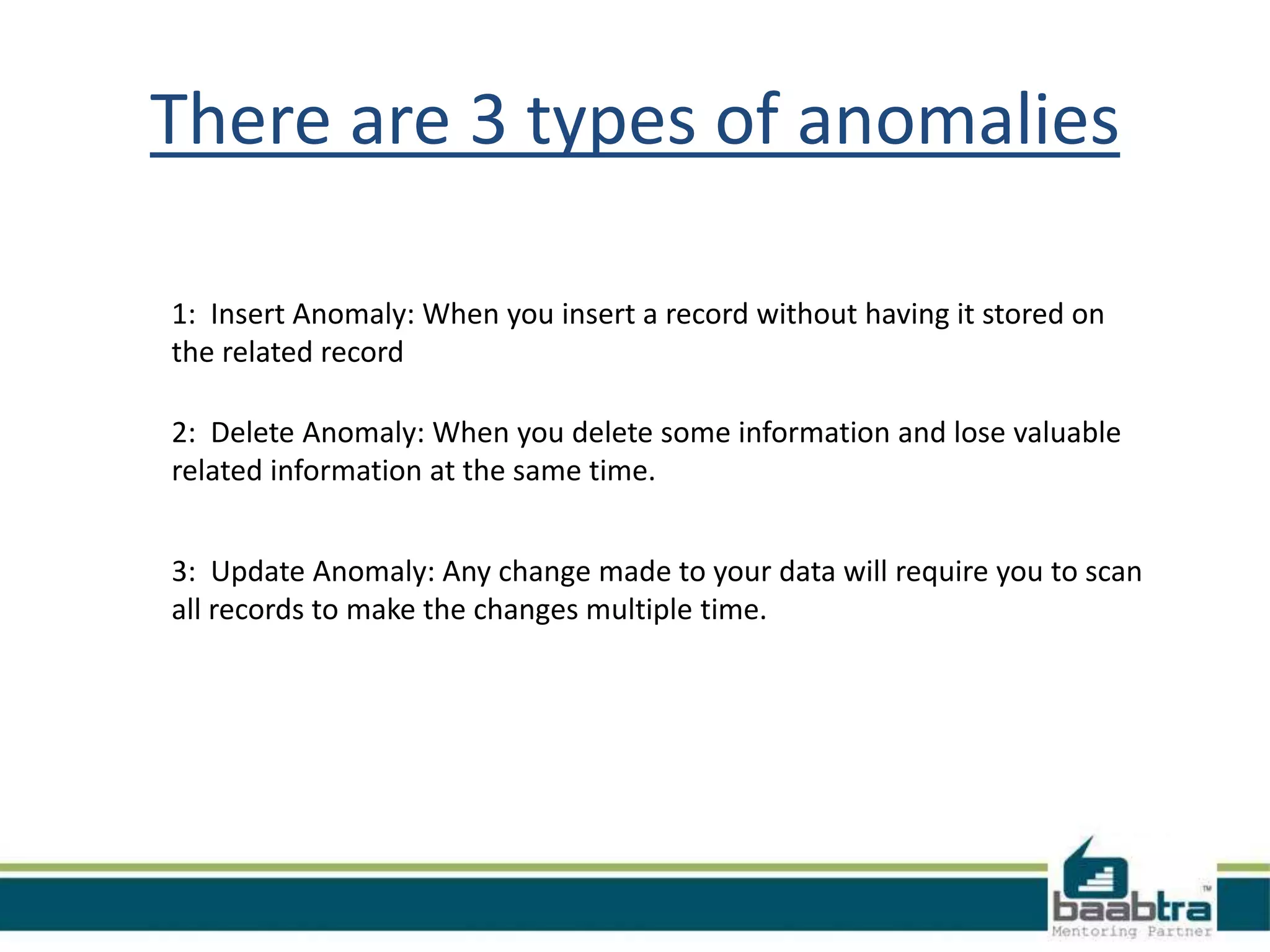
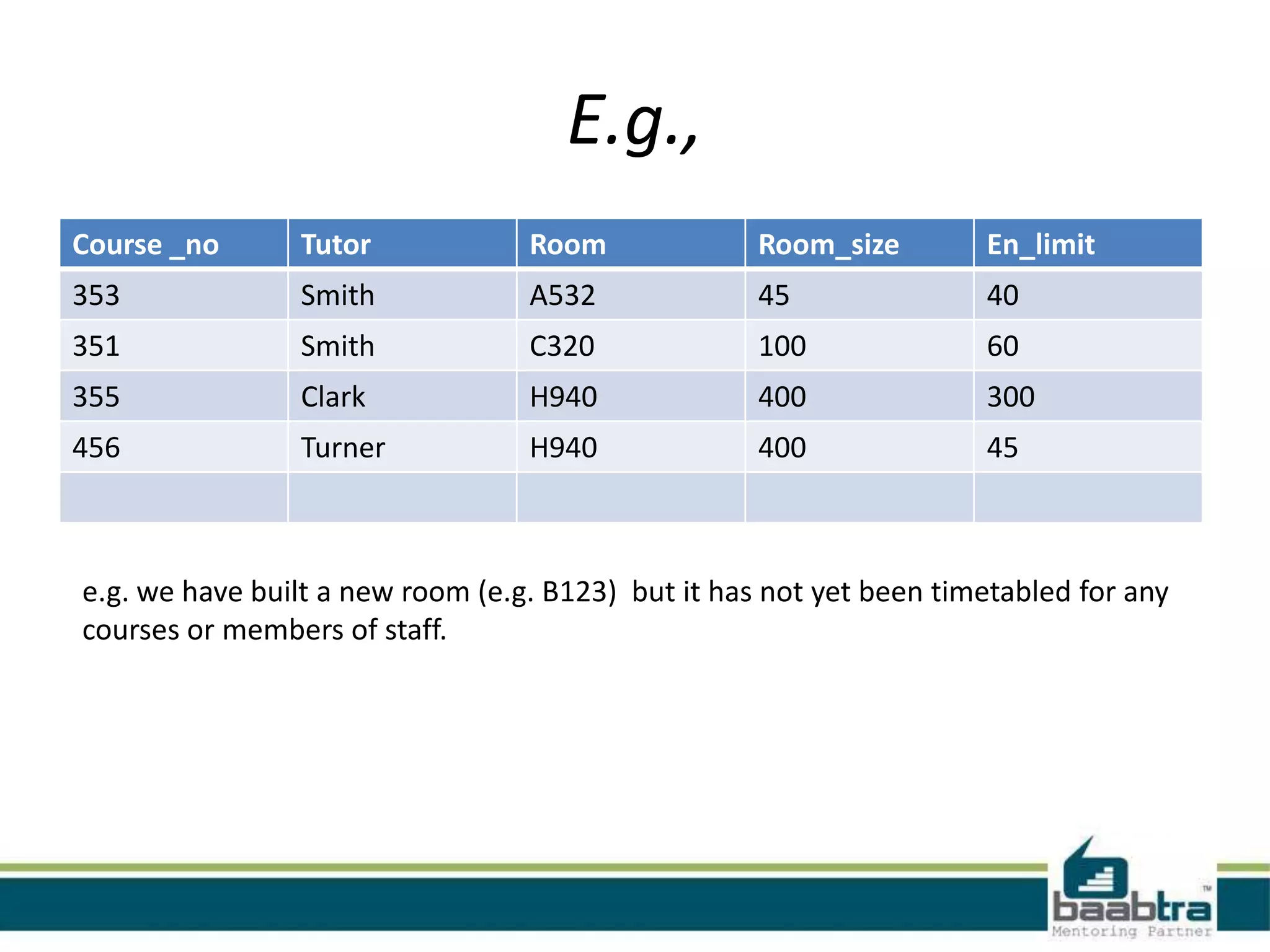
