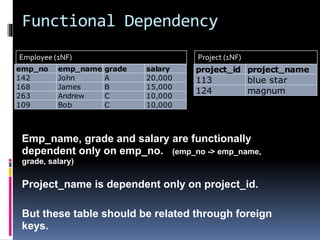
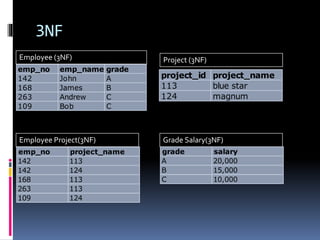
Normalization is the process of organizing data in a database to minimize redundancy and dependency. It involves breaking tables into smaller tables and linking them through relationships. The goals are to eliminate storing duplicate data, ensure related data is stored together, and reduce data anomalies. Normalization is achieved through three normal forms - 1NF, 2NF, and 3NF - which introduce rules to simplify attributes, eliminate partial dependencies, and remove transitive dependencies.