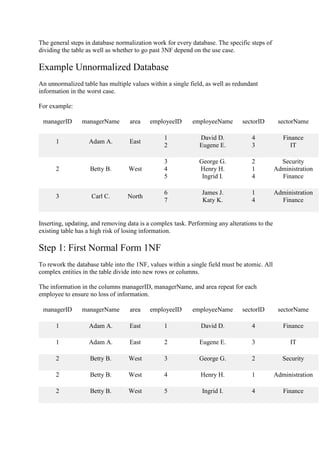
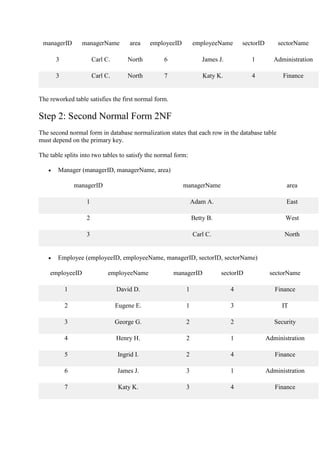
Database normalization is a process of organizing data in a database to minimize redundancy and dependency. It involves decomposing tables, categorizing attributes, and applying normal forms. The goal is to optimize database structure and performance. Some key points:
- Normalization breaks large tables into smaller tables with related attributes.
- It is achieved through normal forms like 1NF, 2NF, 3NF which address different types of redundancies and anomalies.
- The process ensures data dependencies make logical sense and tables can be recombined without losing information.
- A normalized database structure improves data integrity, query efficiency, and maintenance.