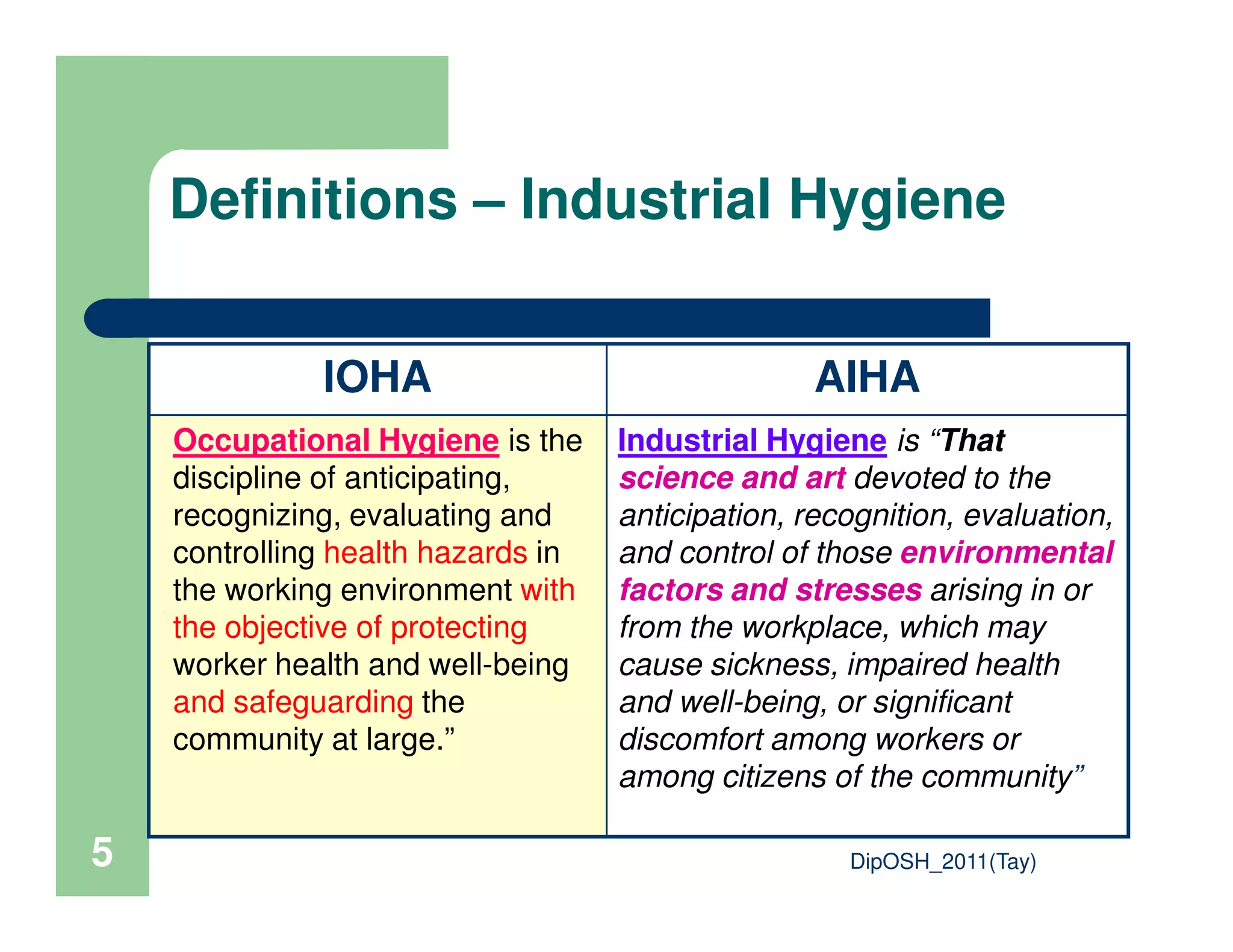
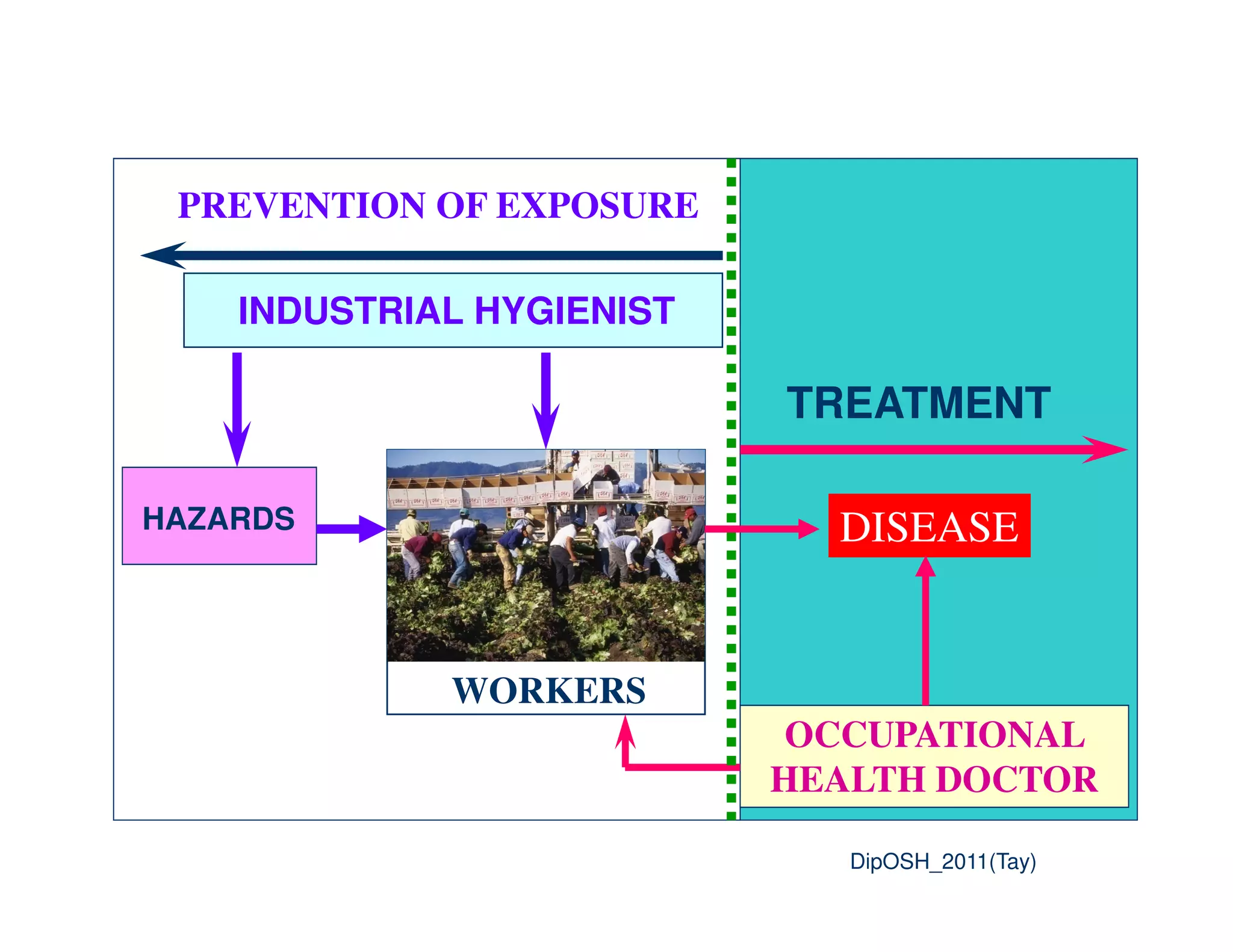
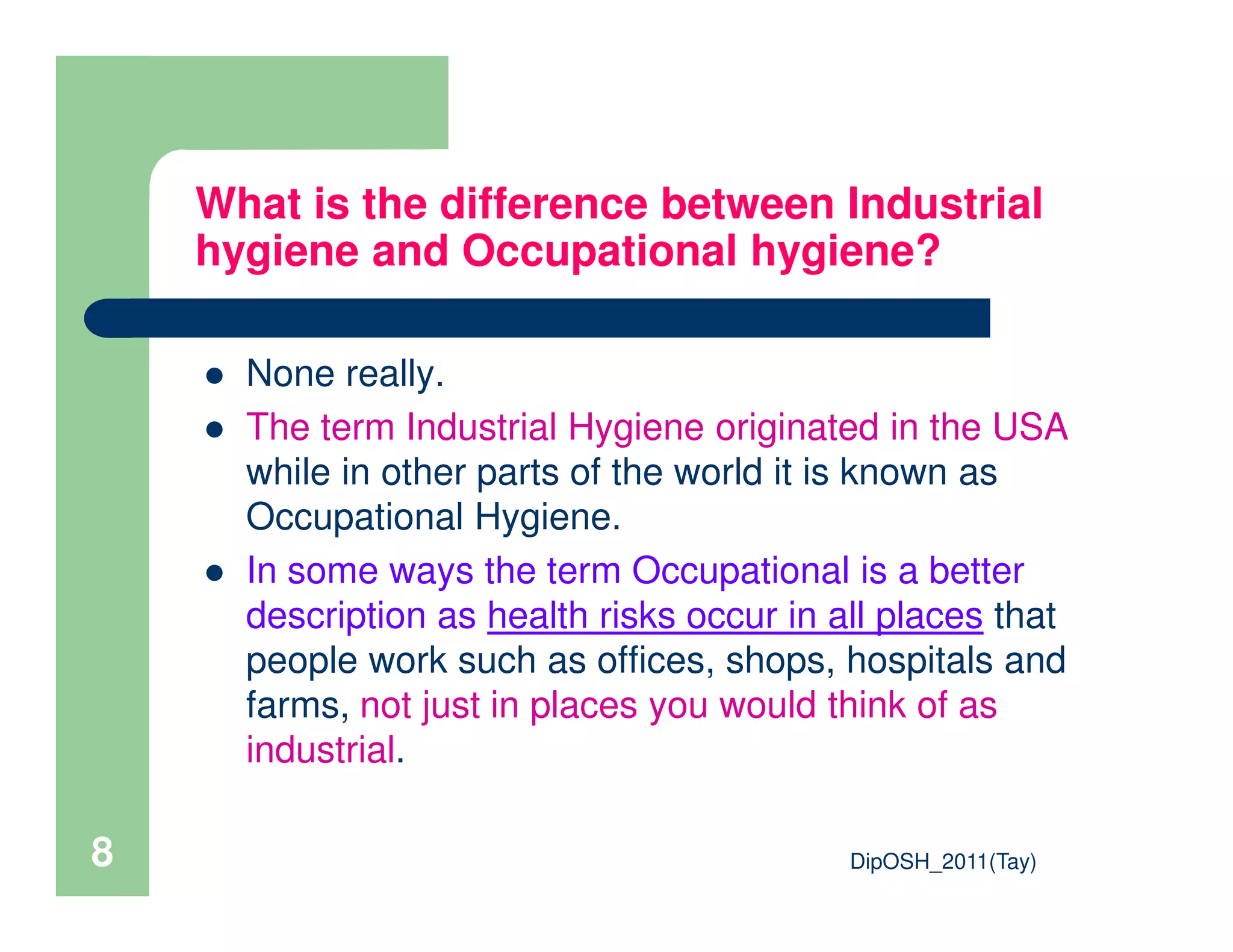
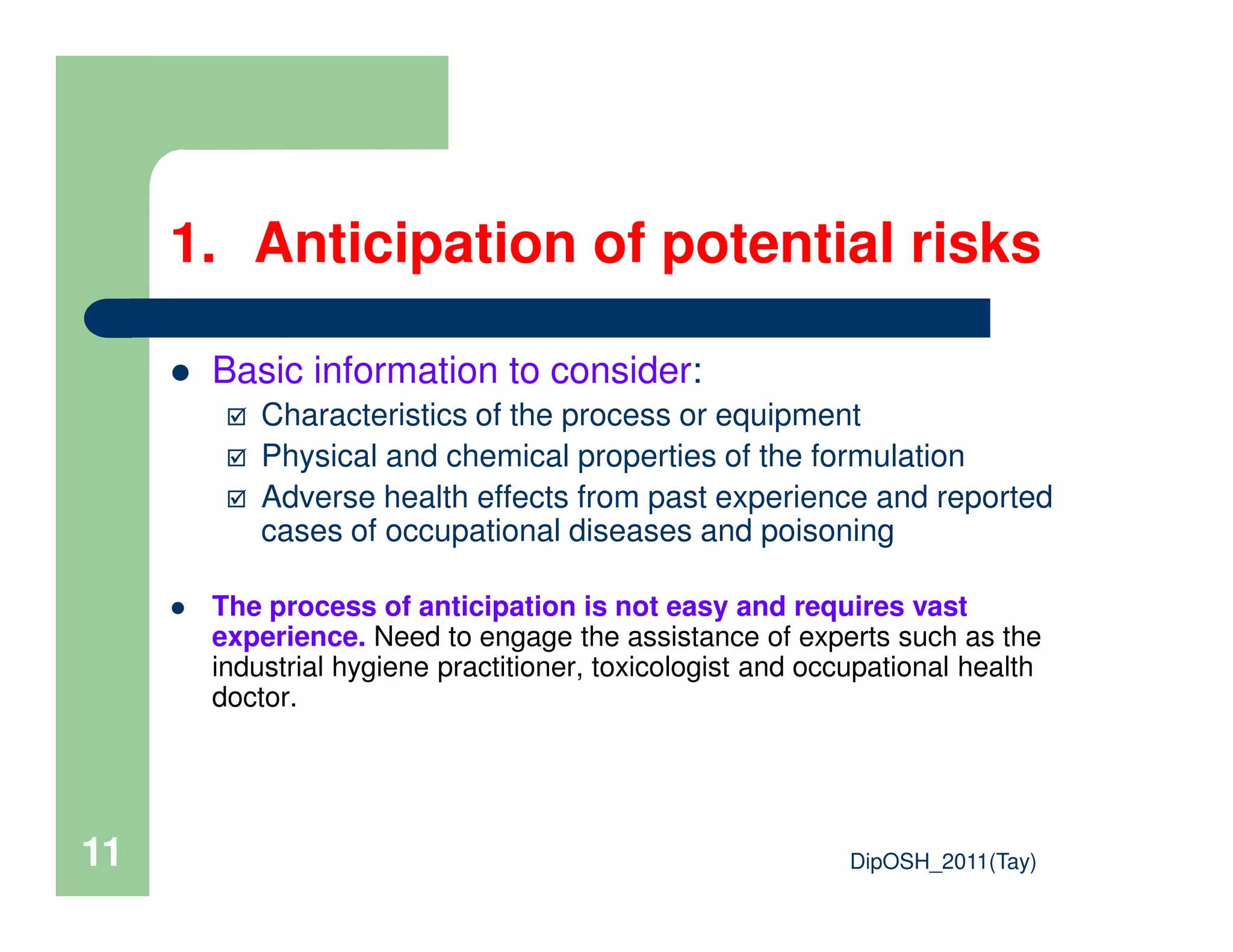
