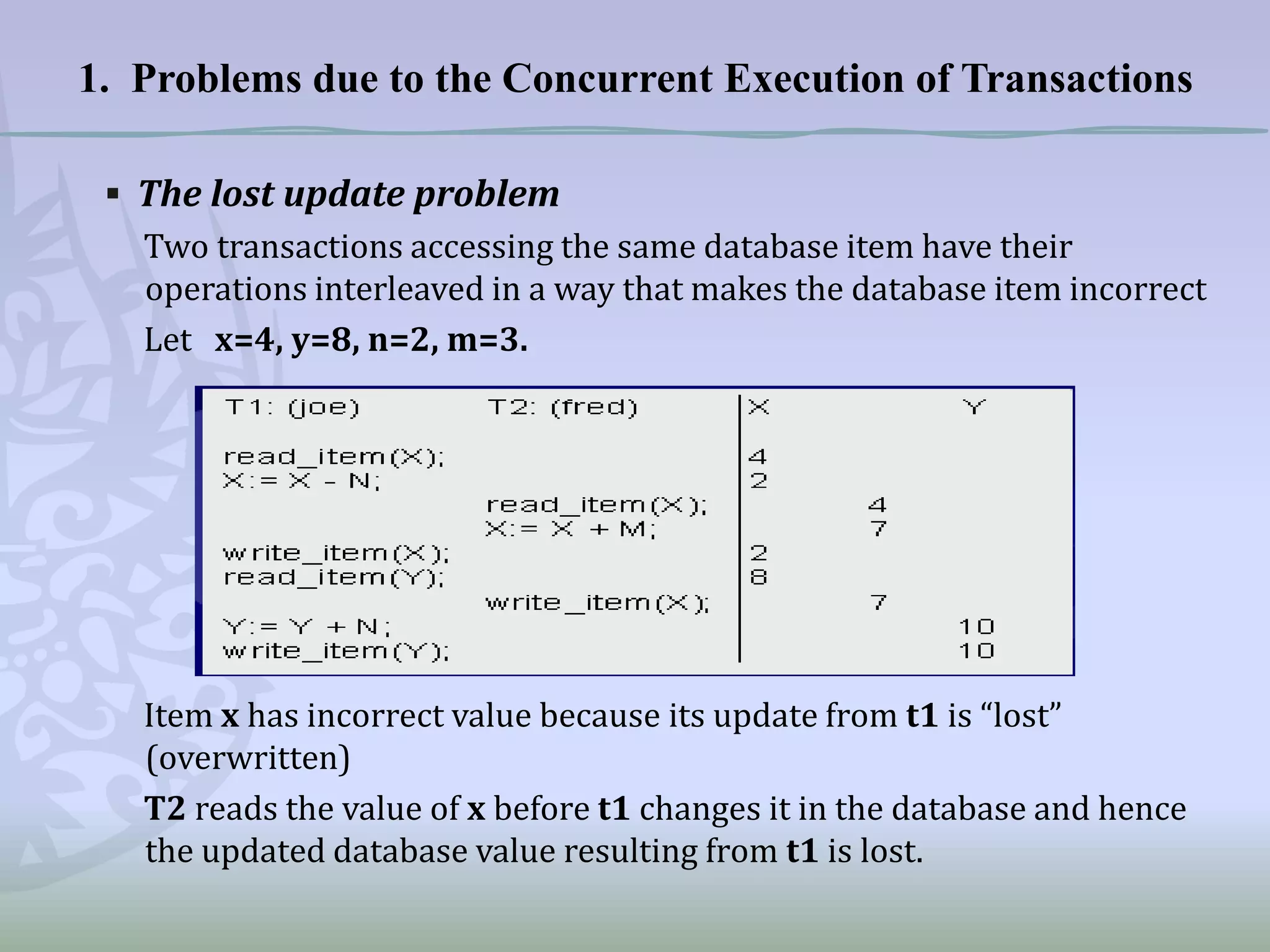
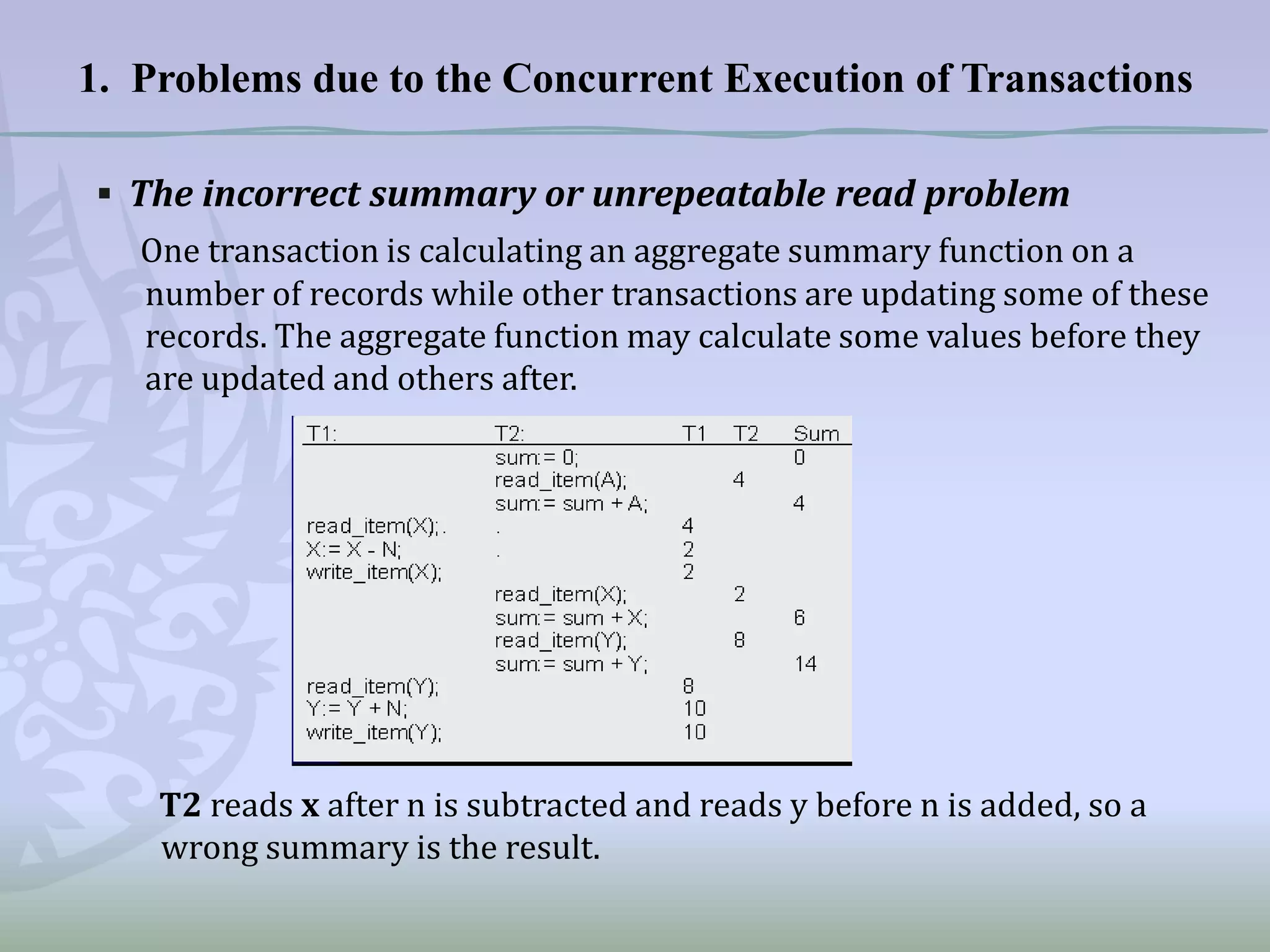
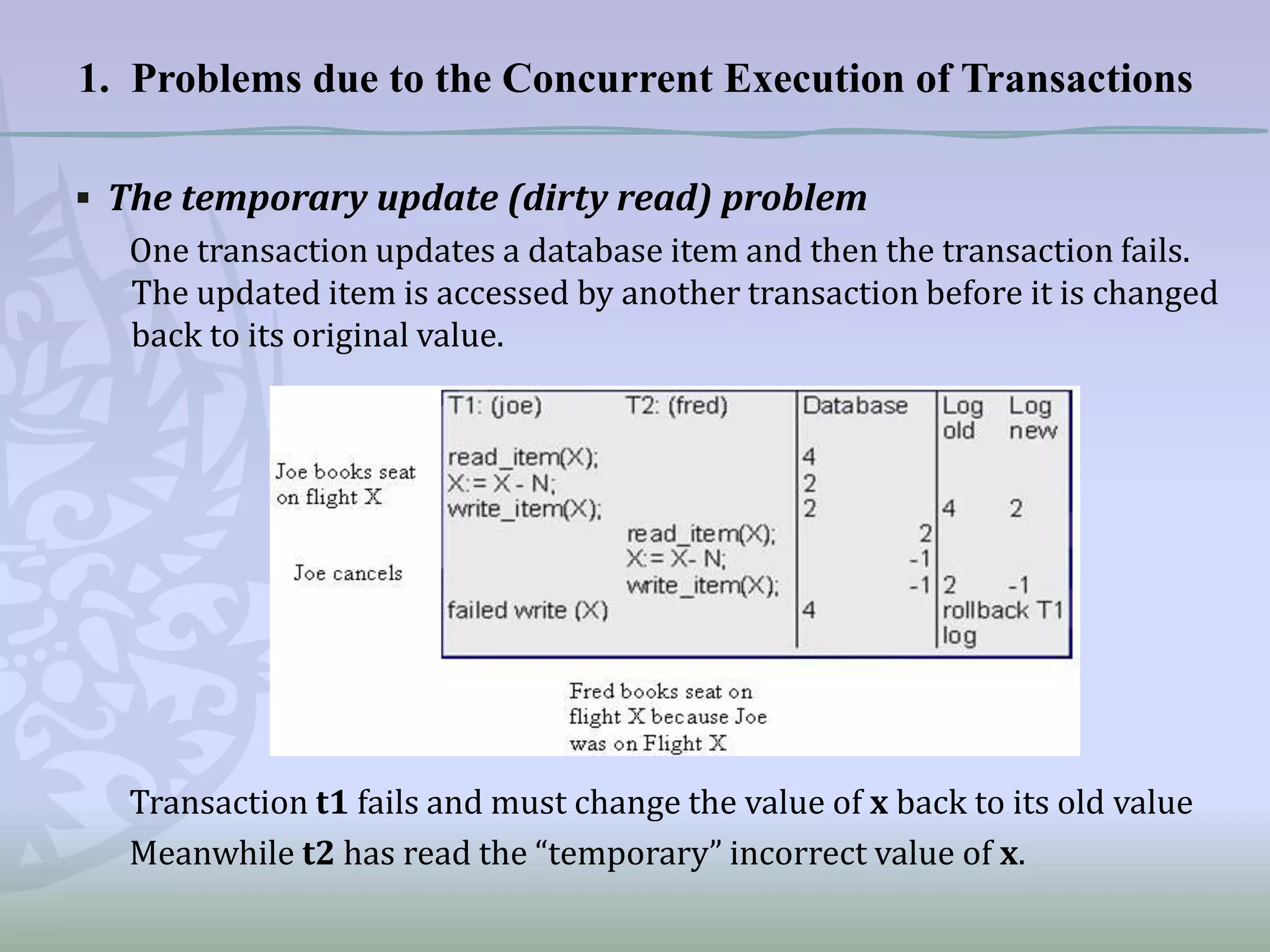
This document discusses concurrency control and methods to ensure serializability when transactions execute concurrently in a database. It begins by describing three problems that can occur with concurrent transaction execution: lost updates, unrepeatable reads, and dirty reads. It then explains two methods for achieving serializability: multi-version concurrency control and timestamp ordering. Timestamp ordering assigns timestamps to transactions and data items and uses the timestamps to determine when transactions can read and write data items to prevent conflicts. The document also briefly mentions using concurrency control protocols that employ locking to serialize transaction access.