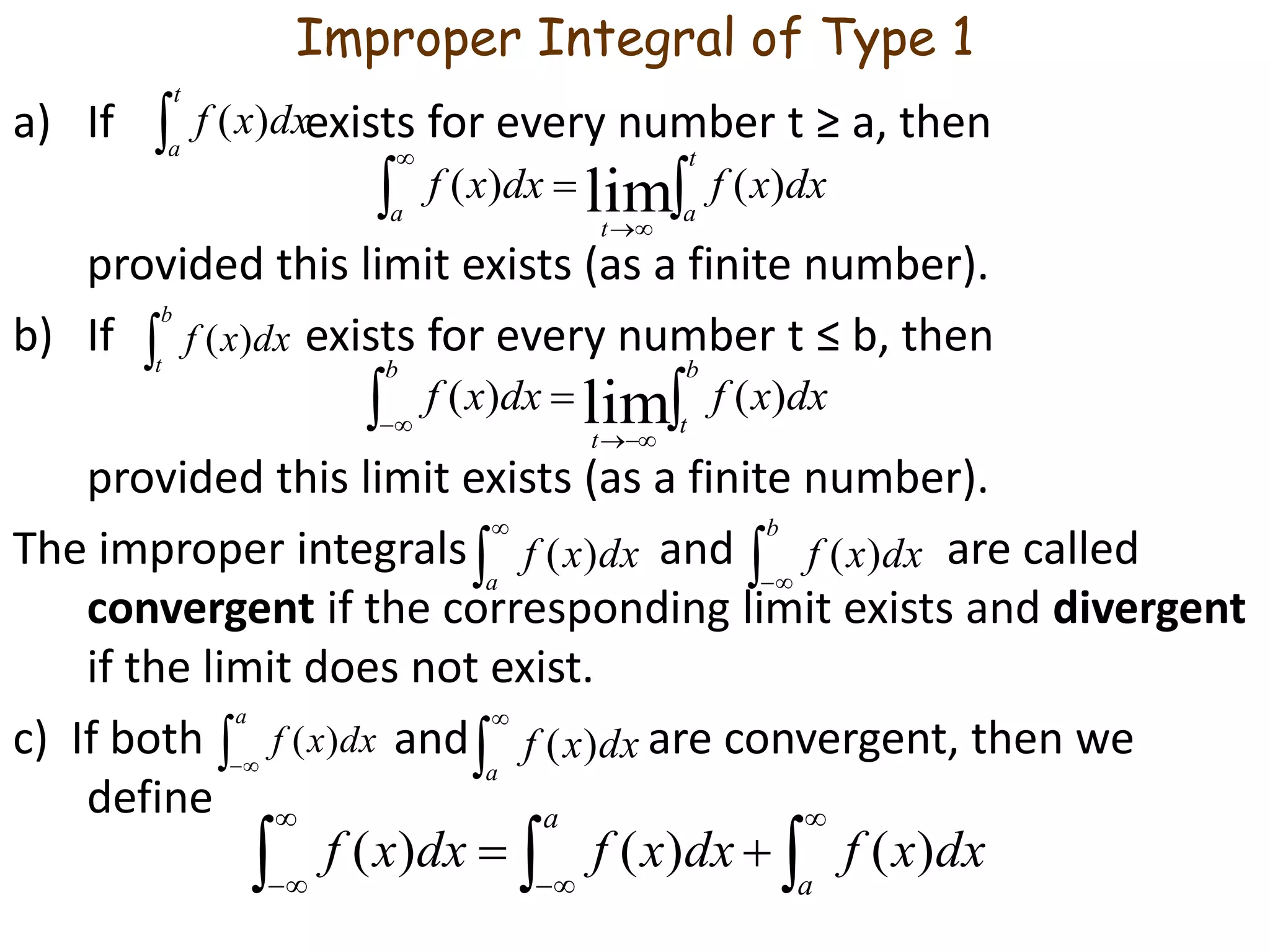


![Definition of an Improper Integral of Type 2
a) If f is continuous on [a, b) and is discontinuous at b, then
if this limit exists (as a finite number).
a) If f is continuous on (a, b] and is discontinuous at a, then
if this limit exists (as a finite number).
The improper integral is called convergent if the
corresponding limit exists and divergent if the limit does
not exist.
c) If f has a discontinuity at c, where a < c < b, and both
and are convergent, then we define
t
a
b
a
bt
dxxfdxxf )()( lim
b
t
b
a
at
dxxfdxxf )()( lim
b
c
dxxf )(
c
a
dxxf )(
b
a
dxxf )(
b
c
c
a
b
a
dxxfdxxfdxxf )()()(](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2-170125100258/75/Unit2-11-2048.jpg)