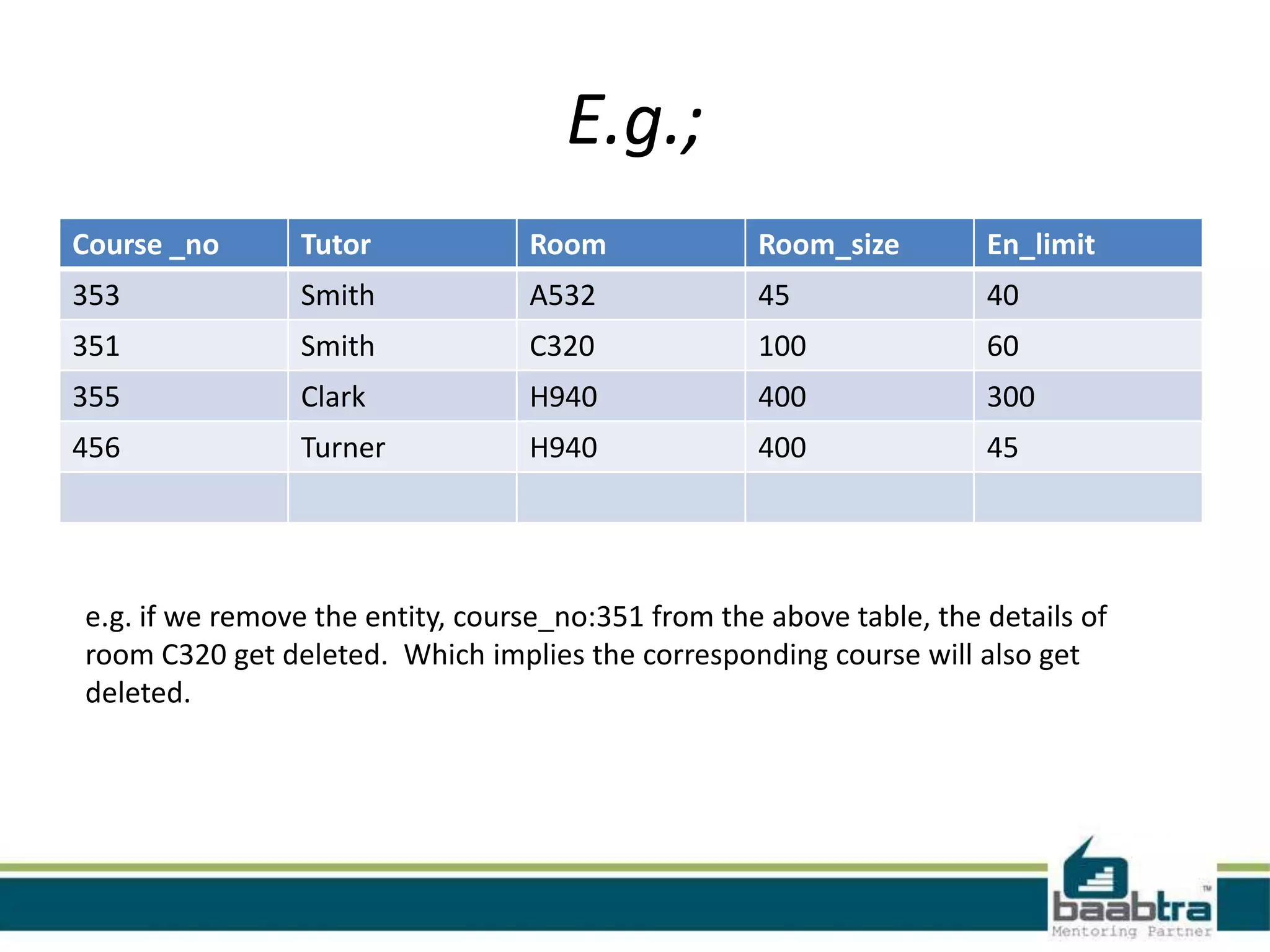
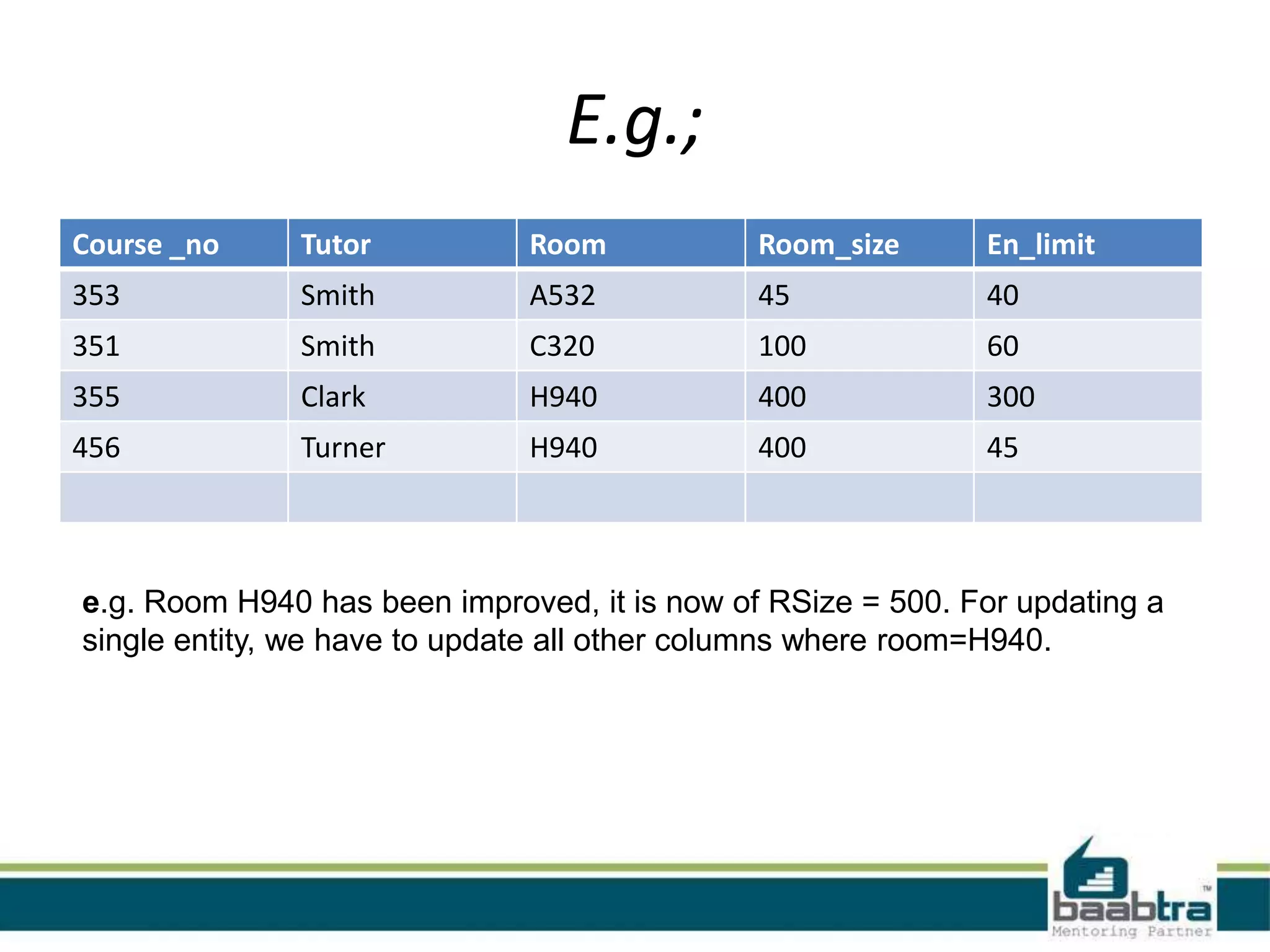
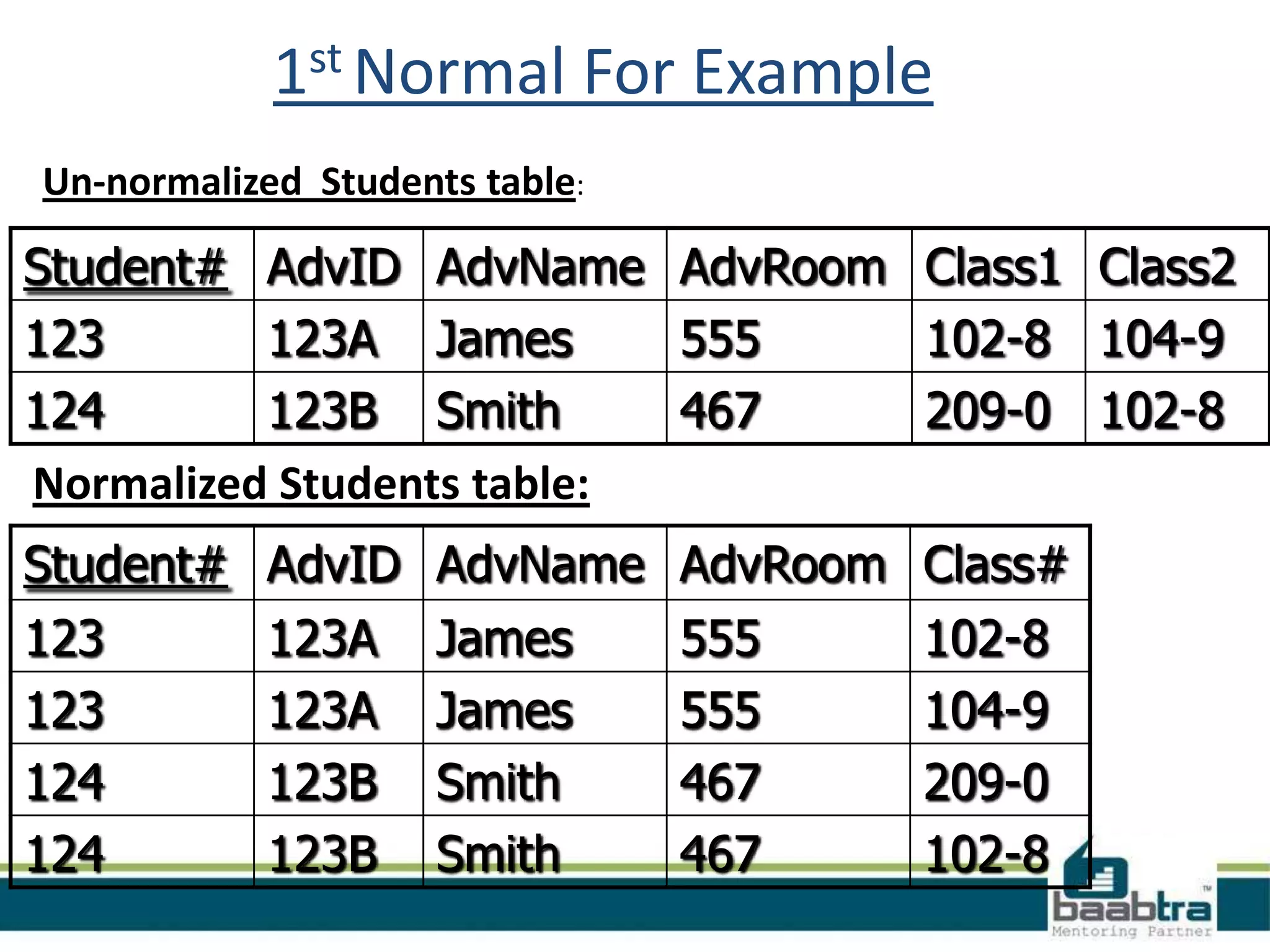
