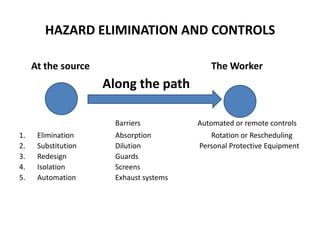
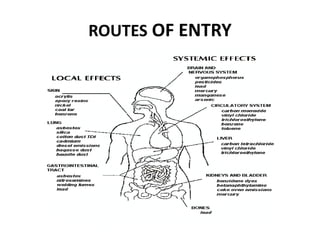
This document defines workplace hazards and provides information on identifying, assessing, and controlling hazards. It discusses the main categories of hazards as safety, health, and environmental. Hazards can be natural, man-made, technological, structural, behavioral, or specific physical, mechanical, chemical, or biological hazards. The key steps for controlling hazards are identification, assessment and evaluation, implementation of controls, and ongoing monitoring and review. Controls include elimination, substitution, isolation, engineering controls, administrative controls, and personal protective equipment. The overall goal is to implement a safety management system to reduce risk and prevent harm from any hazards.