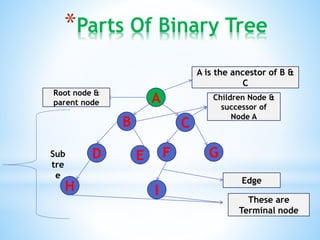
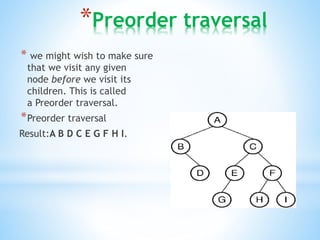
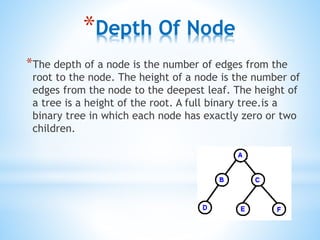
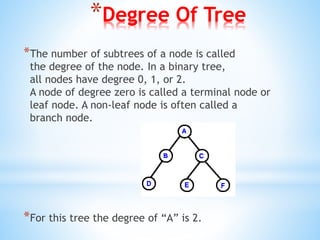
A binary tree is a data structure made up of nodes where each node contains data and pointers to left and right child nodes. It can be empty or consist of a single root node with binary trees as subtrees. Binary trees can be traversed in preorder, inorder, or postorder to process nodes. Properties include the height, depth, degree of nodes, and whether the tree is complete, extended, or a binary search tree. Heaps are binary trees that satisfy the heap property of being either min or max heaps.