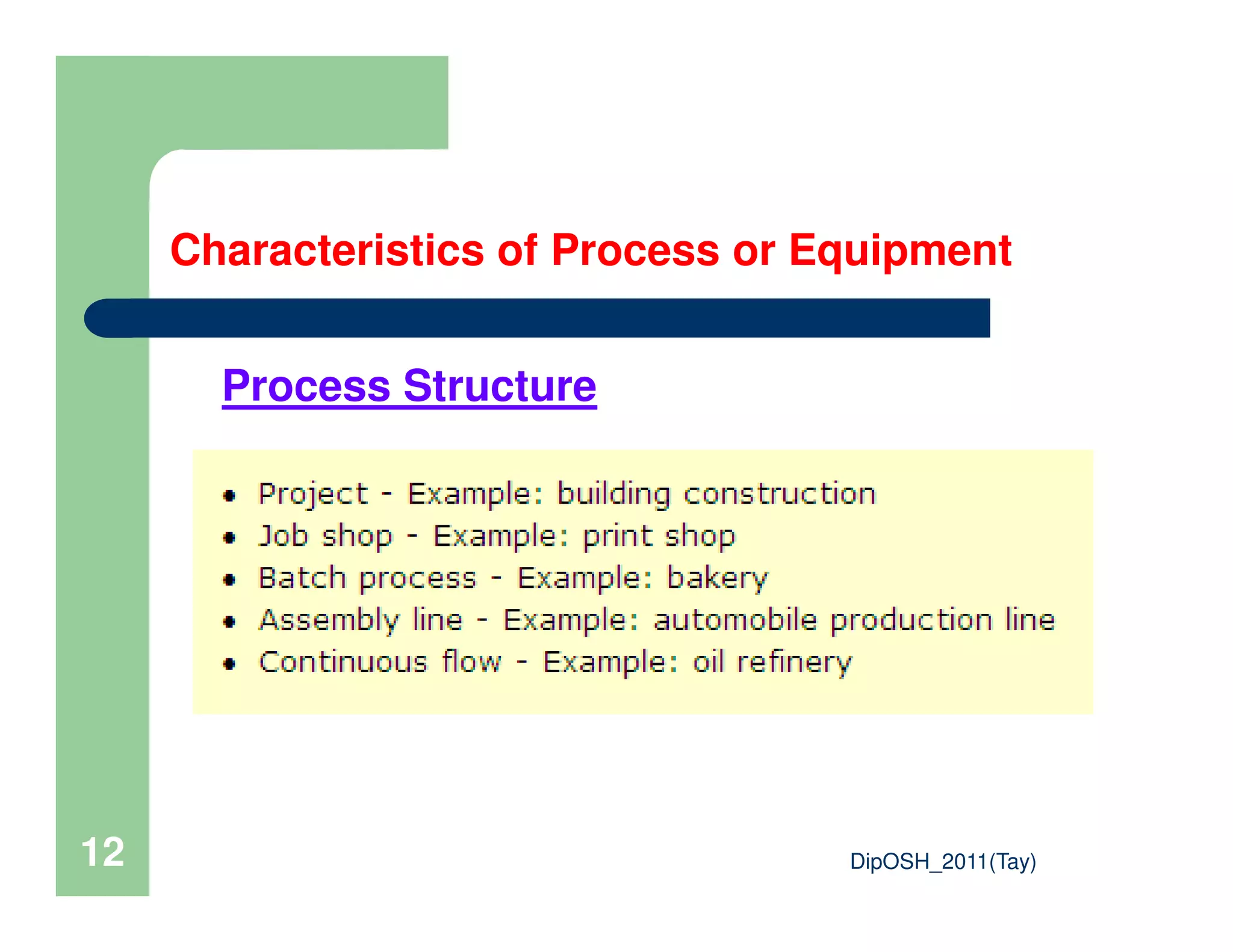
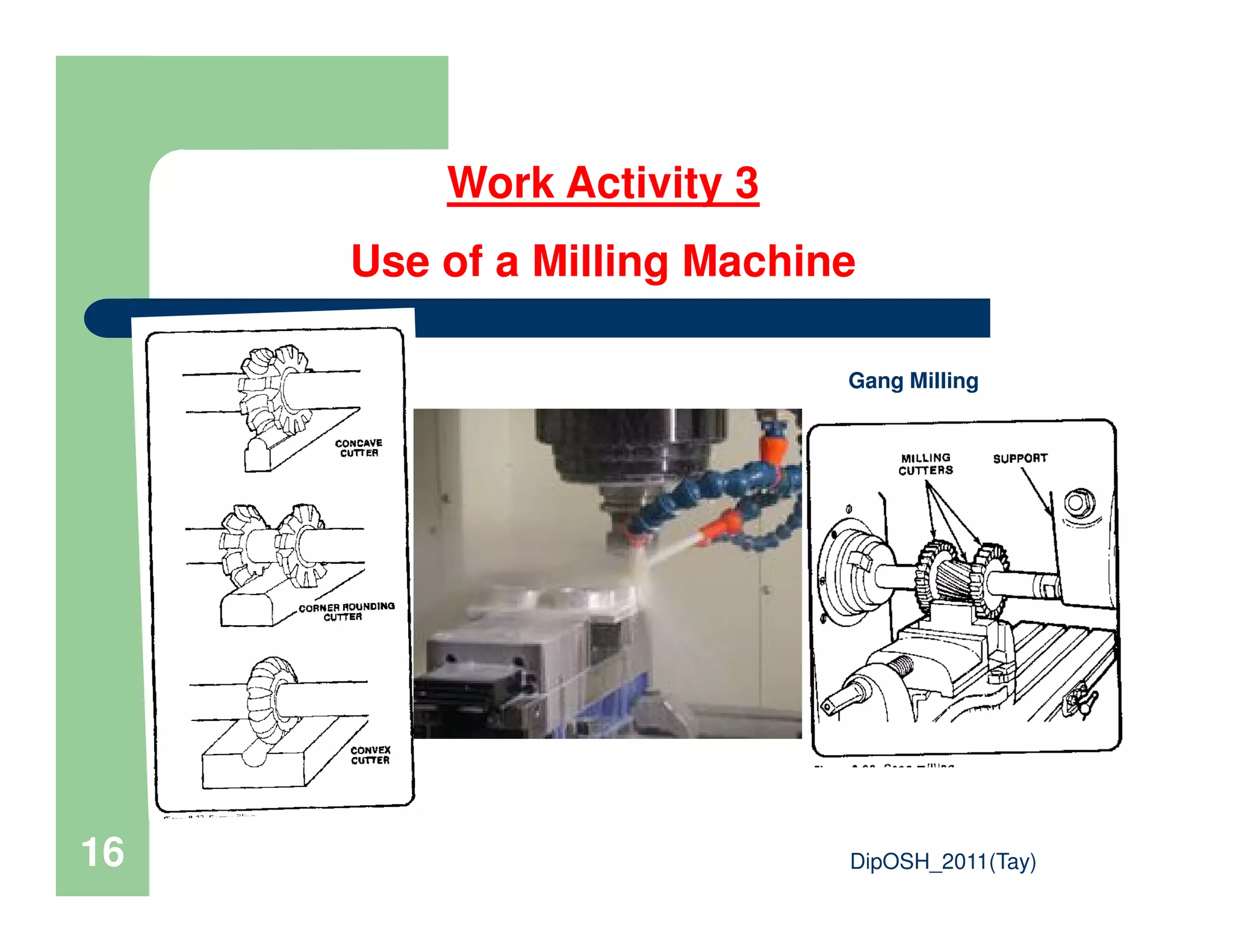
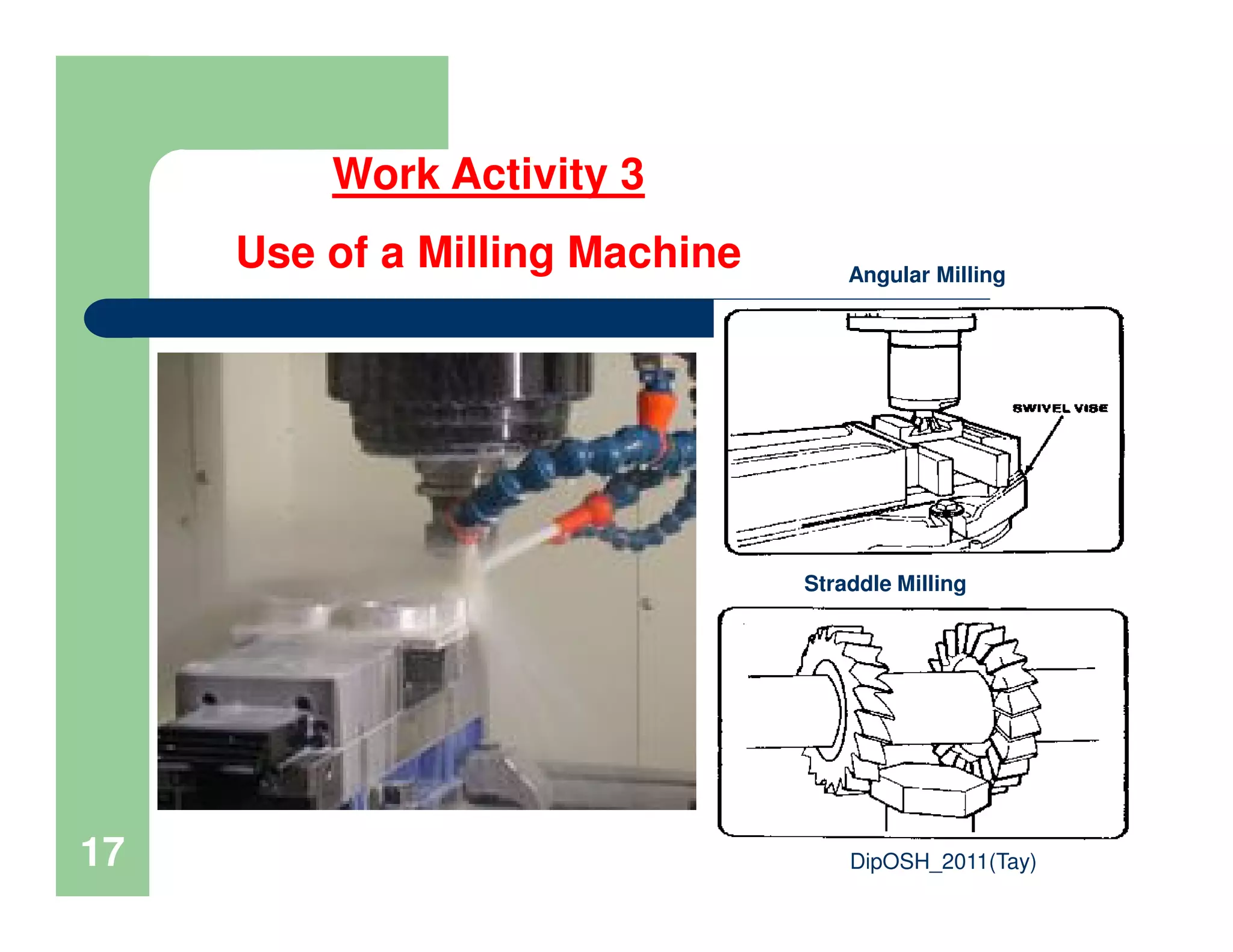
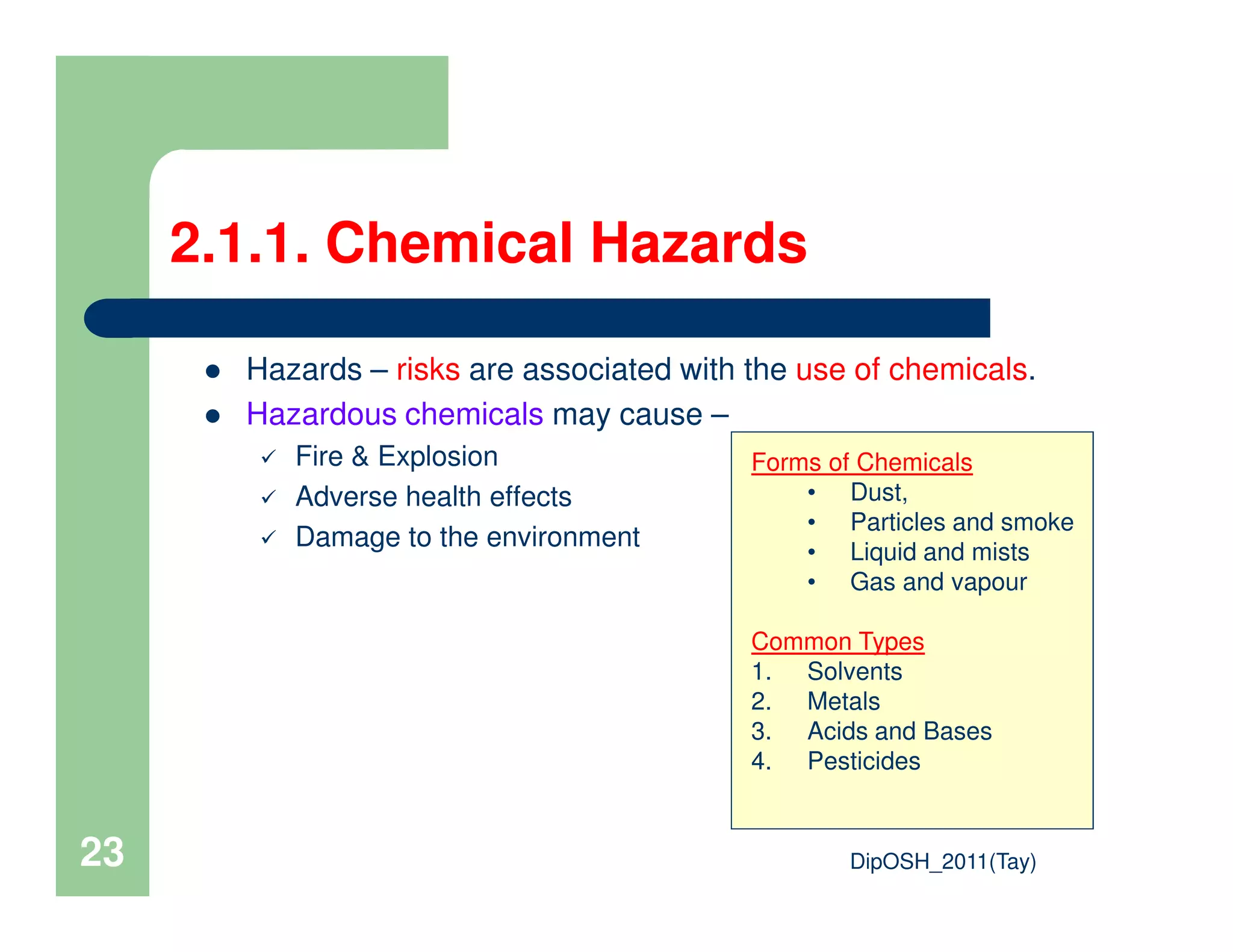
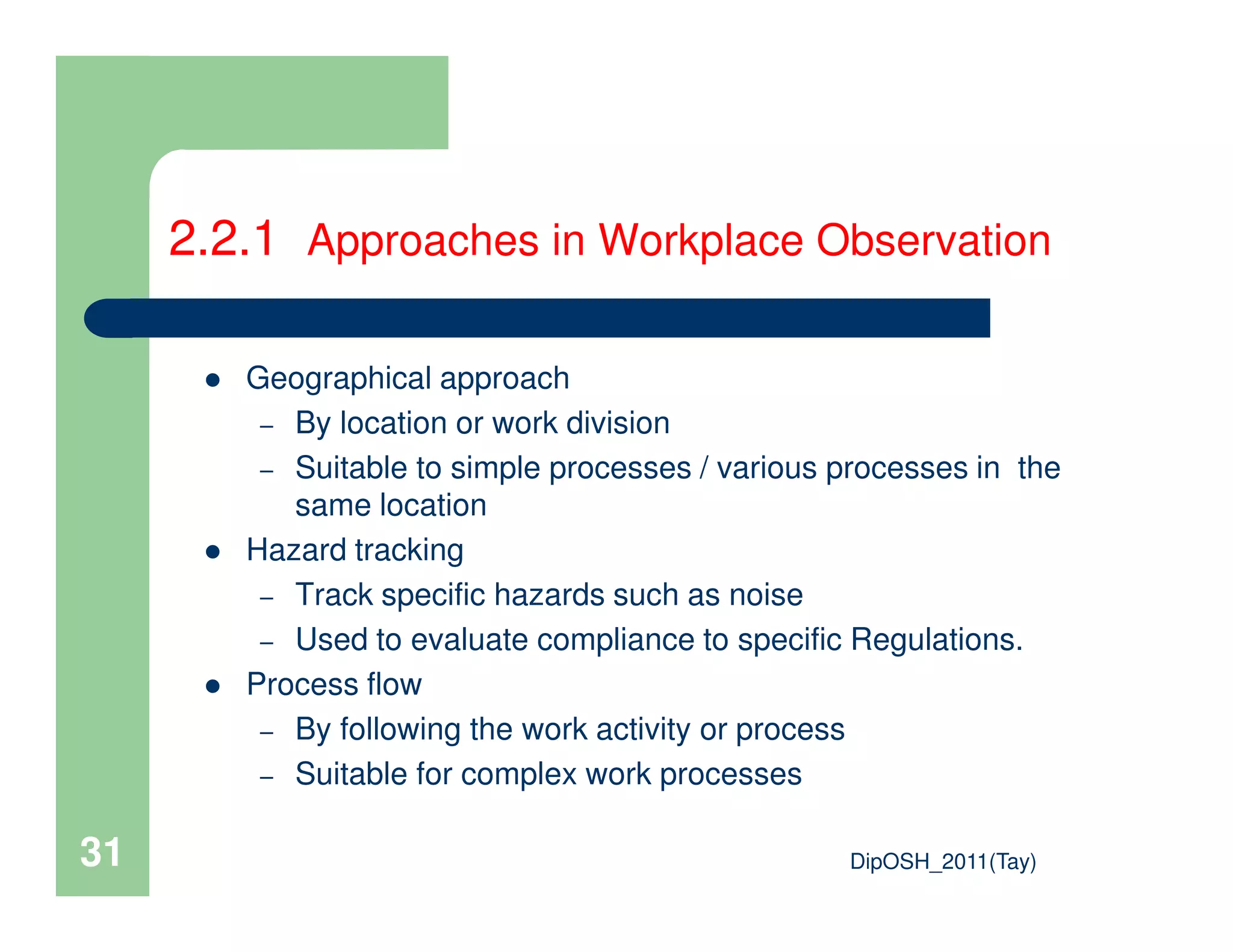
