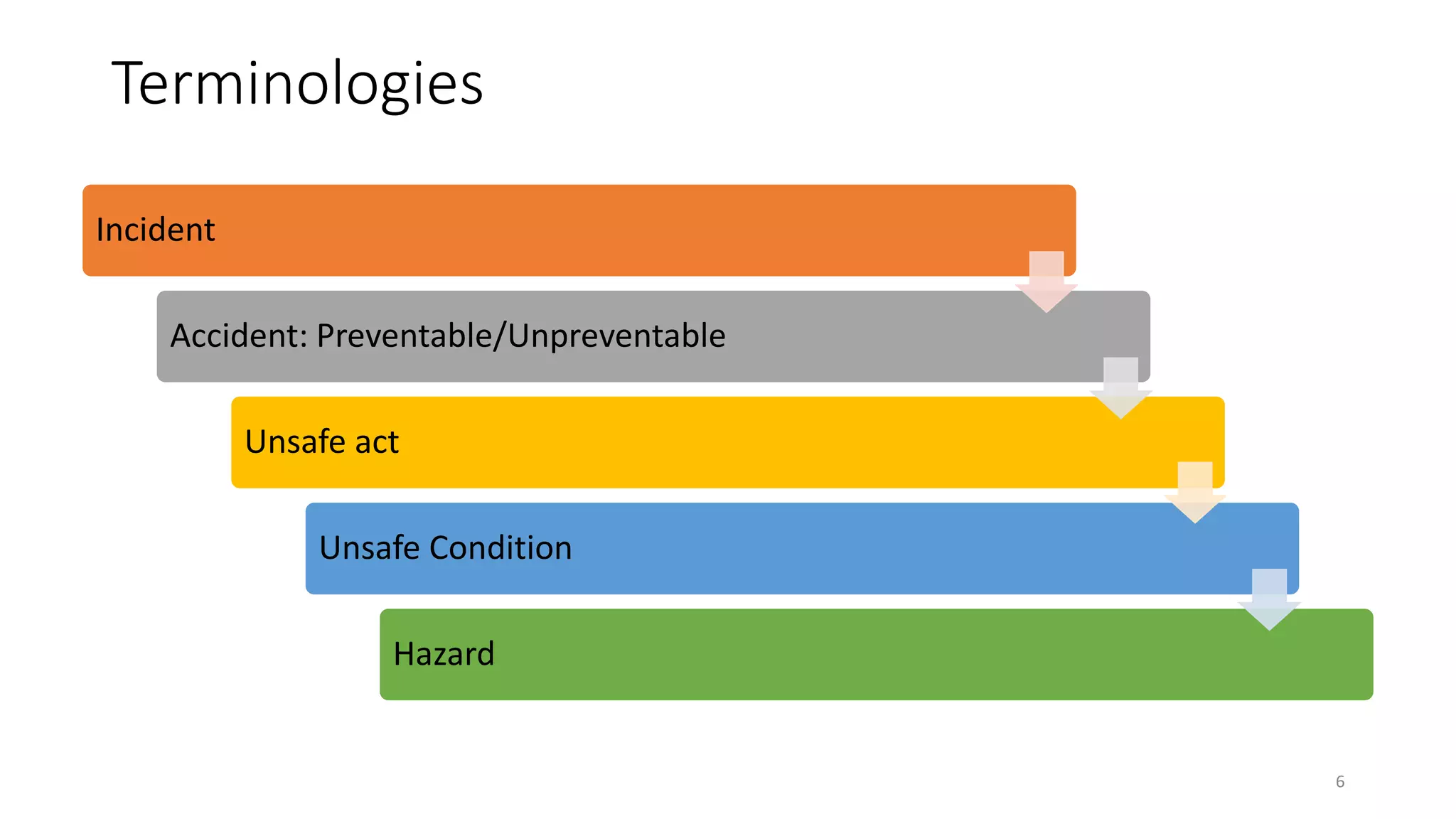
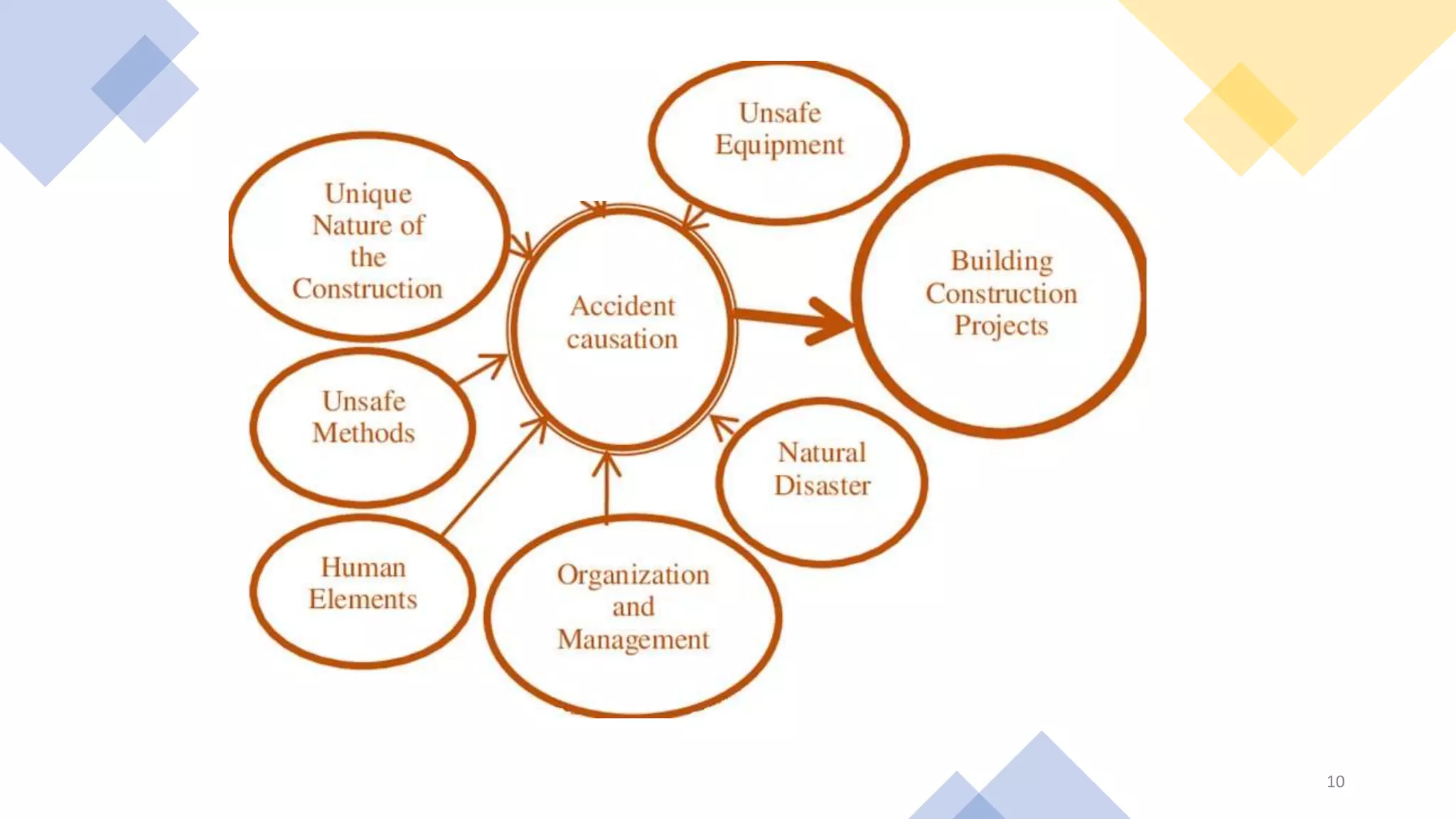
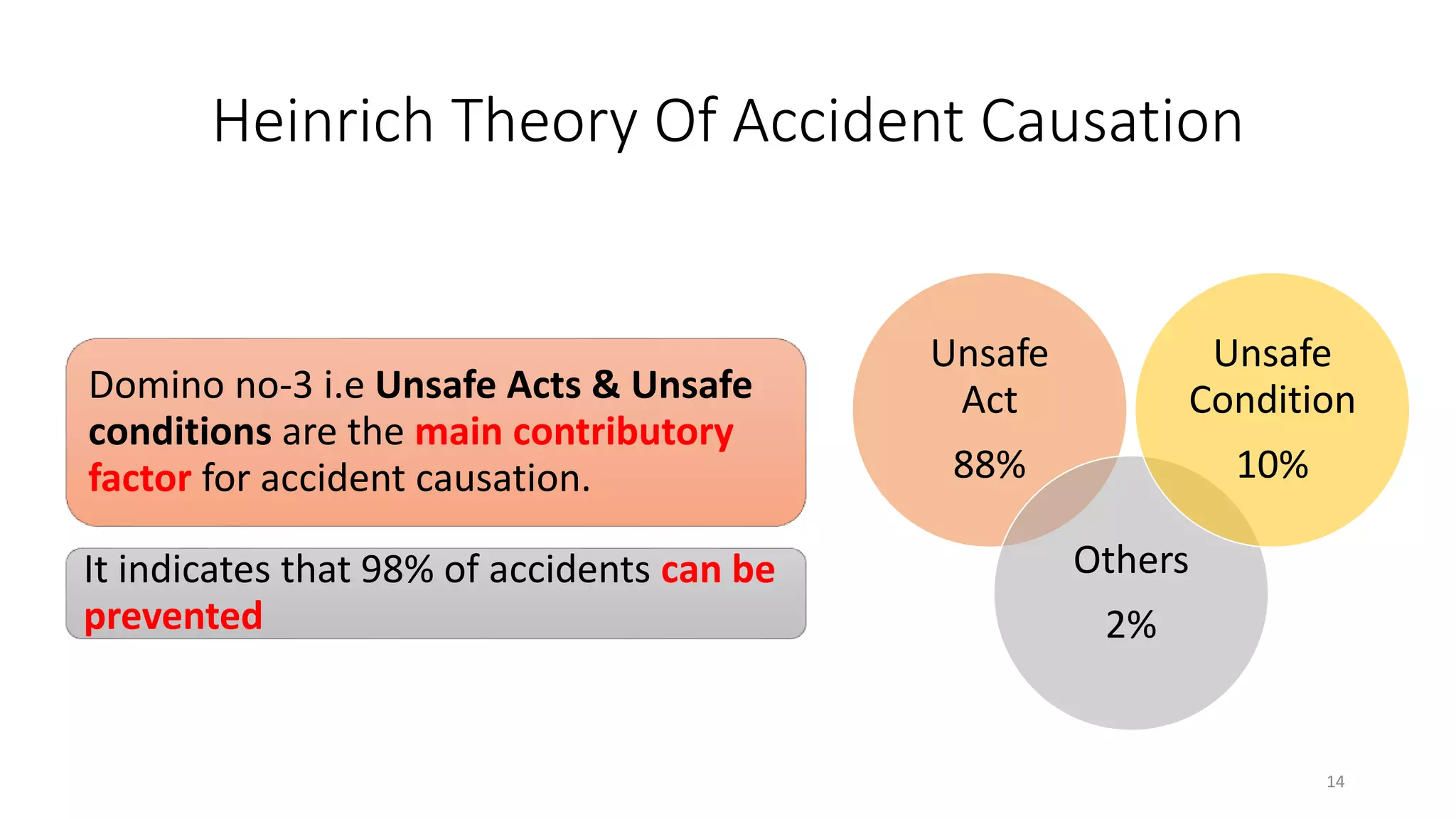
Dr. Soumar Dutta discusses various concepts related to patient safety and accident prevention. He defines key terms like incident, accident, unsafe act, and unsafe condition. Accidents can be preventable or unpreventable. The main causes of accidents according to the Heinrich Theory are unsafe acts and unsafe conditions, which account for 98% of accidents. Successful accident prevention requires identifying hazards, estimating risks, eliminating hazards where possible, using engineering controls, education and training, and enforcement of safety policies. Safety equipment alone is not enough - developing a trained, alert, and safe workforce is most important for any disaster prevention program.