Embed presentation
Downloaded 37 times





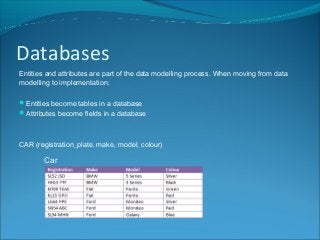
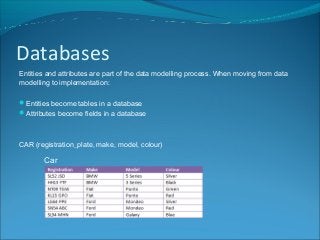
Entities represent people, objects, or abstract concepts and have attributes that describe examples of the entity. Notation defines the entity name in capital letters and attributes in brackets. Entities and attributes are part of data modeling, where entities become database tables and attributes become fields during implementation. Examples provided include a PUPIL entity with attributes like name and DOB, a CAR entity with attributes like make and model, and a DOCTOR APPOINTMENT entity with date and time attributes.