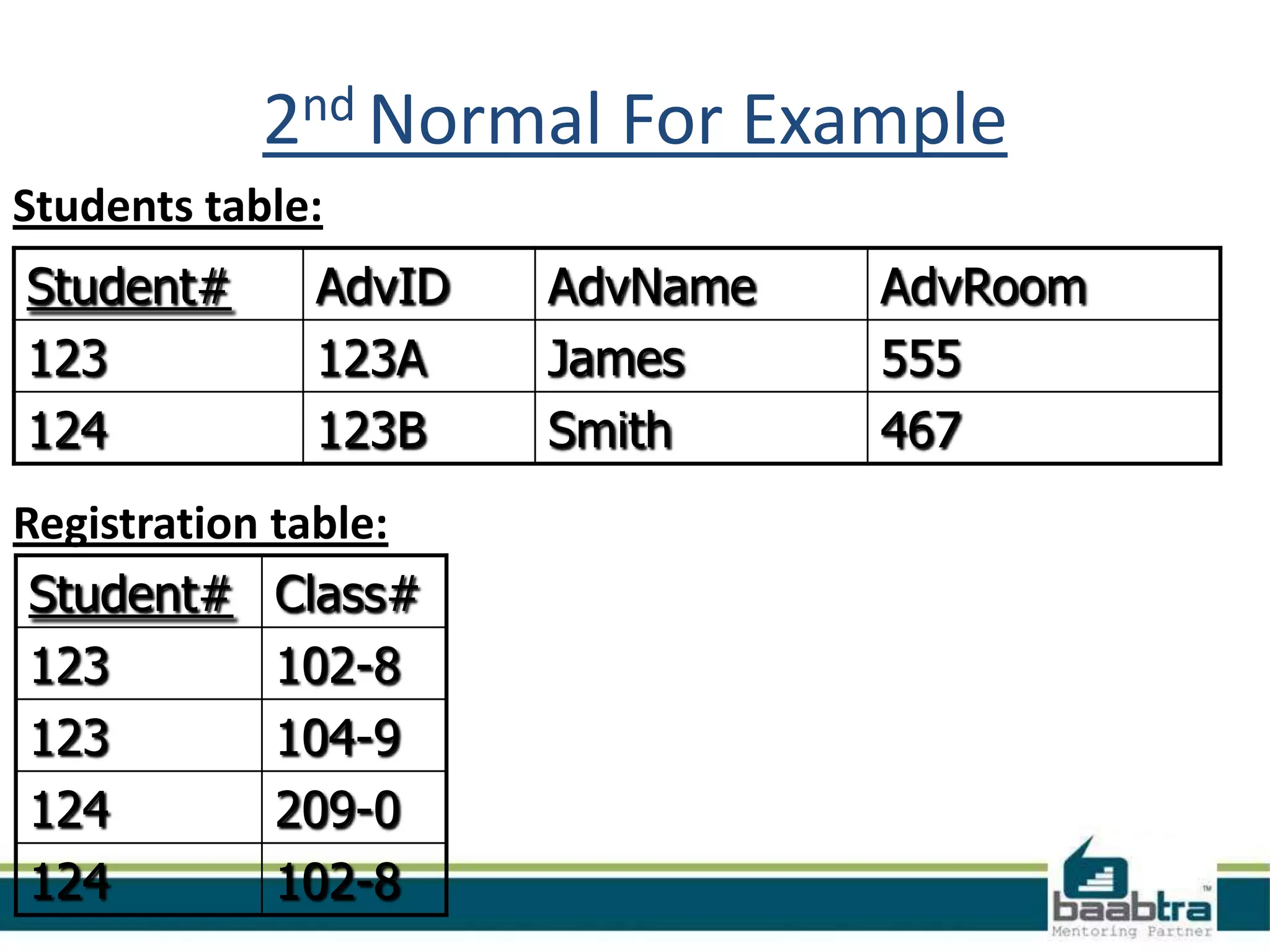
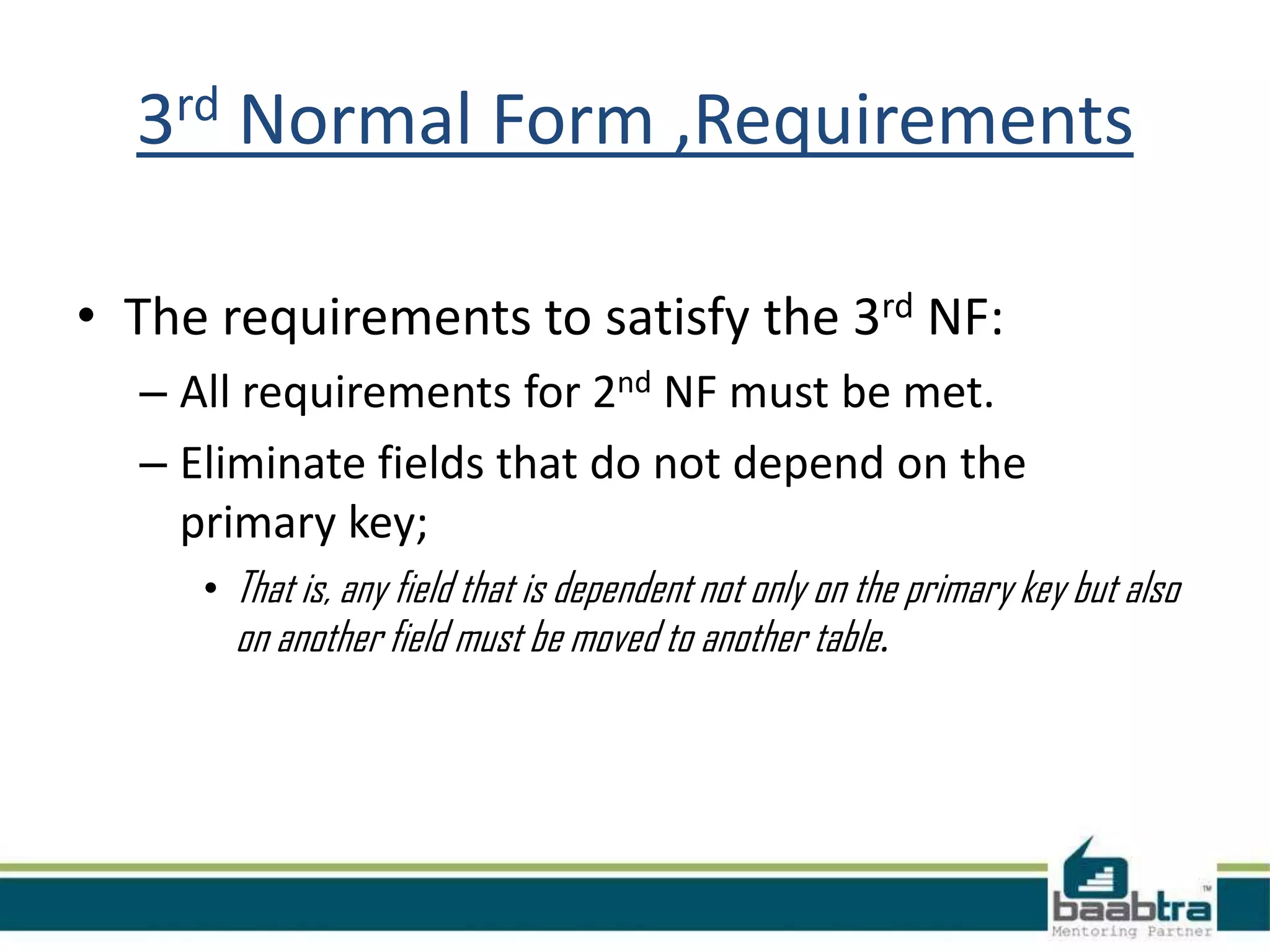
