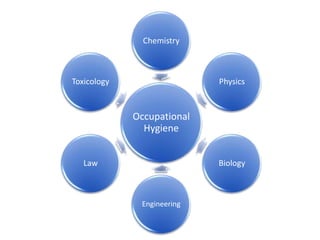
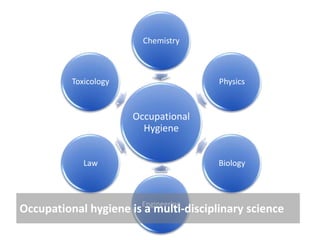
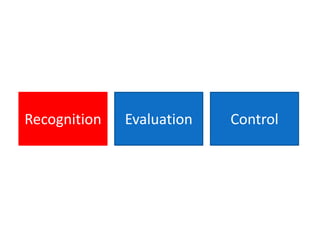
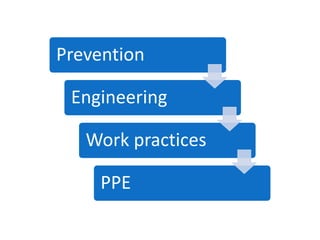
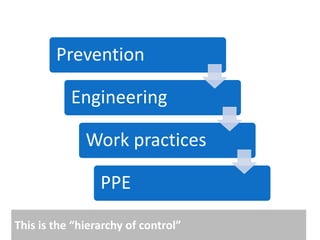
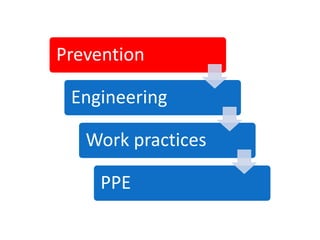
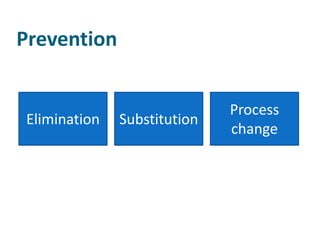
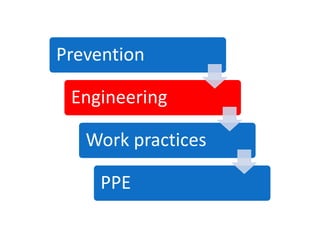
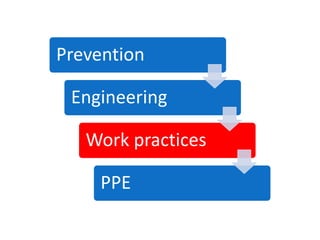
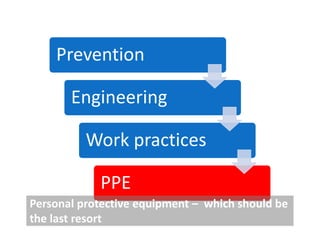
Occupational hygiene aims to prevent illness caused by workplace hazards. It does this through recognizing, evaluating, and controlling hazardous agents via a multidisciplinary approach involving chemistry, toxicology, physics, biology, engineering, and law. Hazards include chemicals, physical agents like noise and vibration, biological agents, and ergonomic risks. Risk is determined by assessing the hazard and level of worker exposure. Controls follow a hierarchy starting with eliminating or substituting the hazard, then using engineering controls, administrative controls like safe work practices, and finally personal protective equipment. Occupational hygienists play a key role in anticipating hazards, conducting exposure assessments, and advising on prevention strategies to protect worker health.