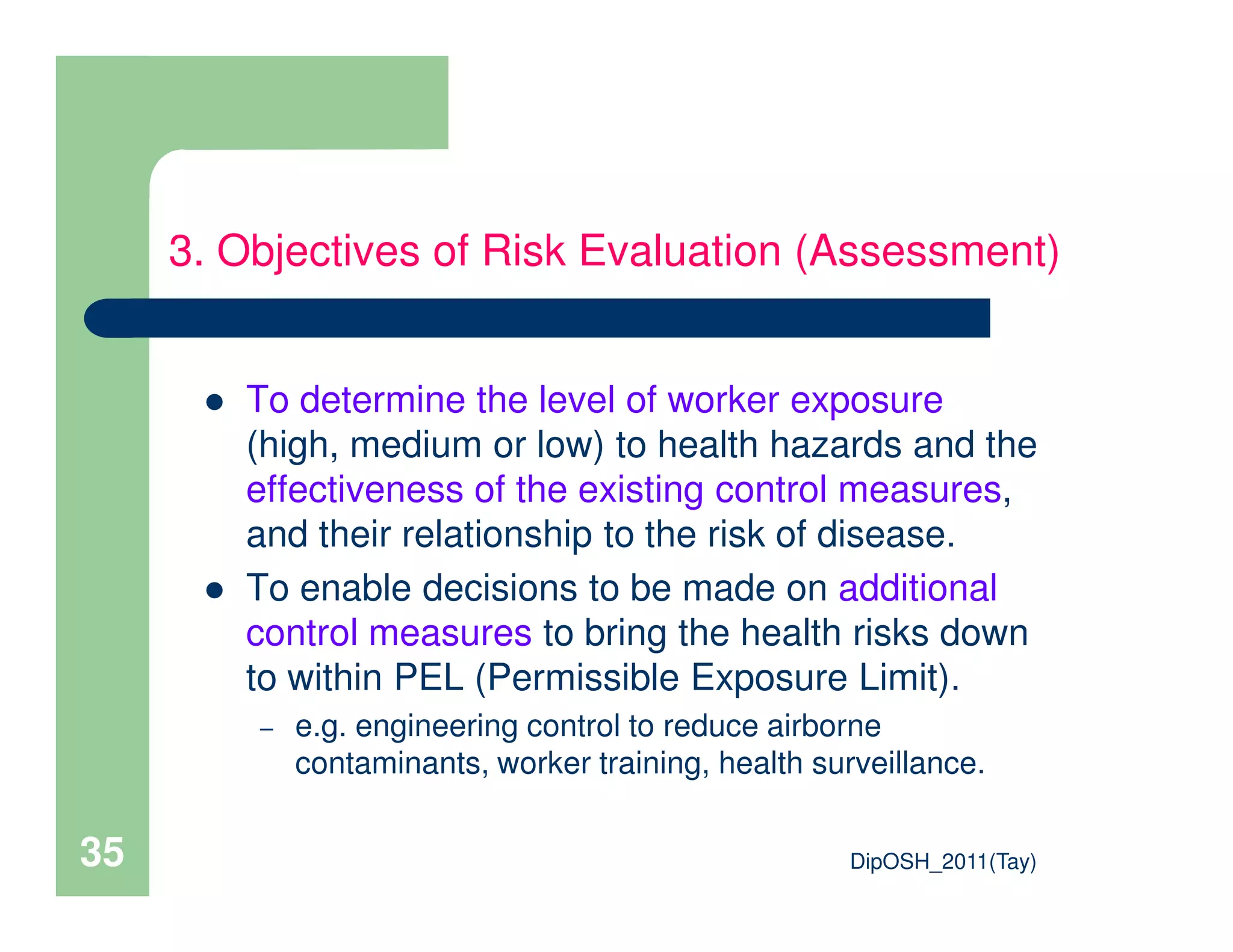
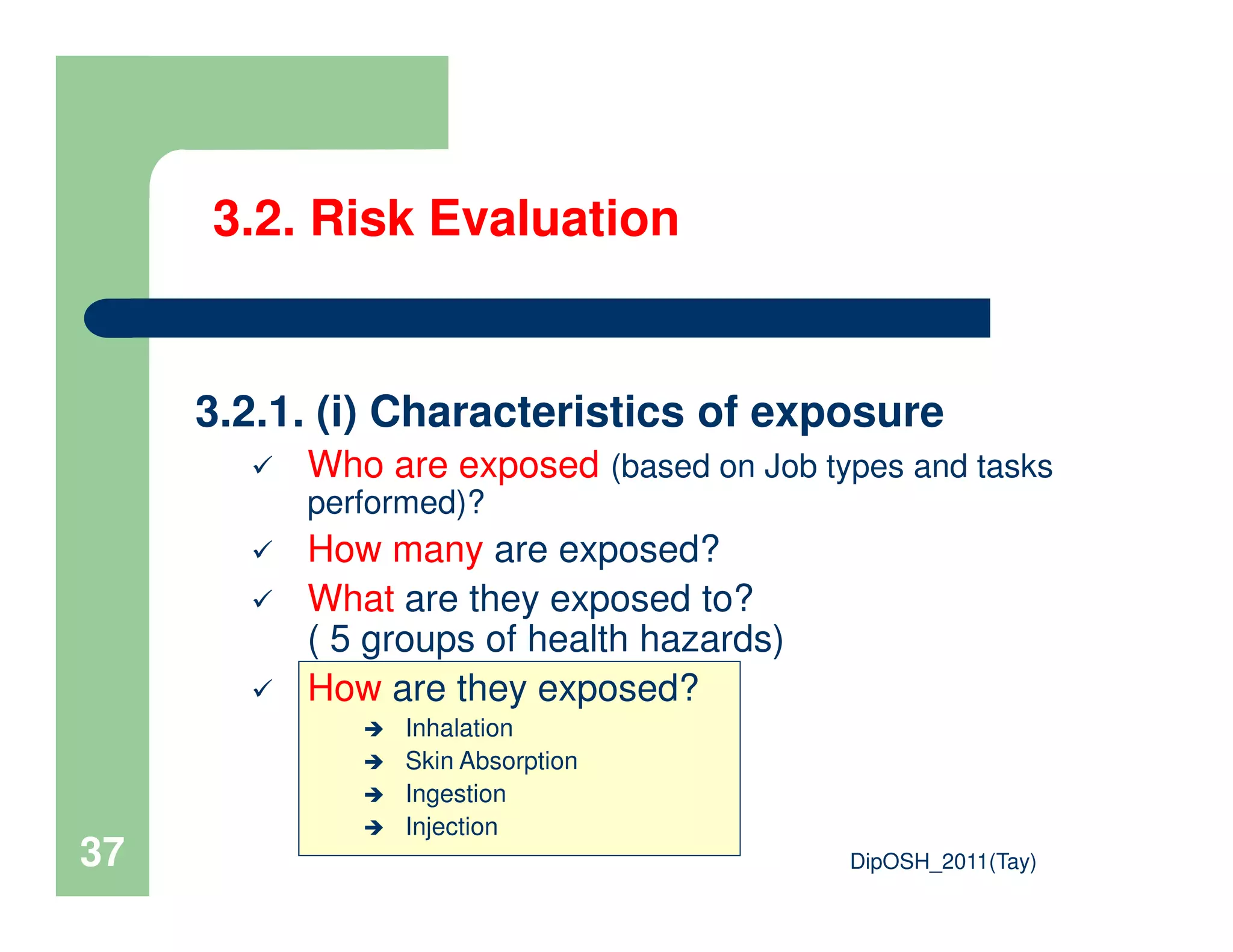
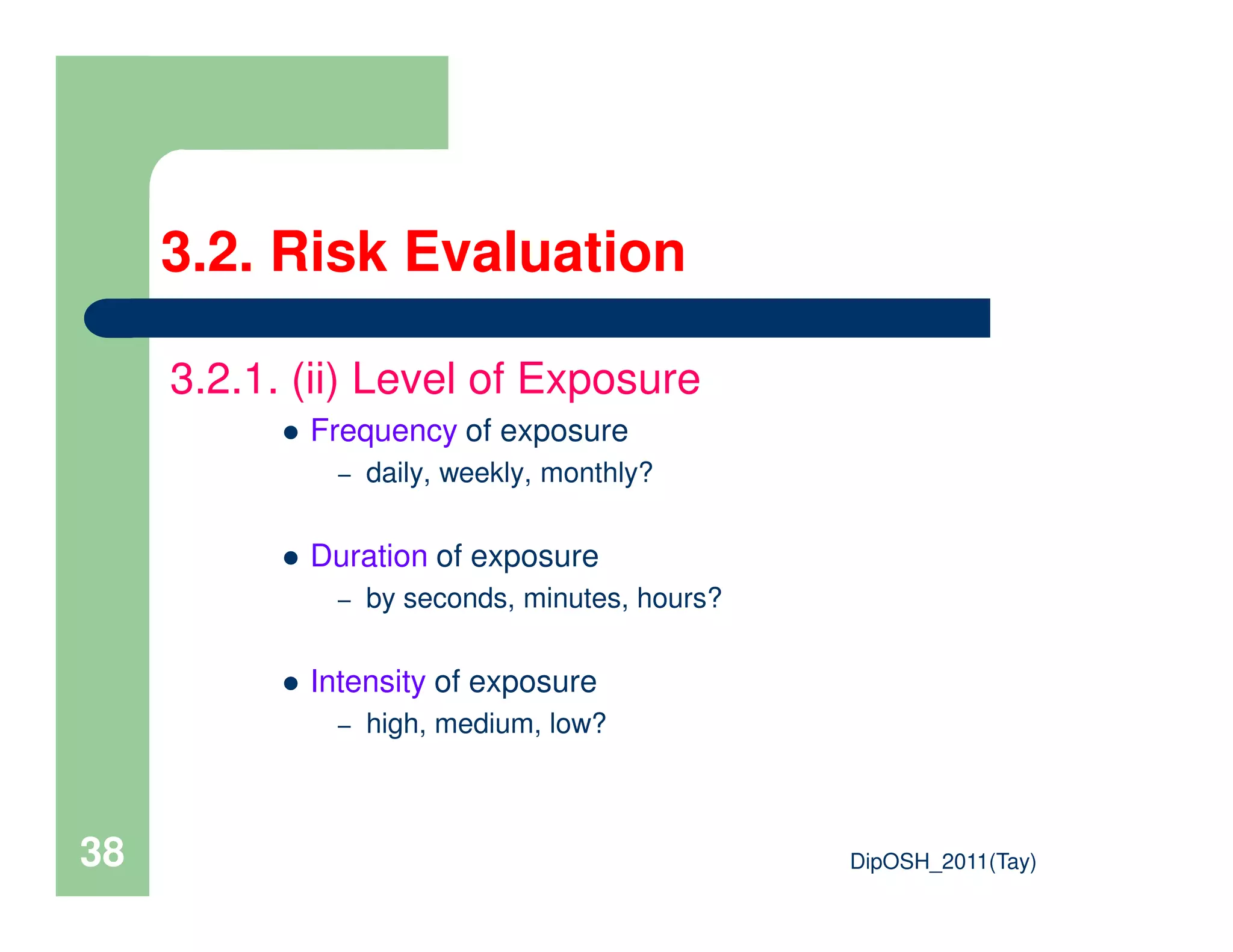
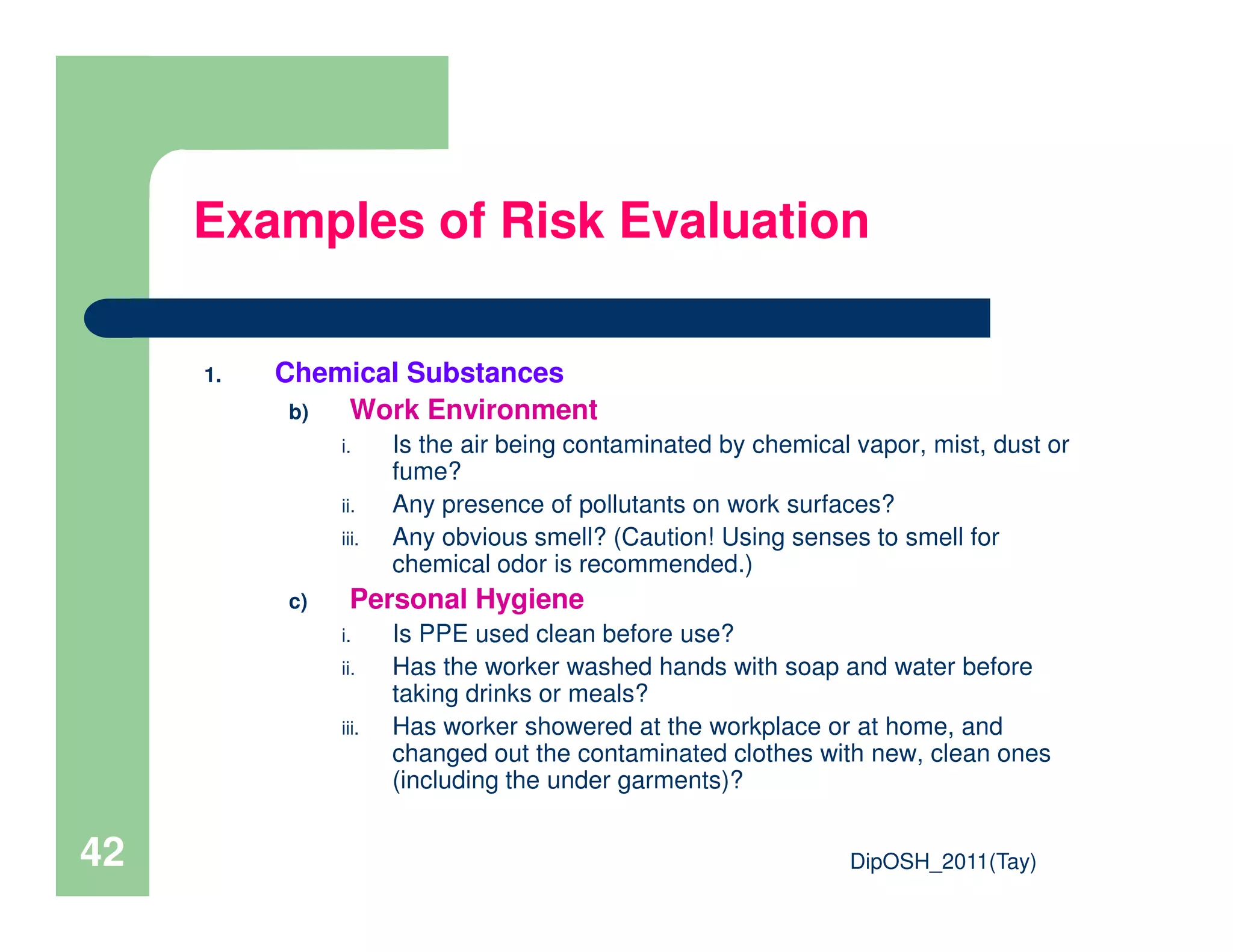