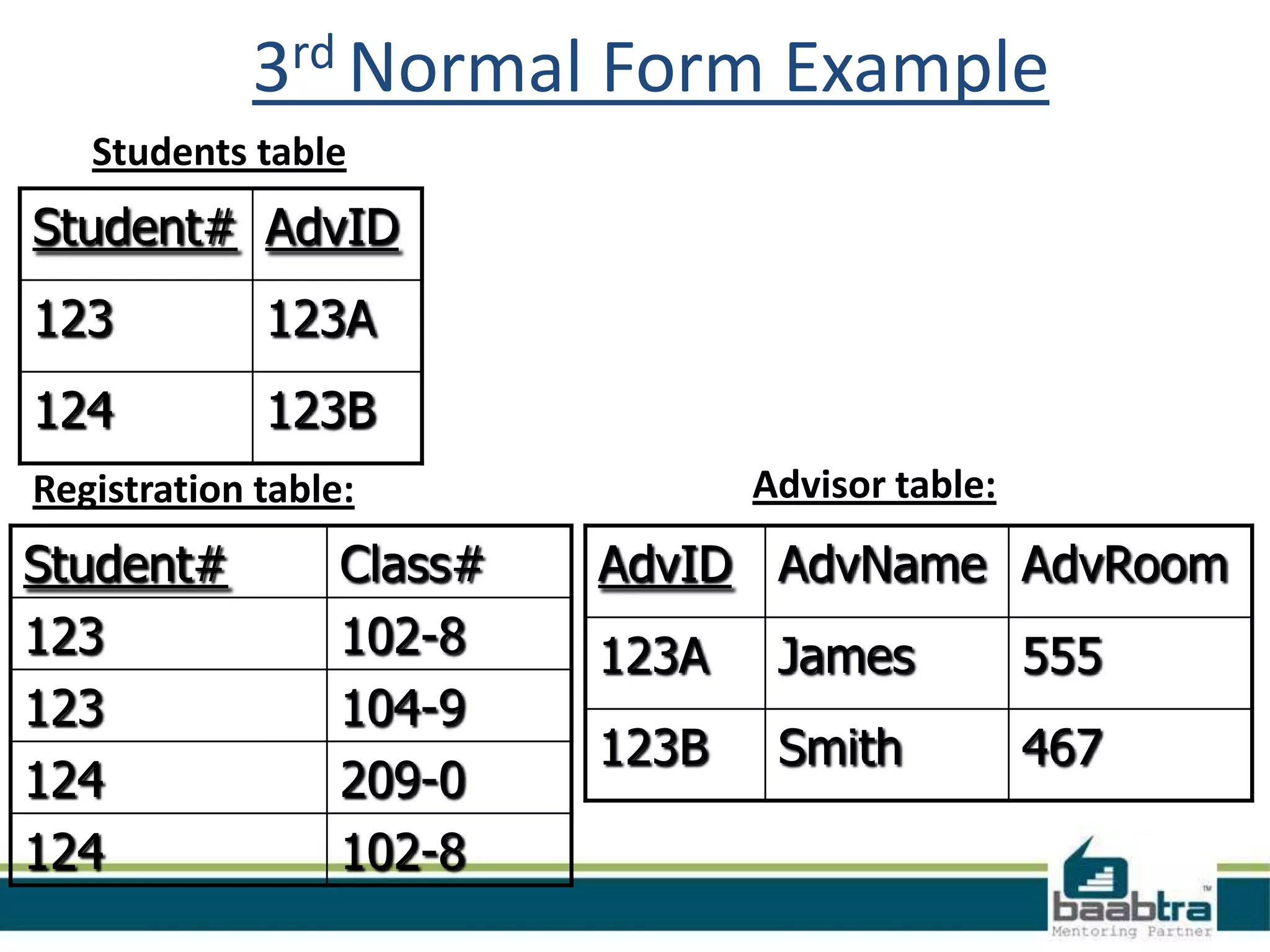
This document discusses database normalization and anomalies. It defines three types of anomalies: insert, delete, and update anomalies. Examples are provided for each. The document then explains the three normal forms - 1st, 2nd, and 3rd normal form. The requirements for each normal form are defined and examples are used to illustrate how normalization reduces anomalies by eliminating redundant data and non-key dependencies from tables.