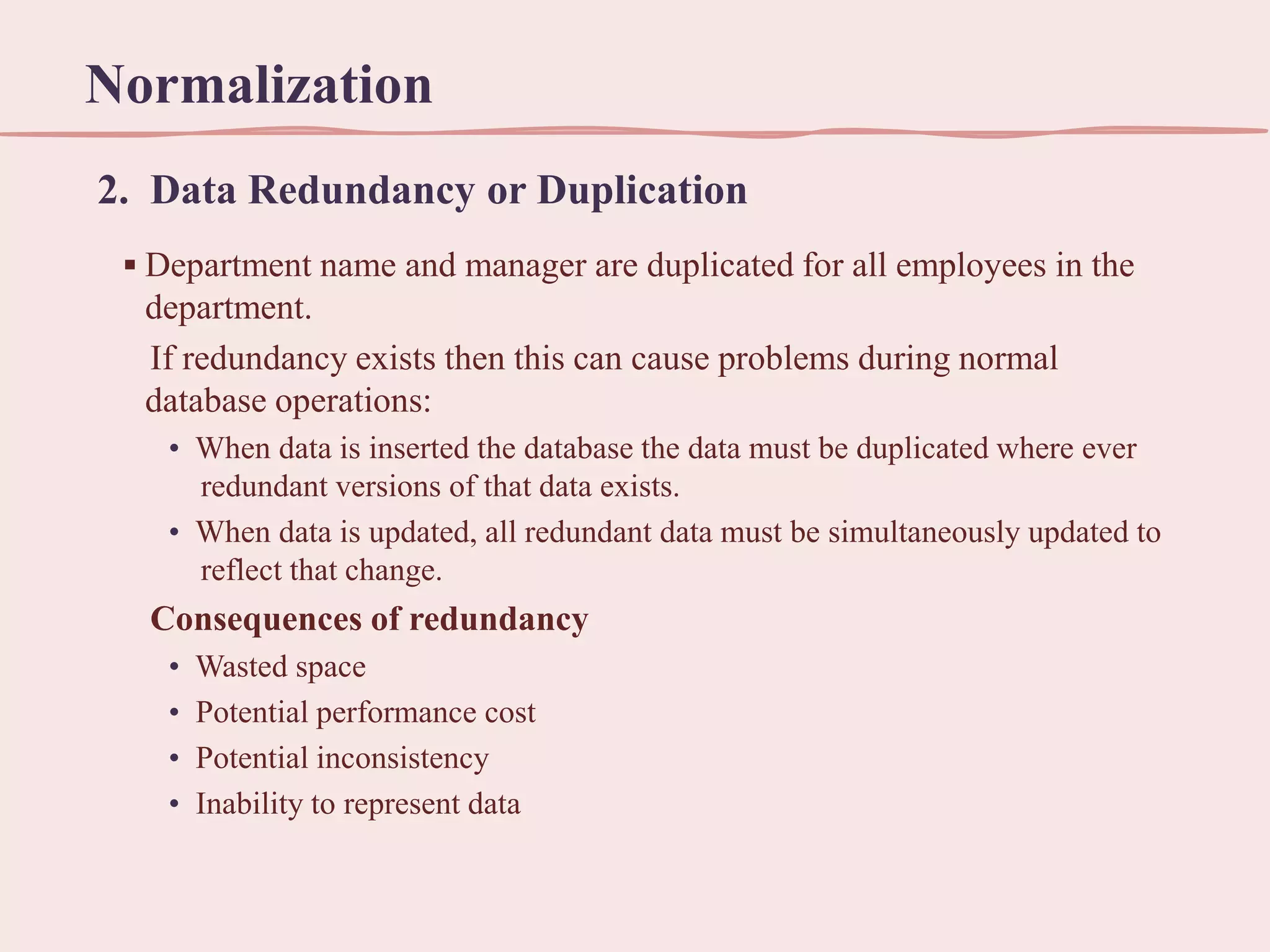
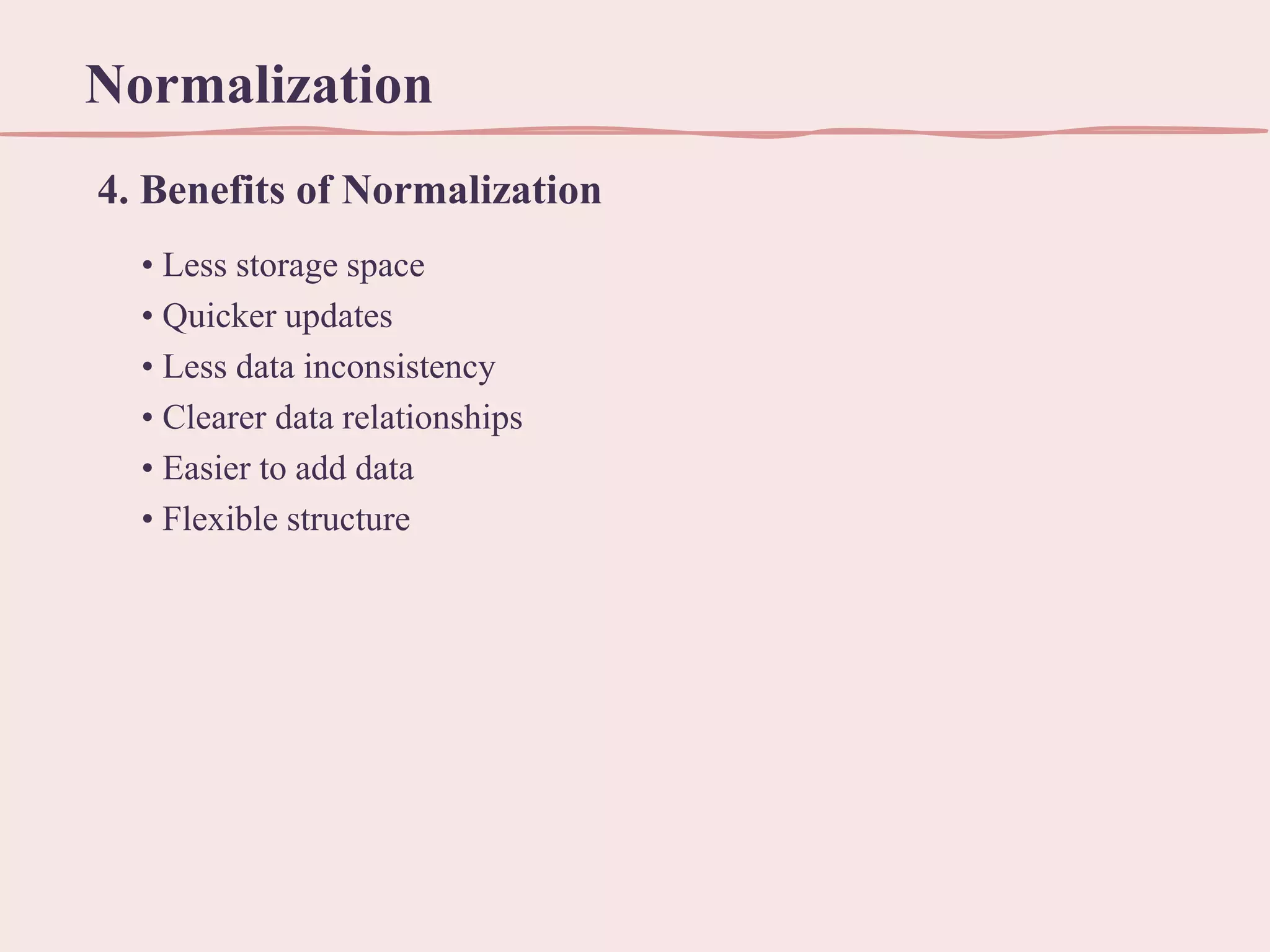
This document discusses normalization, which is the process of organizing data in a database to minimize redundancy and dependency. It defines normalization through various normal forms, including first normal form (1NF), second normal form (2NF), and third normal form (3NF). These normal forms help reduce data anomalies like insertion, deletion, and update anomalies that can occur when data is redundant or dependent on other data. The benefits of normalization include using less storage space, allowing for quicker updates, and reducing data inconsistencies.