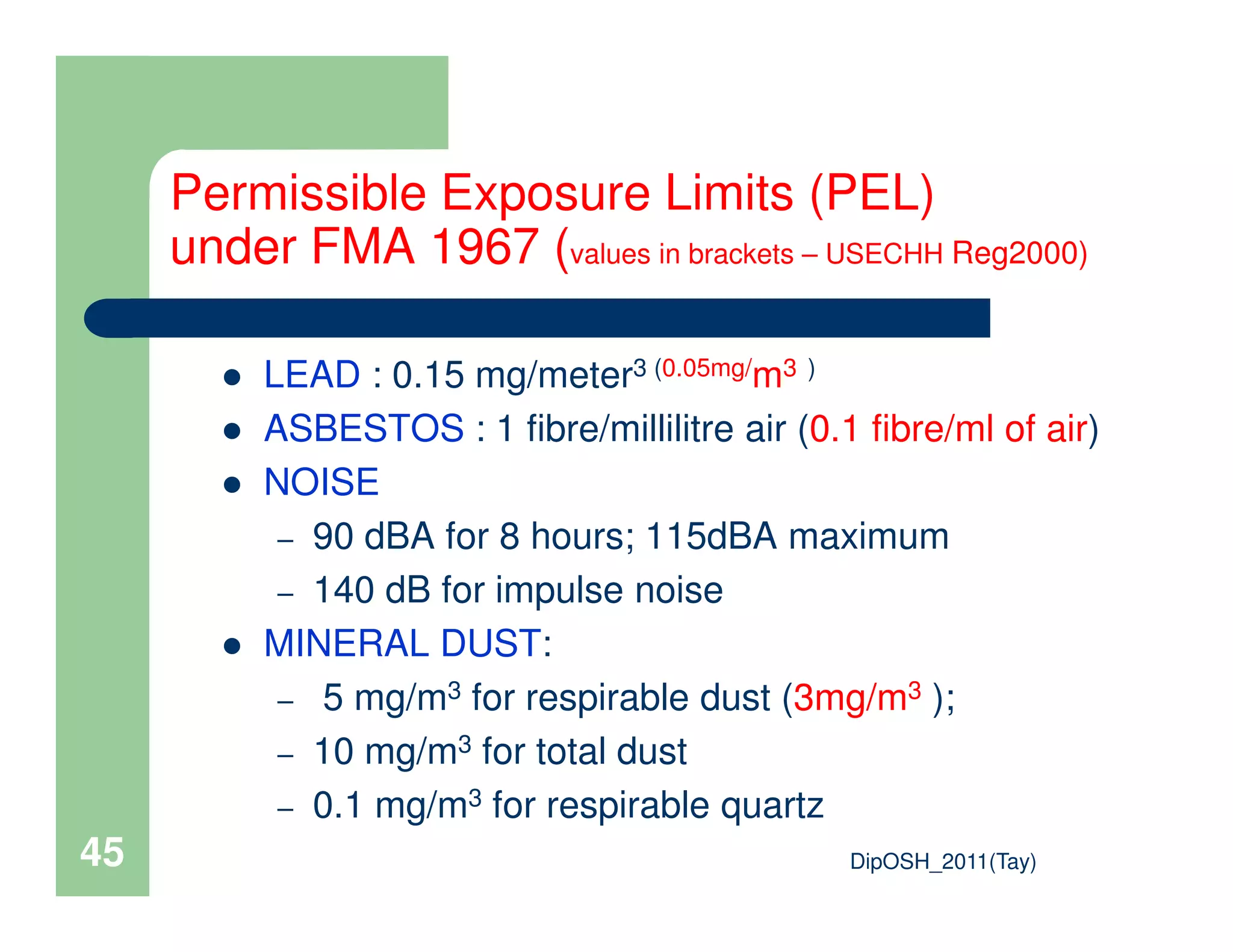
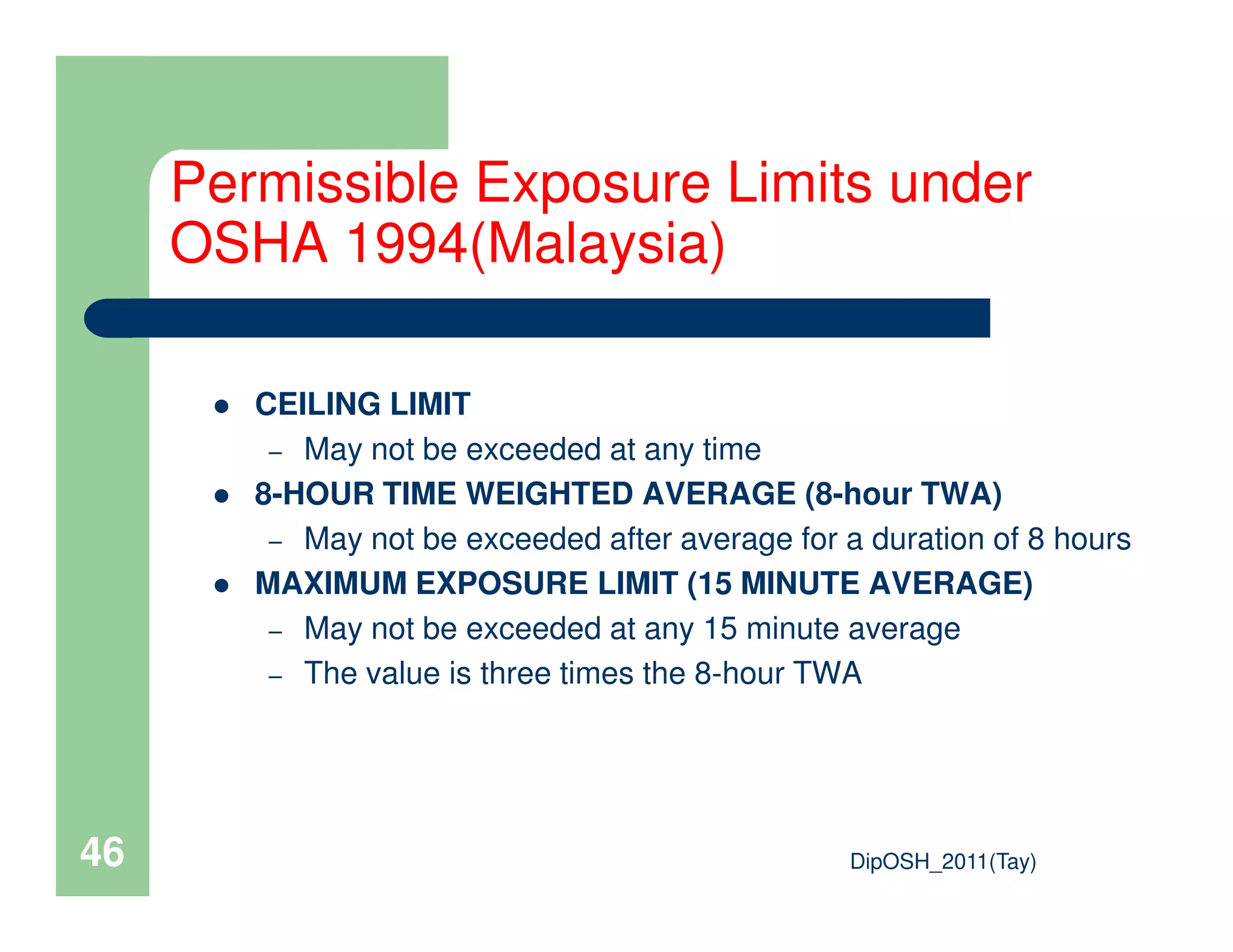
This document provides an overview of industrial hygiene. It defines occupational/industrial hygiene according to the International Occupational Hygiene Association and American Industrial Hygiene Association. The roles of industrial hygienists include anticipating, recognizing, evaluating, and controlling health hazards in the workplace. The basic principles of industrial hygiene are anticipation of potential risks, recognition of existing hazards, evaluation of health risks, and control of unacceptable risks. The document discusses various workplace health hazards including chemicals, physical agents, biological agents, and ergonomic/psychological factors. It also covers risk evaluation and assessment methods like workplace inspections, health monitoring, and permissible exposure limits.